Abstract
Objectives The presence of IgM monoclonal gammopathy can occur in a broad spectrum of diseases, including Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (WM), various B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL), monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), and so on. MYD88 L265P and WHIM-like CXCR4 mutation are highly prevalent in WM. However, the data is lacking in other IgM monoclonal gammopathy related diseases (IgM-RD). Therefore we investigated MYD88 L265P and WHIM-like CXCR4 mutation in various IgM-RD.
Methods Patients with sIFE confirmed IgM monoclonal gammopathy and had enough material for DNA extraction between January 2008 and May 2016 at Peking Union Medical College Hospital were enrolled in this cohort. Bone marrow samples or paraffin-embedded tumor tissues were collected. We performed Real-time allele-specific-polymerase chain reaction (AS-PCR), AS-PCR and Sanger sequencing to explore the presence of MYD88 L265P and WHIM-like CXCR4 mutation.
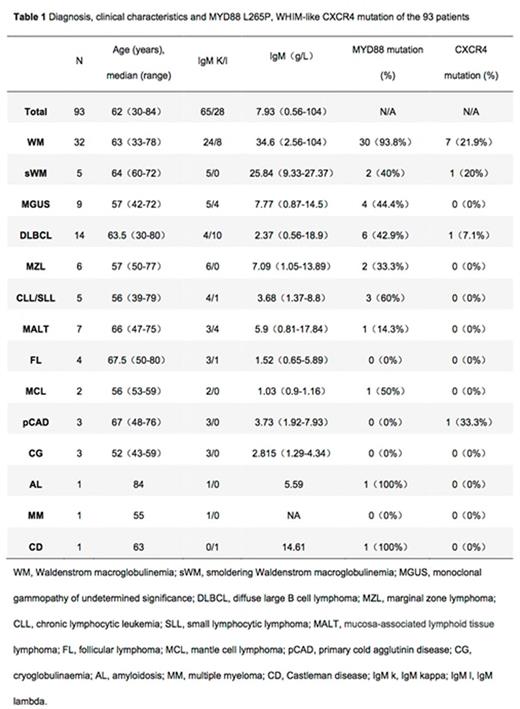
Results Ninety-three patients (51 male and 42 female patients) were included in this retrospective study. Median age at diagnosis was 62 years (range, 30-84 years). As for the type of light chain, 65 patients were IgM kappa (69.9%), 28 patients were IgM lambda (30.1%). The median level of serum IgM was 7.9g/L (range, 0.6-104.0g/L). There were 32 patients (34.4%) diagnosed with WM, 5 patients (5.4%) diagnosed with smoldering WM (sWM), 38 patients (40.9%) diagnosed with B cell NHL and 9 patients (9.7%) were diagnosed with MGUS. We outlined the main diagnosis, clinical characteristics and MYD88 L265P, WHIM-like CXCR4 mutation of the 93 patients in Table 1. MYD88 L265P mutation was detected in 30/32 (93.8%) patients with WM, 2/5 (40%) with sWM, 4/9 (44.4%) with IgM-MGUS, 6/14 (42.9%) with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), 2/6 (33.3%) with marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), 3/5 (60%) with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), 1/7 (4.3%) with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (MALT), 1/2 (50%) with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), 1/1 patients with primary amyloidosis (AL) and 1/1 patients with Castleman disease (CD). WHIM-like CXCR4 mutation was detected 7/32 (21.9%) patients with WM, 1/5 (20%) with sWM and 1/14 (7.1%) with DLBCL.
Conclusion IgM monoclonal gammopathy is most frequently found in WM, but it contains a broad spectrum of diseases. MYD88 L265P mutation is highly prevalent in WM and IgM MGUS, and the prevalence of MYD88 mutation in IgM related NHL is higher than that in not specified NHL reported in the literature. WHIM-like CXCR4 mutation is common in WM, but rare in other IgM-RD.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.