Abstract
Background: Brentuximab vedotin (BV) is an anti-CD30 chimeric antibody conjugated by a protease-cleavable linker to the microtubule-disrupting agent, MMAE. While CD30 expression of malignant cells in HL and ALCL is uniform, in mycosis fungoides/Sezary syndrome (MF/SS), the CD30 expression is more variable. We reported previously (ASH 2012) that BV has clinical activity in MF/SS across all CD30 expression levels. In this final report, we update the clinical data and present new biomarker and correlative tissue analyses.
Methods: Patients (pts) with MF/SS stages IB-IV, ECOG 0-2, with at least 1 prior systemic therapy were enrolled in this investigator-initiated, phase II, single-arm study. CD30 expression levels in the skin (% of total mononuclear cell infiltrate) were evaluated by routine immunohistochemistry (IHC) using the BerH2 antibody. At least 2 skin biopsies were obtained per pt and the max CD30 level was used for CD30 designation. All pts (CD30, 0-100%) were treated with up to 8 cycles of BV (1.8 mg/kg) administered every 3 weeks; optional extension of up to 8 additional cycles was allowed in responders with ongoing clinical improvement. Primary endpoint was overall response rate (ORR) by consensus global response criteria. CD30 expression and clinical response data were confirmed by independent review. Tumor microenvironment was assessed utilizing IHC for CD8, CD20, CD163, FoxP3, and PD-1. Multispectral image analysis was utilized to evaluate CD30 antigen co-expression.
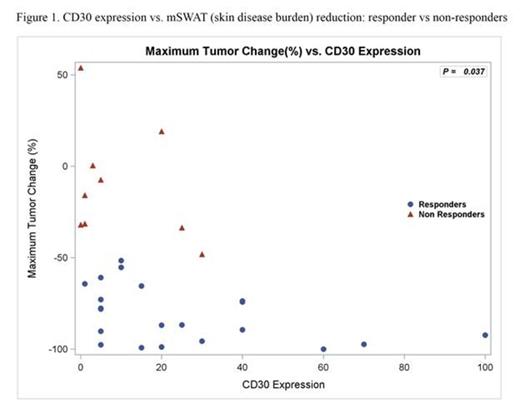
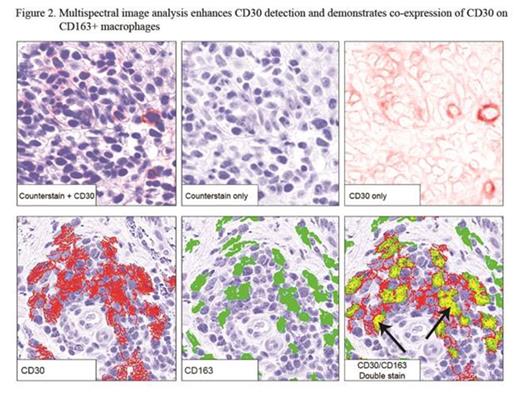
Results: 32 pts were enrolled and all received at least one dose of BV (Table); all included in safety data, 2 excluded in efficacy analyses (no response assessment). Median age was 62 (20-87). 28/32 (88%) had advanced disease, majority with adverse prognostic features (90% large cell transformation or folliculotropism). ORR was 70% (21/30) with responses in all clinical stages. Median best mSWAT reduction (response measure in the skin) was 73% (range, 100% to -54%) with 1 CR, 7 near CR in skin (>90% reduction) (Fig 1). Median time to response was 6.6 weeks (range 3.0-27.0). Kaplan-Meyer estimate shows 79% of responses ongoing and 54% progression-free at 12 months. Related AEs observed were mostly grade 1-2 and limited to AEs previously reported with BV. By IHC, median max CD30 expression level of all pts was 13% (range 0-100%; 6 had <5%), where the median was higher in responders (CR/PR), 15%, vs. non-responders (SD/PD), 3.0%, p=0.037 (Fig 1). The correlation with CD30 level was greatest in IIB/skin tumor subset (p=0.0072). Those with CD30 level <5% had a lower likelihood of clinical response (17% vs 83%; p=0.0046). Multispectral image analysis demonstrated quantifiable CD30 staining in 19/20 (95%) samples that were interpreted as negligible CD30 by routine IHC. Of other tissue biomarkers evaluated, CD163+ cells (macrophages) were most abundant with a median of 40% (range 5-80%) of