Abstract
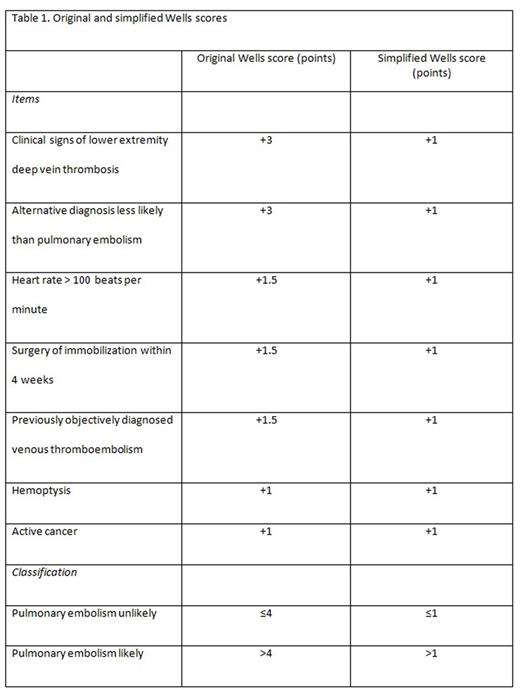
Background: Among patients with suspected pulmonary embolism (PE), imaging can be safely withheld in those with a 'PE unlikely' Wells score and a negative D-dimer. A simplification of the Wells score has been proposed to improve clinical applicability (Table 1), but its performance is less clear, in particular in combination with age-adjusted D-dimer testing.
Objectives: To compare the performance of the original and simplified Wells scores alone and in combination with age-adjusted D-dimer testing.
Methods: Individual patient data from 7,268 patients with clinically suspected PE enrolled in 6 prospective diagnostic management studies were used. The discriminatory performance, calibration, and diagnostic accuracy of the original and simplified Wells scores were evaluated. The efficiency and failure rate of both dichotomized scores combined with age-adjusted D-dimer testing were compared using a one-stage random effects meta-analysis. Efficiency was defined as the proportion of patients in whom PE could be considered excluded based on a 'PE unlikely' Wells score and a D-dimer below the age-adjusted treshold, defined as ≤500 µg/L in patients of 50 years or younger and the patient's age times 10 µg/L in those older than 50 years. The failure rate was defined as the proportion of patients subsequently diagnosed with symptomatic venous thromboembolism during 3-month follow-up.
Results: The discriminatory performance of the original and simplified Wells scores was comparable (c-statistic 0.73 [95% CI 0.72-0.75] vs. 0.72 [95% CI 0.70-0.73]). When combined with age-adjusted D-dimer testing, the original and simplified Wells rules had comparable efficiency (33% [95% CI 25-42%] vs 30% [95% CI 21-40%]) and failure rates (0.9% [95% CI 0.6-1.5%] vs. 0.8% [95% CI 0.5-1.3%]).
Conclusion: Among patients with suspected PE, the original and simplified Wells rules in combination with age-adjusted D-dimer testing have similar performance in ruling out the disease. Given its ease of use in clinical practice, the simplified Wells rule may be preferred.
Huisman:Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co.KG: Other: Grant support; GlaxoSmithKline: Other: Grant support; Bayer HealthCare: Other: Grant support; Pfizer: Other: Grant support; Actelion: Other: Grant support.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.