To the editor:
Ibrutinib is a potent inhibitor of Bruton tyrosine kinase with promising efficacy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). It is well tolerated, and grade 3/4 adverse events are infrequent (12%).1 Lymphocytosis has been reported in ∼70% of patients receiving ibrutinib.1-3 Such lymphocytosis is usually asymptomatic and has no clinical consequence for the patient. We describe a patient who developed tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) with ibrutinib monotherapy.
A 57-year-old man was initially diagnosed with Rai stage II CLL in 2004. A bone marrow biopsy at diagnosis showed 30% to 35% interstitial and focally diffuse involvement. Monoclonal B cells showed κ light-chain restriction and were positive for CD5, CD19, CD20, CD22, CD45, CD23, ζ-associated protein of 70 kDa (ZAP70), and CD38. Neoplastic cells were dim positive for CD79b, but were negative for CD10 and FMC7. Fluorescent in situ hybridization showed deletion of chromosome 11q22 (27.5% nuclei); however, there was no evidence of 17p13 deletion, 13q14 deletion, or trisomy12. Immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (IGHV) somatic hypermutation analysis was negative for IGHV VH2-5 gene mutation. His previous therapies included a fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab regimen followed by rituximab maintenance (2004), pentostatin-cyclophosphamide (2007), bendamustine-rituximab (2009), lenalidomide (2011), bendamustine (2012), and ofatumumab (2013). His other home medications included alprazolam, citalopram, oxycodone, and ranitidine.
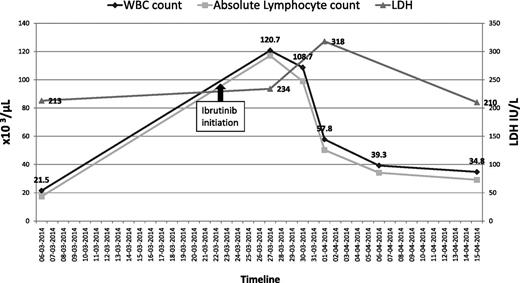
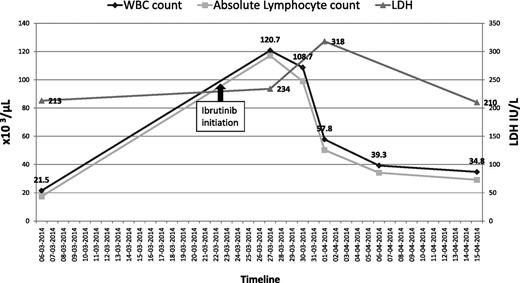
He was started on ibrutinib 420 mg per day, on March 23, 2014 for progressive CLL, characterized by bulky adenopathy (sum of product of diameters, 61.7 cm). Prior to ibrutinib initiation, his baseline white blood cell (WBC) count ranged between 21 × 109/L to 25 × 109/L (normal, 4-10 × 109/L); hemoglobin (Hb), 11 g/dL to 12 g/dL (normal, 13.5-18g/dL); platelets, 110 × 109/L to 120 × 109/L (normal, 150-400 × 109/L); serum creatinine, 0.9 mg/dL to 1.1 mg/dL (normal, 0.6-1.3 mg/dL); lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), 213 U/L (normal, 100-190 U/L); and electrolytes were within normal limits. Three days after starting ibrutinib, his WBC count rose to 120 000/mm3; absolute lymphocyte count (ALC), 116 400/mm3; Hb, 13.7 g/dL; platelets, 73 000/mm3; creatinine, 1.2 mg/dL; potassium, 5.7 mEq/L (normal, 3.5-5.1 mEq/L); and calcium, 8.8 mg/dL (normal, 8.3-10.3 mg/dL).
Seven days after starting treatment with ibrutinib, he presented with generalized weakness and severe fatigue. Physical examination showed a temperature of 98.4°F; heart rate, 48 beats per minute; blood pressure, 98/54 mmHg; and respiratory rate, 28 breaths per minute. He had palpable left supraclavicular and bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy. The remainder of the examination was unremarkable. Laboratory work-up revealed: WBC count, 108 000/mm3 (ALC, 98 280/mm3); Hb, 12.9 g/dL; platelets, 71 000/mm3; potassium, 7 mEq/L; creatinine, 3.4 mg/dL; calcium, 5.8 mg/dL; phosphate > 12 mg/dL (normal, 2.5-4.9 mg/dL); magnesium, 2.1 mg/dL (normal, 1.5-2.4 mg/dL); uric acid, 30 mg/dL (normal, 2.6-8.7 mg/dL); and LDH, 234 U/L. Arterial blood gas analysis showed severe metabolic acidosis but lactate levels were within normal range. An electrocardiogram (ECG) showed marked sinus bradycardia. His blood cultures, drawn at the time of admission, remained negative.
Striking derangements from baseline values of uric acid, potassium, phosphate, and calcium, together with marked sinus bradycardia on ECG, were consistent with grade 3 TLS according to the Cairo-Bishop criteria.4 He was admitted to the intensive care unit and received IV fluids, bicarbonate drip for severe acidosis, calcium gluconate, insulin, dextrose in 50% water and sodium-polystyrene for hyperkalemia, rasburicase for hyperuricemia, and piperacillin/tazobactam for increased WBCs on urinalysis. His ibrutinib was withheld.
Seventy-two hours posthospitalization, his total WBC count decreased to ∼58 000/mm3 (Figure 1). He was discharged on day 8, after normalization of his creatinine and electrolytes, with a WBC count of 39 000/mm3; Hb, 12 g/dL; and platelet count, 161 000/mm3. Three weeks postdischarge, he was restarted on ibrutinib 420 mg per day. He tolerated this rechallenge well, with no subsequent evidence of TLS.
The patient’s total WBC count and corresponding ALC before and after initiation of ibrutinib.
The patient’s total WBC count and corresponding ALC before and after initiation of ibrutinib.
This case highlights that TLS can be precipitated with ibrutinib monotherapy in CLL. Ibrutinib induced a modest increase in B-cell and plasma cell apoptosis in preclinical and in vitro studies.5,6 A possible mechanism is through inhibition of phosphorylation of the p65 subunit of nuclear factor-κB. This prevents its translocation to the nucleus, resulting in downregulation of Bcl-xL, FLICE inhibitory protein, and survivin, thus culminating in caspase-mediated cell death.6 One case of grade 3/4 TLS was reported in a phase 1b/2 study of ibrutinib in CLL.1 However, other causes of TLS such as concomitant medications or spontaneous phenomenon were not mentioned. Two cases of TLS have been described with a combination of ibrutinib with bendamustine-rituximab.7 Such cases have not been reported with other immunotherapy combinations of ibrutinib with rituximab8 or ofatumumab.9 Our patient’s course suggests that clinicians should be aware of TLS as an infrequent but potentially life-threatening complication of treatment of CLL with ibrutinib.
Authorship
Contribution: V.K. collected patient data and wrote the manuscript; R.G. reviewed and edited manuscript; P.M. reviewed manuscript; and J.J. assisted with collecting patient data.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Varinder Kaur, Division of Hematology/Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR 72205; e-mail: varinderdhaliwal@gmail.com.