Abstract
MRD assessment is used for risk stratification, prognosis, and treatment decisions (eg, hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recommendation) in adult and childhood ALL. In Ph+ ALL, three distinct assay methods may be used to detect MRD: polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for clonal immunoglobulin (IG) and T-cell receptor (TR) gene rearrangements, quantitative RT-PCR (RQ-PCR) measurement of BCR-ABL1 transcripts, and flow cytometry (Flow). If results vary by assay method, different treatment decisions might be made. To assess this possibility, we examined the concordance of MRD levels and corresponding HSCT recommendations across the three methods for measuring MRD in patients (pts) enrolled to CA180372, a phase 2 study of dasatinib added to standard of care chemotherapy in pediatric pts with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL.
CA180372 (Children's Oncology Group (COG) AALL1122) was a collaboration between the COG, EsPhALL (European Intergroup Study on Post Induction Treatment of Ph+ ALL), and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Prior to study initiation, validation and proficiency testing were completed for standardization of methods used to detect MRD and for interpretation of IG/TR and BCR-ABL1 in accordance with guidelines developed by the EuroMRD consortium. All Flow analyses were performed at Johns Hopkins University. All pts received continuous treatment with dasatinib (60 mg/m2/d starting at day 15 of induction therapy) added to successive blocks of the EsPhALL multiagent chemotherapy regimen for a maximum of 2 y. MRD was analyzed 4 times during therapy (induction IA/baseline, end induction IA, start high risk block 1 (HR1), and end HR block 3 (HR3)). Pts were recommended for HSCT if:
· Start of HR1 ≥0.05% by IG/TR PCR (or by Flow), less than 3-log reduction in MRD as measured by RQ-PCR for BCR-ABL1 OR
· Start of HR1 0.005-0.05% by IG/TR PCR (or by Flow) or any positivity by BCR-ABL1 AND MRD remains positive at any detectable level (providing the assay limit is at least 0.1%) at the end of HR3
Clinical decisions were based on a single MRDmethodology, with the hierarchy of IG/TR > BCR-ABL1 > Flow. In this report we evaluated the concordance in HSCT recommendation among all three MRD methods.
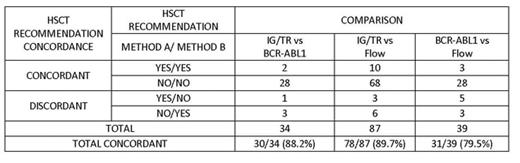
A total of 106 pts >1 y and <18 y were treated. HSCT eligibility could be determined for 89 (84%) pts by IG/TR, 41 (39%) by BCR-ABL1, and 104 (98%) by Flow. HSCT eligibility could not be determined for 17 (16%) by IG/TR due to technical challenges in assay development, 65 (61%) by BCR-ABL1 due to assay-specific requirements not being met, and 2 (2%) by Flow due to data missing from the database.
These data were used to conduct inter-assay HSCT recommendation comparisons (Table). Rates of concordance in HSCT recommendations varied from 79.5-89.7% across methods. Among the discordant HSCT recommendations observed between each pair-wise comparison, 6/9 (IG/TR vs Flow), 2/4 (IG/TR vs BCR-ABL1), and 4/8 (BCR-ABL1 vs Flow) numerical MRD results were within 1-log, but fell on opposite sides of the assay cutoff point; assay-specific protocol criteria resulted in discordant HSCT recommendation in those cases.
All pts enrolled to CA180372 were followed by at least one MRD method. HSCT recommendations could be made for most (98%) pts by Flow, while HSCT recommendation by IG/TR could be made for 84% of pts. Only 39% of pts could be recommended for HSCT based on BCR-ABL1 results. The main reason that BCR-ABL1 results were available for fewer pts was the requirement for at least 10,000 copies at baseline in order to assess if a 3-log reduction was achieved. Re-evaluation of assay-specific requirements is warranted. The overall concordance in HSCT recommendation was approx 80-90% across all three MRD methods. Overall, HSCT recommendation would have differed in 14 pts. Discordance between assays may be attributable (in part) to protocol-specific criteria, assay-specific threshold cut points, and/or differences in MRD results over different marrow pulls. Outcome data are not mature enough at this time to know whether pts recommended against HSCT by one method have increased risk for relapse when found to be eligible for HSCT by another method.
HSCT Recommendation Concordance, by MRD Method
Borowitz:Becton Dickinson Biosciences, Medimmune: Research Funding. Geese:BMS: Employment. Healey:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment. Gastier-Foster:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Hunger:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment; Jazz Pharmaceuticals; Sigma Tau Pharmaceuticals; Erytech: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.