Abstract

Background: DVT and PE are common complications in hospitalized patients. Many hospitals have implemented EMR-based protocols to identify patients who could benefit from prophylactic anticoagulation, because of the increased morbidity, mortality, and cost associated with thrombotic disease. Several groups have sought to characterize the potential seasonal and winter variation in the incidence of DVT and PE, with several international studies supporting a so called "Winter effect" (Damnjanović et al., Hippokratia 2013); however, no study has demonstrated a "Winter effect" on patients within the US (Stein et al., Am J Cardiol 2004).
Objective: (1) To compare mortality rates and length of stay (LOS) in hospitals by month to identify a "Winter effect" in patients diagnosed with either DVT or PE; and (2) characterize other factors that might influence mortality and LOS, using the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS), Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP), Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Methods: The NIS was queried from 1998-2011. Inclusion criteria were a diagnosis of DVT (ICD-9 453.4X, 453.8X) and/or PE (ICD-9 415.1X) in patients aged 18 years or more. The sample was weighted to approximate the full inpatient population of the United States over the period of interest. Admission data was then analyzed to compare mortality rates over those years by month. Demographics, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), length of stay, hospital region, and admission type (emergent/urgent versus elective admissions) were assessed. Linear and logistic models were generated for complex survey design to assess predictors of mortality and LOS.
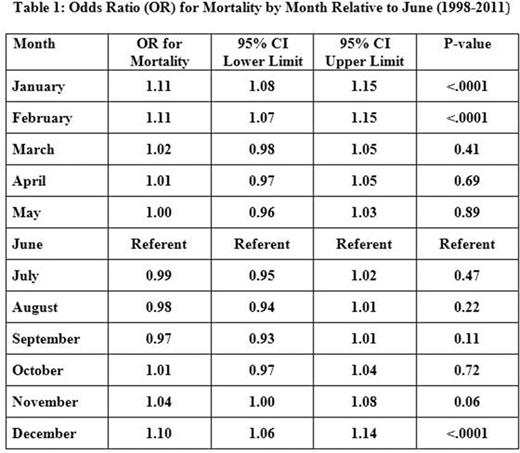
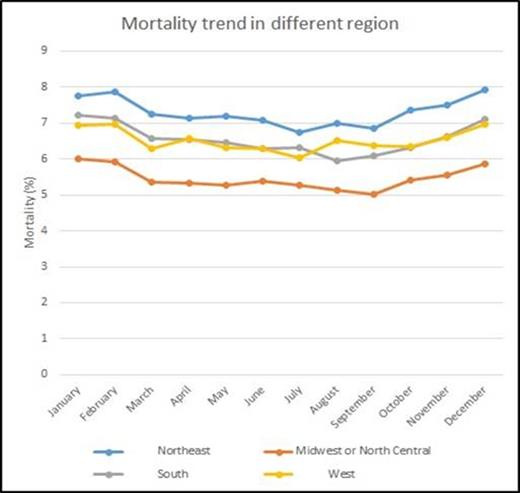
Results: A total of 1,449,113 DVT/PE cases were identified in the NIS (weighted n = 7,150,613). 54.7% of admission were for females, 56.4% were white, and 49% of admissions were at a teaching facility. Mortality over the 12 months was 6.4% and was noted to be higher in four months: November (6.52%), December (6.9%), January (6.94%), and February (6.93%), as indicated in the graph below. A similar trend was noted on a regional basis with higher mortality noted in winter months for all hospital regions (Northeast, Midwest or North Central, South, and West). No significant trend was noted in DVT/PE hospitalization rates between regions over 12 months (p=0.7674). Mortality in the total cohort was found to be significantly higher in December, OR 1.10 (95% CI: 1.06-1.14), p<0.0001; January, OR 1.11 (95% CI: 1.08-1.15), p<0.0001; and February, OR 1.11 (95% CI: 1.07-1.15), p<0.0001 compared to June (Table 1). Mortality was significantly lower in the Midwest or North Central, OR 0.78 (95% CI: 0.72-0.83), p<0.0001; and West, OR 0.80 (95% CI: 0.73-0.87), p<0.0001 compared to the Northeast. Mortality was also significantly higher in teaching hospitals than in nonteaching hospitals (OR 1.16 [95% CI: 1.10-1.22], p<0.0001), with mortality higher in teaching hospitals in all months. Length of stay was also significantly increased in the winter months. Similar results were noted in the subgroups of patients greater than age 80 or with a CCI score of 2 or more.
Conclusion: This national study identified an increased risk of mortality and increased LOS associated with hospitalizations for DVT/PE during the winter months (December, January, and February), supporting the existence of a "Winter effect" on hospital outcomes. Our data differs from previous reports on seasonal variation in DVT/PE in the US because of the database used (Bekkers et al., Clin Orthop Relat Res 2014). Since no regional variation was shown, decreased activity or cold temperature is unlikely to be the cause of this phenomenon. Alternative explanations should be sought.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract