Abstract
Introduction
Haemoglobin E-beta-thalassaemia (EBT) represent approximately 50 per cent of those affected with severe beta thalassemia.The highest frequencies are observed in India, Bangladesh and throughout Southeast Asia. Endocrinopathies are now amongst the common complications of thalassaemia and it is multifactorial in origin. Iron overload in EBT is also multifactorial. This study was undertaken to evaluate the thyroid dysfunction in patients of EBT and its correlation with serum ferritin levels.
Methods
EBT patients were evaluated prospectively to assess thyroid dysfunction status and correlate it with serum ferritin levels. High performance liquid chromatography was performed with Bio-rad beta thalassaemia short program variant II. Serum ferritin estimation was done with microplate immunoenzymometric assay and thyroid assay for TSH, free T4 and T3 were done by access 2 Immunoassay System, Beckman Coulter.
Results
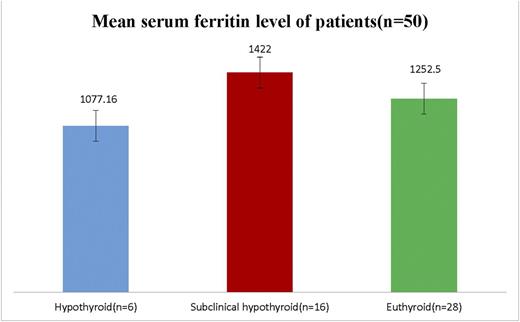
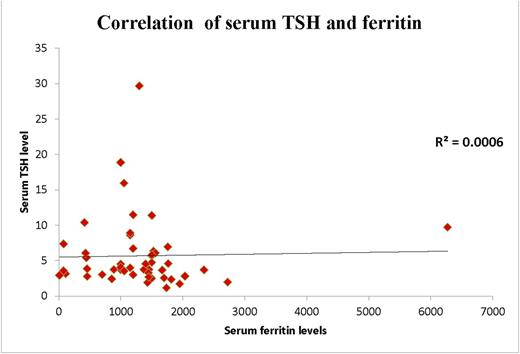
50 patients with EBT were evaluated. The mean age of patients were 19.7 years (range: 12-47). There were 28 males and 22 females. There were 41(82%) and 9(18%) transfusion dependent and transfusion independent patients respectively and 40(80%) were on chelation therapy. In this cohort 22(44%) patients had thyroid dysfunction. Six (12%) and 16(32%) of patients were having hypothyroidism and subclinical hypothyroidism respectively. Mean ± Standard deviation (S.D) of serum ferritin level with hypothyroidism, subclinical hypothyroidism and euthyroidism was 1077 ± 371.8 ng/ml ,1422 ± 1361.0 ng/ml and 1252 ± 664.4 ng/ml respectively with correlation coefficient =0 [Fig 1 and Fig 2]. Serum ferritin levels do not predict thyroid dysfunction in patients of EBT. Male and female have equal preponderance for thyroid dysfunction. Patients with subclinical hypothyroidism were having few symptoms compared to frank hypothyroidism and majority of symptoms in either scenario were masked by thalassemia itself. Earlier age of onset of EBT is associated more with thyroid dysfunction however the association is not statistically significant (p=0.2). There was no association between spleen size and thyroid dysfunction (p=0.7).
Conclusions
Thyroid dysfunction was seen in 42% of EBT patients. Prevalence of hypothyroidism was found to be higher in EBT patients compared to general population but a definite correlation with the serum ferritin levels could not be established.
Mean serum ferritin level and thyroid status
Correlation of serum TSH and ferritin level (correlation coefficient =0)
Correlation of serum TSH and ferritin level (correlation coefficient =0)
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.