Abstract
Introduction: Interleukin (IL)-10 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine with potent inhibitory effects in immune response. Higher expression of IL-10 has also been detected in classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL), and it has been suggested that the cytokine is involved in the pathogenesis of these tumors. CTLA-4 has long been recognized as regulatory function, potentially decreasing antitumor immune response. Augmentation of the immune response via blockade of CTLA-4 has shown an improvement in survival for patients with metastatic melanoma, Overexpression of PD-L1 on Reed-Sternberg cells is related with downregulation of effector T cell function and represents a potent mechanism of tumor evasion. PD-L1 inhibitors have shown excellent results in refractory cHL patients.
Objectives: The aim of the study was to evaluate the immune gene expression profile in peripheral blood of cHL patients at diagnosis and post-treatment and correlate these findings with clinical and epidemiological aspects.
Patient and Methods: This is an open multicenter study and, so far, we included 51 patients consecutively from February 2011 to November 2015. Twenty consecutively diagnosed cHL patients, with whole blood RNA extracted at diagnosis and after treatment, were recruited for this study and prospectively evaluated. The general expression of 96 messengers RNAs present in the peripheral blood and involved in immune response was performed by a customized quantitative real-time PCR array (TaqMan¨Low Density Array). The data was normalized with B2M mRNAs levels and relative gene expression was calculated by the 2^DDCt method, considering Wilcoxon test and Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment to correct p-values. In this study, only cHL patients whose histology could be confirmed were studied. All patients were HIV negative and received ABVD chemotherapy protocol and radiotherapy if necessary.
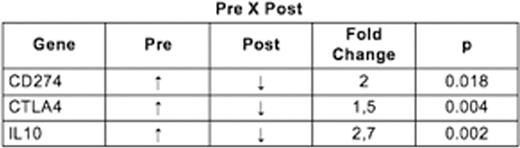
Results: From the 20 patients included in this study, 12 (60%) were male, 5 (31%) had Epstein Barr virus related cHL, 18 (90%) patients presented with B symptoms, 19 (95%) patients had advanced disease at diagnosis (stage IIBX, III and IV). Results of immune gene expression profile in paired samples from 15 patients before (pre) treatment and after (post) treatment are summarized in the following table:
We observed higher expression of CD274 (PD-L1), CTLA-4 and IL-10 mRNAs in patients at diagnosis compared to expression after treatment. We found no association between relapse and immune gene expression or epidemiological and clinical characteristics.
Conclusions: In this study we showed that IL-10, CD274 (PD-L1) and CTLA4 are downregulated after therapy, which suggests a mechanism for tumor immune evasion that was reverted by ABVD chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Understanding cHL associated immunosuppression and the immune reconstitution after treatment maybe the key to develop new prognostic factors and treatment strategies.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.