Abstract
Introduction:
Long-term survival rates among patients with chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukaemia (CP-CML) have remarkably improved since the introduction of imatinib, a BCR-ABL1 tyrosine-kinase inhibitor (TKI), as the standard first-line therapy. Several prognostic scores have been employed to predict clinical response and survival of CP-CML patients treated with TKIs. The EUTOS long-term survival (ELTS) score was recently introduced and shown to predict the probability of CML-specific death in long-term surviving patients on imatinib therapy, more effectively than the existing scores. The ELTS score was calculated by a formula that included age at diagnosis, spleen size below costal margin, platelet count and blast percentage in peripheral blood as prognostic factors. In our study, we evaluated the ELTS score in predicting the probabilities of CML-specific death, long-term overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) rates in Asian CML patients treated with imatinib. As genetic differences, particularly the BCL-2 like 11 (BIM) deletion polymorphism, have been shown to confer intrinsic resistance to imatinib in East-Asian patients, we also explored the role of BIM deletion polymorphism profiling as a prognostic biomarker for CML-specific death among different risk groups stratified by the ELTS score.
Methods:
A retrospective analysis was performed on CP-CML patients treated with first-line imatinib within one year of diagnosis in Singapore General Hospital from June 2001 to November 2014. The ELTS score was obtained with online calculator at www.leukemia-net.org. Low-risk group was defined as a score ≤1.568, intermediate-risk group as a score >1.568 but ≤2.2185, and high-risk group as a score >2.2185. Progression was defined as transformation to accelerated or blast phase or death from any cause. OS and PFS were calculated with the Kaplan-Meier method and compared by the log-rank test. Cumulative incidence probabilities of CML-specific death were compared by the Gray test.
Findings:
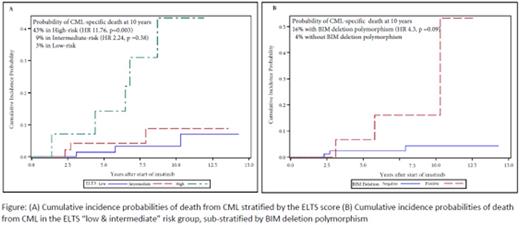
134 patients were included for analysis. 63% were Chinese, 17% were Malays, 8% were Indians and 12% were of mixed ethnic origin. Median age at diagnosis was 45 years and 60% were male. Median follow-up was 7.7 years (range: 0.4 to 13.2 years). 17 deaths out of 134 patients (13%) were recorded, of which 11 were CML-specific (65%). 54% of patients were categorised as low-risk, 36% as intermediate-risk and 10% as high-risk by the ELTS score. The cumulative incidence probabilities of CML-specific death at 10 years were 43% in high-risk (hazard ratio (HR): 11.76, 95% confidence interval (CI): (2.32, 59.71), p=0.003) and 9% in intermediate-risk (HR: 2.24, 95% CI: (0.37, 13.49), p=0.38) compared to 3% in low-risk groups.10-year OS probabilities were 50%, 82% and 93% in high-, intermediate- and low-risk ELTS groups respectively (p=0.001). 10-year PFS probabilities were 50%, 84% and 89% in high-, intermediate- and low-risk ELTS groups respectively (p=0.004).
Among 103 East-Asian patients with low- and intermediate-risk ELTS sub-groups, 15% harboured BIM deletion polymorphism. The probability of CML-specific death at 10 years in this subset was 16% with BIM deletion polymorphism, but 4% without polymorphism (HR 4.30, 95% CI: (0.76, 24.35), p=0.099). 10-year OS probabilities in the subset were 75% and 89% in patients with and without BIM deletion polymorphism respectively (p=0.014).
Conclusions:
The ELTS score was able to predict the probability of CML-specific death and identify high-risk patients in our multi-racial Asian CML patients treated with imatinib. Genetic profiling using BIM deletion polymorphism provided further stratification by identifying a subset of inferior long-term survivors with high probability of CML-specific death among otherwise non high-risk patients.
Chuah:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Chiltern: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.