Abstract
Background: The nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) gene is not only commonly mutated in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), but also encodes several linear splice isoforms, one of which was recently shown to be of prognostic importance. Furthermore, circular RNAs (circRNAs) are transcribed from the NPM1 gene which demands further investigation with regard to function in normal hematopoiesis and impact on leukemogenesis.
Aims: We aimed to investigate circRNAs derived from NPM1 and gain insights into their regulation and function. Additionally, we wanted to determine changes in the circular RNAome in the course of hematopoietic differentiation and leukemic transformation.
Methods: Circular NPM1 transcripts were detected by PCR and sequenced in leukemic cell lines (n=7) and healthy control samples (n=3, peripheral blood-derived mononuclear cells). Expression of hsa_circ_0075001 and total NPM1 was measured in a cohort of 23 NPM1 wildtype (NPM1wt) and 23 NPM1 mutated (NPM1mut) AML patients via quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR), and Affymetrix U133plus2 microarray data was set in relation to the expression levels. Principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted to identify groups with similarities in gene expression patterns and differentially expressed genes were subjected to pathway analysis. Next, ribosomal RNA-depleted RNA-seq was performed for 5 NPM1mut and 5 NPM1wt AML cases, as well as 10 healthy control samples derived from 4 FACS-sorted myeloid differentiation stages (myeloblasts, promyelocytes, metamyelocytes and neutrophils). PCA and unsupervised hierarchical clustering were performed based on circRNA expression.
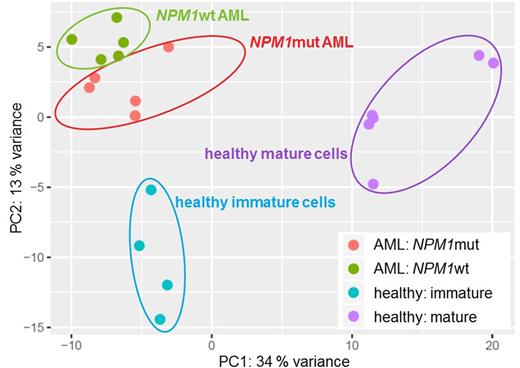
Results: We detected and sequenced multiple circular NPM1 transcripts (n=23) in leukemic as well as in healthy control cells. As hsa_circ_0075001 showed differential expression between different AML cell lines in a semi-quantitative PCR analysis, quantification in 46 AML patients via qPCR was performed. This analysis revealed that total NPM1 and hsa_circ_0075001 expression were independent of the NPM1 mutational status. Furthermore, the hsa_circ_0075001 expression status defined distinct leukemia subgroups characterized by similarities in gene expression as determined by PCA. For example, differentially expressed genes between high versus low hsa_circ_0075001 expression groups (dichotomized at the median) were significantly enriched in components of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway, which was downregulated in patients with high hsa_circ_0075001 expression. Expression of hsa_circ_0075001 correlated positively with total NPM1 expression, and RNA-seq analysis further revealed a global correlation of circRNA and parental gene expression. In total, in our cohort circRNAs were found for 19 % of all expressed genes. PCA based on circRNA expression illustrated that immature and mature hematopoietic cells, as well as NPM1wt and NPM1mut AML samples, exhibit distinct circRNA signatures (Figure 1). Thus, circRNA expression seems to play a role during differentiation of normal hematopoietic cells, but also seems to be severely deregulated in AML.
Figure 1: Altered circular RNA expression in AML patients compared to healthy control samples. Principal component analysis (PCA) of circRNA expression data of 5 NPM1mut patients (red), 5 NPM1wt patients (green), and 10 healthy control samples, of which 4 were derived from immature (blue) and 6 from more mature myeloid differentiation stages (purple). Data was generated via RNA-Seq and reads derived from circRNAs were aligned and quantified using STAR, and normalized and transformed using DESeq2. PCA was performed based on 500 genes with the highest variance of circRNA expression across all samples.
Conclusions: circRNAs transcribed from the NPM1 gene showed differential expression in AML cell lines and healthy cells, and higher hsa_circ_0075001 expression defined an AML subgroup characterized by downregulation of the TLR signaling pathway. These findings provide evidence for the relevance of circular NPM1 transcripts and add another level of complexity to the multifaceted gene NPM1. In general, circRNA expression seems to be involved in the regulation of hematopoietic differentiation, which is in line with previous observations, but, based on distinct circRNA expression profiles in AML, they might also play a significant pathogenic role in leukemic transformation.
Paschka:Celgene: Honoraria; Pfizer Pharma GmbH: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Medupdate GmbH: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy; ASTEX Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.