Abstract
The human BCL6 gene encodes a transcriptional repressor that is needed for germinal center B cell development and T follicular helper cell differentiation, and it is best known for its association with certain human lymphomas, especially the diffuse large B-cell type. We devised a cell system in which the BCL6 repressive effects are inhibited with the goal of detecting the consequently upregulated BCL6 target genes. In order to do this, we converted the BCL6 zinc fingers (BCL6ZF), which can bind DNA but lack repressive effects, into a transcriptional activator and used this construct to compete with endogenous BCL6 in BJAB cells (Burkitt lymphoma cell line) which express high levels of BCL6. We used subtractive hybridization methodology to amplify differentially expressed sequences and identified the Pontin gene (also called Pontin 52, RUVBL1, TIP49, NMP238) as a potential target of BCL6 repression.
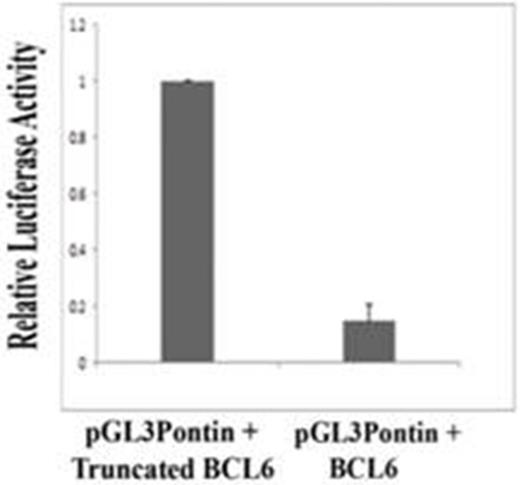
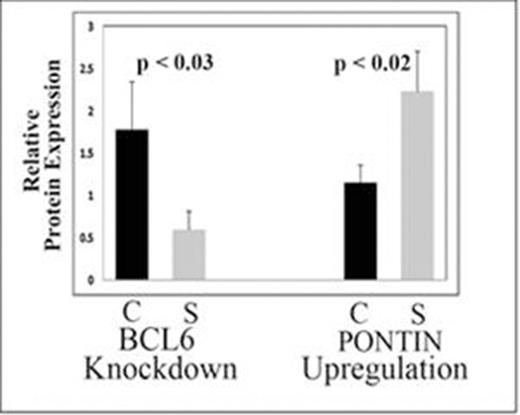
We confirmed Pontin as a BCL6 target. Northern blots prepared from BJAB cells that had been transfected with the BCL6 ZF construct or the vector in which it was cloned were hybridized with the cDNA fragment of Pontin obtained from cDNA subtraction and amplification. Scanning densitometry, used to normalize relative band intensity to β -actin, indicated that differential expression of Pontin as compared with the vector control was 2.6-fold (p < 0.02). We found an exact match to 7 (out of 8) bases described as a preferential BCL6 binding site in the promoter region of the Pontin gene. ChIP assays indicated that BCL6 was bound to this site, but the appropriate controls did not enrich DNA from this region. Transfection assays showed that the BCL6 protein represses transcription from the BCL6 consensus binding site in the Pontin promoter (Fig. 1, 6.8-fold as compared with the control, p < 0.0001). Transfections of siRNAs targeting the BCL6 protein in BJAB cells led to a significant increase in endogenous Pontin (Fig. 2, 2-fold, p < 0.02). Finally, immunohistochemistry performed on 21 randomly selected B and T cell lymphomas showed an inverse relationship between BCL6 and Pontin in a majority of the tumors.
Pontin is a transcriptional cofactor with ATPase activity that is part of the AAA+ (ATPases Associated with diverse cellular Activities) superfamily which includes a large group of ring-shaped complexes that are involved in multiple cellular processes. The Pontin protein is expressed virtually ubiquitously, is evolutionarily conserved, and is expressed in both the cell nucleus and cytoplasm.
The BCL6 protein, also expressed ubiquitously and evolutionarily conserved, is upregulated 3 to 34 times in the nucleus of lymph node germinal center B cells as compared with resting B cells. It has been called a "master regulator" of the germinal center. It is possible, judging from the many essential functions of Pontin, that it, too, is a kind of "master regulator." Further understanding of the relationship between BCL6 and Pontin may help to provide new insights concerning the initiation and progression of B and T
cell lymphomas.
Transfection assays: The BCL6 Protein represses transcription from the Pontin Promoter
Transfection assays: The BCL6 Protein represses transcription from the Pontin Promoter
Knockdown of BCL6 protein levels by siRNA increases Pontin protein expression
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.