total infiltrate. To distinguish expression of CD30 by neoplastic CD4+ vs. tumor-infiltrating cells, double staining for CD30 and CD8 or CD163 was assessed. We observed significant co-expression of CD30 by CD163+ macrophages (median 9.7% of total cells assessed, range 1.0-40.9%) or CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (median 1.7%, range 0.2-14.8%) (Fig 2). Those with lower CD163 relative to CD30 stain (CD163/CD30 ratio) by routine IHC were associated with clinical response (p=0.033). This may simply reflect the influence of CD30 level; however, in light of the co-localization data, it might also suggest that infiltrating macrophages that co-express CD30 may play a role as a microenvironment factor in clinical response to BV.
Conclusions: Our final analysis confirms significant clinical activity of BV in MF/SS with expected AE profile. Although clinical response was observed at all levels of CD30 expression, the likelihood of response was lower in those with negligible or very low (<5%) level. We utilized multispectral imaging to enhance detection of CD30 and also show co-expression of CD30 by tumor-infiltrating cells. These findings suggest that further studies of biomarkers are warranted and may help optimize management strategies with BV.
| Characteristic | All Pts n=32 | Evaluable n=30 | ORR n (%) | ||||
| n (%) | CR | PR | SD | PD | |||
| Clinical Stage | All pts IB IIB IV/SS | 32 (100) 4 (13) 18 (56) 10 (31) | 1 0 0 1 | 20 3 14 3 | 4 1 2 1 | 5 0 2 3 | 21/30 (70) 3/4 (75) 14/18 (78) 4/8 (50) |
| Transformed or folliculotropic MF | 29 (91) | 1 | 19 | 3 | 5 | 20/28 (71) | |
| # prior systemic tx | <3 >=3 | 15 (47) 17(53) | 0 1 | 8 12 | 2 2 | 4 1 | 8/14 (57) 13/16 (81) |
| Characteristic | All Pts n=32 | Evaluable n=30 | ORR n (%) | ||||
| n (%) | CR | PR | SD | PD | |||
| Clinical Stage | All pts IB IIB IV/SS | 32 (100) 4 (13) 18 (56) 10 (31) | 1 0 0 1 | 20 3 14 3 | 4 1 2 1 | 5 0 2 3 | 21/30 (70) 3/4 (75) 14/18 (78) 4/8 (50) |
| Transformed or folliculotropic MF | 29 (91) | 1 | 19 | 3 | 5 | 20/28 (71) | |
| # prior systemic tx | <3 >=3 | 15 (47) 17(53) | 0 1 | 8 12 | 2 2 | 4 1 | 8/14 (57) 13/16 (81) |
Kim:Actelion: Consultancy; Celgene: Advisory, Advisory Other; Eisai: Research Funding, SAC/Advisory, SAC/Advisory Other; Galderma: Advisory, Advisory Other; Millennium/Takeda: Research Funding, SAC/Advisory Other; Kyowa-Hakko-Kirin: Research Funding, SAC/Advisory Other; Oncosec: Advisory Other; Seattle Genetics: Advisory, Advisory Other, Research Funding; SHAPE: Consultancy, Research Funding. Off Label Use: Treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, also recently added to NCCN NHL practice guidelines in CTCL. Wood:Millennium: IDMC Other. Advani:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding. Horwitz:Millennium: Consultancy, Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Kiowa-Kirin: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Spectrum: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.