Abstract
Background: Expression of p190 BCR-ABL mRNA is generally considered to be confined to patients with acute lymphoid or more rarely myeloid leukemias, whereas p210 BCR-ABL mRNA is the hallmark of CML. In reality it is not uncommon the presence of p190 m-RNA in p210 CML in chronic phase, due to alternative or missplicing1. Its presence seems to have no impact on prognosis in the pre-TKI era, although it may be expression of genomic instability.
Aim: Primary object of this study was to investigate if the co-expression might influence the rate of early outcome surrogate endpoints such as such as early complete cytogenetic response in patients treated with imatinib. The secondary endpoint was the evaluation of failure free survival (FFS) measured from the start of imatinib to the date of any of the following events: progression to accelerated or blastic phase, death for any cause and switch to nilotinib/dasatinib for resistance or intolerance.
Methods: Were evaluated patients with CML in chronic phase treated with imatinib at our institution. We excluded cases with less than one year of treatment and/or treated with other TKIs or conventional chemotherapy.The fusion transcripts BCR-ABL were evaluated at diagnosis in peripheral blood by NESTED-PCR2 and the cytogenetic response were evaluated in bone marrow cells with G-banding technique and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)3. The patients were divided into two groups, "double transcripts" (DT) and "single transcript" (ST). All patients received imatinib 400 mg/die.
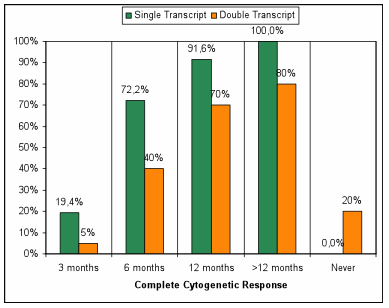
Results: A total of 56 patients were analyzed. The median age of patients was 58 years (range 28-80 years) and 35 (62%) were male. Twenty patients (36%) were DT and thirty-six (64 %) ST. The distribution according to Sokal score was: 7 (35%), 8 (40%) and 5 (25%) patients for low, intermediate and high risk in the DT, whereas 18 (50%), 15 (42%) and 3 (8%) low, intermediate and high risk in ST, respectively. The complete cytogenetic response at 3 months was achieved in 2 patients with DT and 7 patients with ST (10% vs 19% p 0.35), at 6-month complete cytogenetic response was achieved in 8 patients with DT and 27 patients with ST (40% vs 75% p 0.01) (Table 1). After median follow-up of 1966 days, the FFS was significantly different between the DT and ST (55% vs 5 % p< 0.001) (figure 1), 11 patients in the DT group and 5 patients in ST group had shift to TKI 2¡ generation (55% vs 14% p 0.001) and 4 patients in DT group not achieved complete cytogenetic response.
Summary/Conclusion: In our study the co-expression of p190 and p210 BCR-ABL transcripts influences the early cytogenetic response to imatinib and suggesting the need for a larger validation study
Reference
1). van Rhee F, Hochhaus A, Lin F, Melo JV, Goldman JM, Cross NC. : "p190 BCR-ABL mRNA is expressed at low levels in p210-positive chronic myeloid and acute lymphoblastic leukemias."Blood. 1996 15;87:5213-7.
2). Hermans A, Selleri L, Gow J, Wiedemann L, Grosveld G: "Molecular analysis of the Philadelphia translocation in chronic myelocytic and acute lymphocytic leukemia." Leukemia 2:628,1988.
3) Landstrom AP, Tefferi A.: "Fluorescent in situ hybridization in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment monitoring of chronic myeloid leukaemia".Leuk Lymphoma.2006;47:397-402.
Table 1 : Complete Cytogenetic response:
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.