Abstract
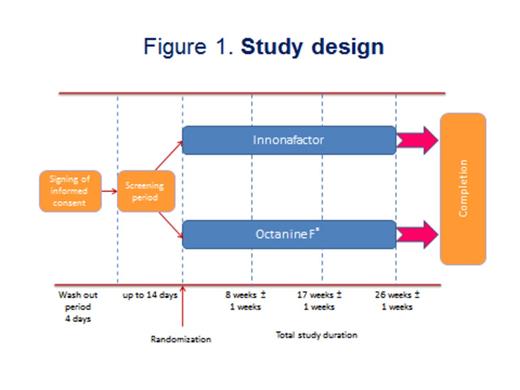
During a controlled, randomized, open, prospective, multicenter clinical trial the efficacy and safety of a new domestically produced recombinant factor IX (FIX, nonacog alfa, CJSC "GENERIUM", Russia) were investigated in comparison with plasma drug Octanine® F (filtered) ("Octapharma pharmazeutika produktionsges mbH", Austria) for the prophylactic treatment of bleedings in patients with severe and moderate hemophilia B. After screening and a 4-day washout period 18 patients with moderate (n=8) and severe (n=10) hemophilia B were divided into 2 groups according to randomization: the 1st group patients (n=9) received the nonacog alfa, the 2nd group (n=9) Octanine F (fig. 1). In the 1st group there were 4 patients with severe hemophilia B (activity of FIX was less than 1%) and 5 patients with the moderate form of the disease (activity of FIX was 1-3%). In the 2nd group 6 patients had severe and 3 moderate hemophilia B (activity of FIX was 1-2,6%). In order to prevent bleeding nonacog alfa was injected slowly intravenously at a dose of 50±5 IU kg-1. Octanine F was infused at a dose of 30±5 IU kg-1. Drugs were injected 2-3 times per a week during 26±1 weeks (6 months). The main criterion of drug efficacy was the average number of bleedings within 6 months of prophylactic treatment. Anticipated average number of bleedings was determined based on the effectiveness of the original drug Benefix® (Pfizer, USA) and was 9±3 cases. Additional criteria of efficacy were severity of bleeding, activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) and FIX activity before and 30 min after drug administration compared with normal values.
In the 1st group 2 moderate bleeding episodes occurred in 2 patients, while in the 2nd group 10 hemorrhagic episodes occurred in 4 patients (1 episode was severe, 1 - moderate, and 8 were low grade). There were no significant differences in frequency of bleeding events.
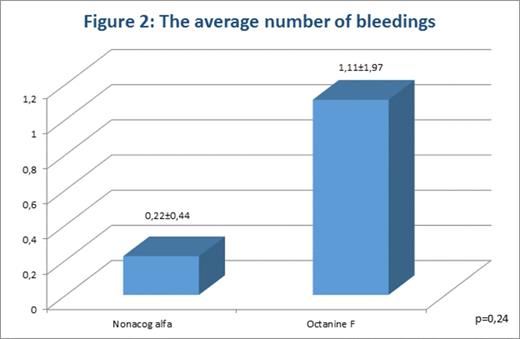
The average number of bleedings during the analyzed period in patients of the 1st group was 0,22±0,44. In patients of the 2nd group it was 1,11±1,97; the differences were statistically insignificant (p=0,24).
In patients of both groups, the average number of bleeding was within planned range (fig. 2).
Pharmacokinetics was evaluated by K-value (incremental recovery) and in vivo recovery (IVR).
After carrying out of prophylactic therapy during 6 months, Incremental recovery of nonacog alfa was 1,24 ± 0,32 IU/DL per IU/kg. The Incremental recovery (K-value) of Octanine F was analogous and amounted to 1,14 ±0,29 IU/DL per IU/kg.
During 6 months IVR of nonacog alfa was 47,56 ±13,56% and the IVR of Octanine F was not different and amounted to 49,05 ±15,68%.
Prophylactic therapy was accompanied by normalization of coagulation activity of blood. On the 26th week of therapy APTT values taken 30 minutes after drug administration were 38,04 ±3,63 sec. in 1st group and 41,49 ± 3,44 sec. in the 2nd group.
Safety assessment was performed in 18 patients. There were 6 adverse events in the 1st group and 12 in the 2nd group. All adverse events were not associated with drugs administration. Thus, the study shows that nonacog alfa (Innonafactor) is effective in prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with severe and moderate hemophilia B. The results are comparable with the results of the use of Octanine F.
The study demonstrated that nonacog alfa (Innonafactor) with its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic characteristics is comparable to Octanine F. Administration of nonacog alfa (Innonafactor)to patients with severe and moderate hemophilia B was accompanied by normalization of APTT and FIX activity and rising activity of FIX and its degree of recovery. Treatment with nonacog alfa (Innonafactor) was safe and without side effects, infection transmission, de novo inhibitor incident.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.