Abstract
Introduction: Despite the improved outcomes seen with rituximab-CHOP (R-CHOP) in patients (pts) with newly diagnosed DLBCL, a significant number of pts with high risk disease (defined by IPI) are not cured; thus, new therapies are needed. Obinutuzumab (GA101, G) is a glycoengineered type II anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody with improved direct cell death and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity compared to rituximab. In addition, polatuzumab vedotin (PoV) is an antibody drug conjugate (ADC) designed to deliver the potent microtubule inhibitor MMAE to cells expressing CD79b. Thus, PoV has the potential to replace vincristine with a targeted agent. The incorporation of G and PoV would potentially increase the efficacy of the standard R-CHOP regimen. We report preliminary results from the dose-escalation portion of this Phase Ib/II study of PoV combined with obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (G-CHP) (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01992653).
Methods: This multicenter, open-label study will evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating doses of PoV with standard doses of G (1000 mg on days 1, 8, and 15 in cycle 1, and 1000 mg on day 1 of each subsequent cycle) and CHP. Adults, aged 18-80 years, with newly diagnosed or relapsed/refractory B-cell NHL were given PoV intravenously 1.4 or 1.8 mg/kg with G-CHP every 21 days for a total of 6 or 8 cycles. Doses were escalated in a 3+3 design based on dose limiting toxicity assessment during cycle 1. Assessments for anti-tumor activity were performed following 4 cycles of study treatment (tx) and at the end of study tx (EOT).
Results: As of Feb. 5, 2016, 12 pts (50% male) enrolled in the G-CHP + PoV dose-escalation (esc). The median age was 69.5 years (range 32-77) for all pts. Pts had untreated DLBCL (n=8), relapsed follicular lymphoma (FL, n=2), and untreated mantle cell lymphoma (MCL, n=2). At baseline, pts had stage I/II (n=5), III/IV (n=7) disease and ECOG status of 0-1 (n=12). Of 8 DLBCL pts, 3 had IPI 0-1, 2 had IPI 2, 2 had IPI 3, and 1 had IPI 4. At the time of this report, 8 pts in the dose escalation phase have completed study tx and all 12 had received interim assessments.
The most common adverse events (AEs) in > 30% of pts were alopecia (67%), neutropenia (50%), nausea (42%), anemia (33%), fatigue (33%), cough (33%), and rash (33%). Across both dose levels, 10 pts had 30 Gr 3/4 AEs including neutropenia (58%), anemia (25%), thrombocytopenia (25%), febrile neutropenia (17%), pneumonia (8%), C. difficile (8%), sepsis (8%), device related infection (8%), acute kidney injury (8%), hyponatremia (8%), atrial fibrillation (8%), SVT (8%), tachycardia (8%), syncope (8%) and hypertension (8%).
Three pts experienced 10 serious AEs (SAEs). One pt in the 1.4 mg/kg cohort had SAEs of febrile neutropenia (also a DLT), thrombocytopenia, and an atrial fibrillation exacerbation. Two pts in the 1.8 mg/kg cohort experienced a total of 7 SAEs. One pt experienced syncope, C. difficile, and febrile neutropenia while the other pt had sepsis, pneumonia, acute kidney injury, and cardiac complications including SVT and 3 vessel bypass surgery. Four (33%) pts experienced Gr 1 peripheral neuropathy (PN) during tx which did not lead to dose modifications. The reported terms included hypoaesthesia, PN, and paresthesia. There was 1 pt with PN in the 1.4 mg/kg cohort and 3 in the 1.8 mg/kg cohort. 3 pts discontinued study treatment: 1 due to recurrent neutropenic fevers (no subsequent tx), 1 due to pneumonia (followed with R-CVP), and 1 due to physician decision due to lack of treatment response (followed with R-ICE). No deaths were reported.
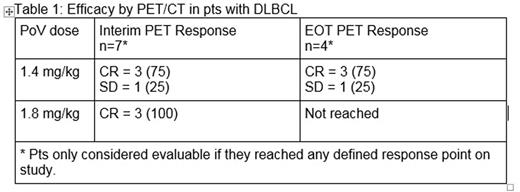
Efficacy: PET/CT response for pts with 1L DLBCL as of February 5, 2016 is reported in Table 1.
Of the 2 pts with FL, both achieved CR by PET/CT (1 at 1.4 mg/kg and 1 at 1.8 mg/kg). Of the 2 pts with MCL, both achieved CR by PET/CT (1 at 1.4 mg/kg and 1 at 1.8 mg/kg).
Conclusions: Early results show that PoV plus G-CHP has an acceptable safety profile in pts with previously untreated DLBCL and other B cell malignancies. Although the protocol-specified MTD was not formally reached, the recommended phase 2 dose of PoV was established at 1.8 mg/kg based on other studies. The study's Phase 2 PoV+R-CHP expansion and PoV+G-CHP dose expansion are ongoing.
Forero-Torres:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Research Funding; Juno: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding. Kolibaba:Pharmcyclics: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; GSK: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Cell Therapeutics: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Honoraria, Research Funding. Jones:Genentech, Inc.: Employment. Lee:Genentech, Inc.: Employment. Sharman:Gilead: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.