Abstract
Introduction The severity of sickle cell disease (SCD) increases with absolute neutrophil count (ANC, Eur J Haematol. 1998; 60: 267-8) and expression of adhesion molecules by leukocytes (Eur J Haematol. 2002; 69: 135 -144.). Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM 1) on vascular endothelium mediates leukocyte adherence to the blood vessel wall. This contributes to vaso-occlusion, the main mechanism of tissue damage in SCD. Micro-RNA 221 (MIR 221) regulates the gene for ICAM-1 (J Cell Science 2011; 124, 999-1006). How the severity of SCD relates with expression of MIR 221 was evaluated in this study.
Methods Following IRB approval and informed consent by appropriate persons, 25 healthy HbAA control persons and 73 HbSS patients (45M, 28F; age 2-18 yrs) were consecutively enrolled from University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Enugu. Patients who had blood transfusion in the previous 3 months were excluded. Information from medical records and clinical assessment was used to determine the SCD Severity Score according to the system previously validated by Cameron et al (J Nat Med Assoc. 1983; 75: 483-7). This system assigns scores to age at which the first symptom of SCD occurred, number of hospital admissions due to SCD per year, number of painful episodes per year, type of sickle cell crisis, number of major organ complications of SCD, pneumococcal sepsis, and the degree of failure to thrive assessed with patient's height and weight percentiles. A total score up to 4 indicates mild, 5-8 moderate, and 9-21 severe SCD.
Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) and Hb level were determined with an automated blood analyser, plasma level of soluble ICAM-1 (sICAM-1) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and expression of MIR 221 in leukocytes by polymerase chain reaction with fluorescent probes to enable quantification. To obtain a composite picture of the relationship between study parameters, 4mls of venous blood from each patient was analysed during vaso-occlusive crisis; and 4 weeks after the crisis had resolved (steady state). To help evaluate the degree of resolution of the crisis and the level of inflammation in each patient, the concentration of C-reactive protein was measured by ELISA in blood samples taken during crisis and steady state. The GraphPad Prism statistical package version 5.03 was used for data analyses. Following D'Agostino and Pearson's Omnibus normality test which showed that the values of MIR 221expression, sICAM 1 concentration, and ANC did not have a normal (Gaussian) distribution, median values and non-parametric tests were used for statistical analyses of these data.
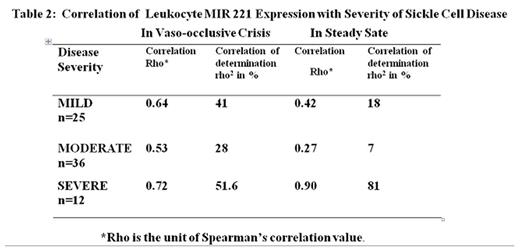
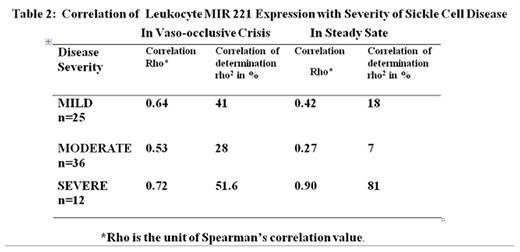
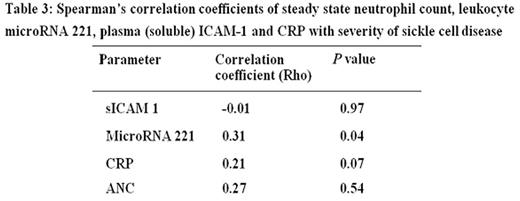
Results Based on Cameron Severity Scores, 25 patients had mild, 36 moderate and 12 severe SCD. The mean severity score for all patients was 5.85± 2.31. Median leukocyte MIR-221 of 3,092 copies/5ul of cDNA in steady state was comparable to 3,764 copies/5ul of cDNA in crisis (p = 0.6, Table 1). Both values were significantly higher than the median leukocyte MIR221 of 1428 copies/5ul of cDNA in healthy HbAA controls; P<0.0001. The quantity of MIR221 in leukocytes in mild SCD (median 3092 copies/5ul of cDNA) was significantly different from that in moderate disease (median 4004 copies/5ul of CDNA) which, in turn, differed significantly from that in severe SCD (median 5587 copies/5ul of cDNA, p< 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis Test). Spearman's correlation coefficient (Rho) between the Cameron Severity Scores in patients with severe SCD and the quantity of MIR 221 in leukocytes during steady state was high at 0.72 (Table 2). The quantity of MIR 221 in leukocytes during steady state emerged as a stronger correlate of SCD severity than ANC (Table 3). As crisis resolved and steady state returned, the inflammatory markers C-reactive protein (Kruskal-Wallis test, p=0.0003) and ANC (Wilcoxon matched pairs test; p<0.0001) reduced.
Conclusions The strong correlation between severity of SCD and the quantity of leukocyte MIR 221 in steady state suggests that leukocyte MIR 221 is a candidate biomarker for assessing the severity of SCD. The quantity of MIR 221 in leukocytes, unlike ANC, did not change significantly from crisis to steady state in this study; and could be a more consistent and stronger index of SCD severity than absolute neutrophil count. As a regulator of the gene for ICAM 1 which contributes to leukocyte adhesion and organ damage, the role of MIR 221 in SCD deserves further studies in view of the potential benefit of anti-adhesion therapy.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.