Abstract
Introduction: A recent study revealed an antiproliferative and apoptotic effect of propranolol on multiple myeloma (MM) cells. Our previous small matched case-control study showed longer survival in patients with propranolol and other beta-blockers (BB) intake than those without. This larger scale study was conducted to confirm the positive association of BB and MM survival.
Methods: We identified 1971 newly diagnosed pts seen at Mayo Clinic between 1995 and 2010. Cardiac medication usage after diagnosis of MM was extracted from patient records and categorized based on BB intake. Cause of death was collected with death due to MM as the primary interest event and death due to cardiac disease or other reasons as competing risk events. The primary outcomes were MM disease-specific survival (DSS) and overall survival (OS). Cumulative incidence functions and Kaplan-Meier method were used to estimate the 5-year cumulative incidence rate (CIR) of MM death and OS rate, respectively. DSS and OS were compared by Gray's test and log-rank test, respectively. Multivarable Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the adjusted cause-specific HR (HRCSadj.) and hazard ratio (HRadj.) for DSS and OS, respectively, adjusting for demographics, disease characteristics, diagnosis year, and various chemotherapies.
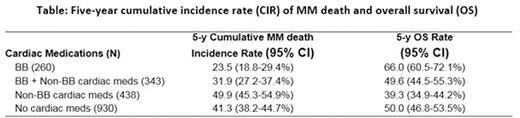
Results: 930 (47.2%) of MM patients had no intake of any cardiac medications; 260 (13.2%) had BB only; 343 (17.4%) used both BB / non-BB cardiac medications; and 438 patients (22.2%) had non-BB cardiac drugs. Five-year CIR of MM death and OS rate were shown in table. Superior MM DSS was observed for BB only users, compared to patients without any cardiac drugs (HRCSadj., .53, 95% confidence interval [CI], .42-.67, padj.<.0001) and non-BB cardiac drugs users (HRCSadj., .49, 95% CI, .38-.63, padj.<.0001). Patients received both BB and other cardiac drugs also showed superior MM DSS than non-cardiac drugs users (HRCSadj.., .54, 95% CI, .44-.67, padj.<.0001) and non-BB cardiac drug users. (HRCSadj., .50, 95% CI, .40-.62, padj.<.0001). MM DSS does not differ between BB users with and without other cardiac drugs (padj.=0.90). Multivariable analysis showed the same pattern for OS. None of the MM therapies impacted the differences in DSS and OS among BB intake groups (interaction padj.>.60).
Conclusion: MM patients with BB intake showed reduced risk of death due to MM and overall mortality compared to patients who used non-BB cardiac or never used cardiac drugs. The result warrants further investigation for anti-cancer effect of BB in MM.
Shi:Mayo Clinic: Employment. Kumar:Onyx: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Array BioPharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Skyline: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Research Funding; Glycomimetics: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Noxxon Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Millennium: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy; Kesios: Consultancy. Gertz:NCI Frederick: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Med Learning Group: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Research to Practice: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Alnylam Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Prothena Therapeutics: Research Funding; Ionis: Research Funding; Annexon Biosciences: Research Funding; GSK: Honoraria; Sandoz Inc: Honoraria. Kapoor:Celgene: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding. Dispenzieri:pfizer: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Alnylam: Research Funding; Jannsen: Research Funding; GSK: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Prothena: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.