Abstract
Introduction: Advances in treatment strategies and supportive care have resulted in a growing number of survivors of adolescents and young adults (AYA: diagnosed 15-39y) with hematologic malignancies. In the general U.S. population, cardiovascular disease (CVD: heart failure, stroke, myocardial infarction) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, and cardiovascular risk factors (CVRFs: diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia) are well-established modifiers of CVD risk. While considerable effort has been made to characterize long-term CVD outcomes in survivors of childhood (<21y) cancer, there is a paucity of information on the magnitude and modifiers of CVD risk, as well as outcomes after onset of CVD in survivors of AYA cancers. AYAs diagnosed with hematologic malignancies may be at a higher risk of CVD when compared to the general population because of exposure to cardiotoxic therapies (anthracyclines, radiation), and the development of new CVRFs as they age.
Methods: Using a retrospective cohort study design, 779 2+y survivors of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL: N=274), Hodgkin lymphoma (HL: N=323), and acute leukemia (Leuk: N=182), diagnosed at age 15-39y between 1998 to 2009, and treated at Kaiser Permanent Southern California (KPSC) were included in the study. KPSC is the largest integrated managed care organization in Southern California, with documented 5-year insurance retention rates for AYA cancer survivors approaching 80% (J Adolesc Young Adult Oncol 2013 2:59). A non-cancer comparison group (N=8,062) was constructed by selecting individuals enrolled in KPSC and matched to cancer survivors (1:10) on age at diagnosis, sex, health plan membership and calendar year. Time-dependent Poisson regression was used to derive incidence rate ratio (IRR) estimates and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for CVD (ICD-9 definition: heart failure, stroke, or myocardial infarction), adjusted for relevant covariates. Kaplan-Meier curves were generated for cancer survivors, stratified by CVD status. Definition of CVRFs (hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia) was per an algorithm developed by KPSC's case management system, which uses a combination of ICD-9 codes, laboratory test results, and documentation of receipt of medications for these conditions (Am J Epidemiol. 2014 179:27).
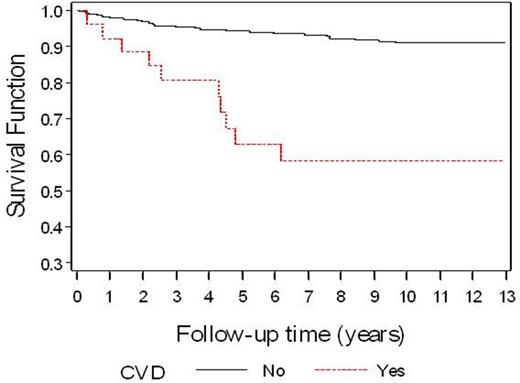
Results: Median age at cancer diagnosis was 29y (range: 15-39 years); 53.4% were male; 58.2% were non-Hispanic white; diagnoses: HL (41.5%), NHL (35.2%), Leuk (23.4%). In cancer survivors, median time from cancer diagnosis to end of follow-up was 5.4y (range: 2-14.9y), representing 4,961 person-years of follow-up. Comparison with non-cancer controls: Multivariable analysis adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, CVRFs, smoking history and overweight/obesity, revealed a significantly increased risk of CVD across all cancer diagnoses (Overall: IRR=3.5, 95%CI, 2.0-6.1) and by certain cancer types (Leuk: IRR=4.5, 95%CI, 1.8-11.2; HL: IRR=3.0, 95%CI, 1.0-8.9; NHL: IRR=2.0, 95%, 0.7-5.6) when compared to non-cancer controls. Modifiers of CVD risk: Hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia were independent modifiers of CVD risk. Hypertension was associated with a 5.1-fold (95%CI, 2.1-12.1) increased risk, diabetes was associated with a 4.4-fold (95%CI, 1.9-9.9) increased risk, and dyslipidemia was associated with a 2.8-fold (95%CI, 1.2-6.6) increased risk of CVD in AYA survivors when compared to survivors without these CVRFs. Outcomes by CVD status among cancer survivors: Overall survival was significantly worse (5y: 64%, 10y: 56%) among cancer survivors who developed CVD when compared to survivors without CVD (5y: 95%, 10y: 91%), p<0.01 (Figure).
Conclusions: Survivors of AYA hematologic malignancies are at increased risk for developing cardiovascular disease when compared to a matched non-cancer controls. In these survivors, overall survival following onset of CVD is especially poor, and cardiovascular risk factors are independent modifiers of delayed cardiovascular disease risk. Taken together these data form the basis for identifying high-risk individuals for population-based targeted surveillance, as well as aggressive management of cardiovascular risk factors.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.