Abstract

Introduction: Lung cancer (LC) is the commonest cause of cancer mortality in USA. Thromboembolism (TE) is the second leading cause of death in cancer patients. The ambulatory thromboprophylaxis (ATP) in solid cancer patients remains uncertain. However, LC is at least an intermediate risk for TE according to Khorana scoring system. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs to determine the benefit and risk of ATP with low-molecular weight heparins (LMWH) in LC patients receiving chemotherapy.
Methods: We performed a comprehensive literature search using MEDLINE and EMBASE databases through June 30, 2016. The RCTs with reduction in TE as a primary or secondary endpoint and the major bleeding (MB) as a safety outcome were included in the analysis. Mantel-Haenszel method was used to calculate the estimated pooled risk ratio (RR), and risk difference (RD) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Fixed effects model was applied.
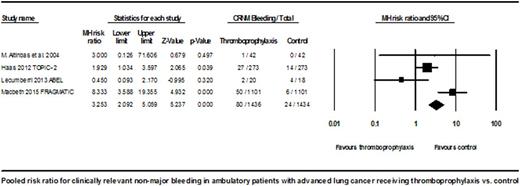
Results: A total of 4315 patients with LC from 4 RCTs and a subgroup of another 2 RCTs were included in our analysis. The prophylactic doses of dalteparin, nadroparin, certoparin, semuloparin and bemiparin were used in the studies. The ATP duration ranged from 3 to 6 months. The randomization ratio was 2 to 1 in PROTECHT study and 1 to 1 in other studies. The TE incidence was 89 (4.007%) in ATP group and 166 (7.927%) in control group with a RR of 0.510 (95% CI: 0.397 to 0.654, P < 0.001). The absolute RD was -0.039 (95% CI: -0.053 to -0.025, P < 0.001) with an estimated number needed to treat (NNT) of 25 to prevent one TE event. MB events were 24 (1.506%) in ATP group compared to 15 (1.019%) in control group according to an analysis of 4 RCTs. The pooled RR for MB was statistically nonsignificant at 1.468 (95% CI: 0.785 to 2.746, P = 0.229). Clinically relevant nonmajor (CRNM) bleeding events were 80 (5.571%) in ATP group and in 24 (1.674%) in control group on an analysis of 4 RCTs. The RR for CRNM bleeding was statistically significant at 3.253 (95% CI: 2.092 to 5.059, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: In our study, the relative risk reduction for TE is 49% with a NNT of 25 to prevent one TE without increasing MB. Nevertheless, CRNM bleeding episodes were significant at a ratio of 3.253. Based on the findings, selection of LC patients who are at high TE risk is important. Further studies are necessary to define a subset of LC patients who may benefit from ATP.
Oo:Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract