Abstract
The Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) are a group of clonal hematopoietic stem cell diseases characterized by cytopenias, dysplasia in one or more myeloid cell lines, ineffective hematopoiesis and increased risk for development of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).The pathological hallmark of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) is marrow dysplasia, which represents the basis of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of these disorders. However, morphological diagnosis of MDS may have difficulties, with poor inter-observer agreement.Recently, Della Porta and col.(on behalf of Rete Ematologica Lombarda (REL) Network), described a new morphological score system to define dysplasia, that showed high sensitivity and specificity (>90%) andbetter inter-operator agreement (Leukemia 2015;29:66-75). In addition, new toolsfor diagnostic and prognostic purposes were developed.Flow cytometry (FCM) was addedin standard European Leukemia Net guidelinesasrecommended tool for diagnosis and prognosis in MDS, and a simple MDS-FCM scoring system based on four parameters (mainly CD34 and granulocytic cells) by Ogata and col. showed a good specificity (Haematologica 2009;94:1066-1074).
The aim of this study is to correlate morphological and immunophenotypic features in suspicion of MDS.
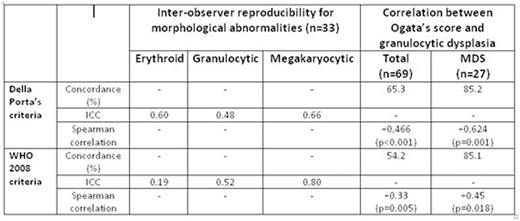
The study comprised two steps: the first used for morphological validation, included 33 bone marrow (BM) smears from patients with suspected MDS with or without therapy, reviewed by four experts hematologists blinded to clinical data. Dysplasia was evaluated using WHO 2008 criteria and Della Porta's score: 100 erythroblasts, 100 granulocytic cells and 30 megakaryocytes for dysplasia and 500 nucleated cells for blast cells percentage. The second step included 69 BM samples from patients with suspected MDS (27 with final diagnosis of MDS) and was used to correlate cytology and immunophenotypic findings. The morphological aspects were reviewed by one of the expert hematologists, using the same previous criteria and blinded to clinical data. Inter-operator reproducibility of morphological analyses was assessed by Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC). Acceptable reproducibility was defined as ICC > 0.4. The correlation of minimal morphological criteria with immunophenotypic criteria of Ogata and col. was assessed by Discordance rate and Spearman correlation.
The results are shown in table.
In conclusion our study shows good inter observer reproducitibility, in both used criteria. The use of new criteria of Della Porta to the erythroid series was slightly better, suggesting that can be useful in diagnosing myelodisplasias. Immunophenotypic data had a good agreement with morphologic data in confirmed cases of MDS.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.