Abstract
Background: Delayed platelet (plt) recovery and secondary thrombocytopenia occur in 5-25% of patients (pts) after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and is of adverse prognostic significance. Plt transfusion to prevent bleeding remains a mainstay of therapy and role of thrombopoietic agents is not known. In this phase I/II multicenter open trial, we investigated the safety and efficacy of romiplostim (Nplate; Amgen, thousand Oaks, CA) for (pts) with transfusion-dependent thrombocytopenia after allogeneic HSCT (NCT01980030).
Patients and methods: Adult pts undergoing standard of care allogeneic HSCT for any disease except myelodysplastic syndrome were eligible for this study 45 days or more after transplantation if they had plt count ² 20 x 109/L sustained for 7 days (² 50 x 109/L with a history of bleeding) or if they were plt transfusion dependent. Pts were excluded if they had abnormal liver function tests, serum creatinine ³ 176.8 μmol/L or had prior venous thrombosis. Pts were given weekly romiplostim for 12 weeks with intra-pt weekly dose escalation from 1µg/Kg to a maximum dose of 10 µg/Kg (with a dose reduction schema in case of plt overshoot). The study was composed of a 12-week treatment period. The primarysafety endpoint was the incidence of any grade 3 or 4 adverse events after HSCT, excluding those expected from the HSCT, as well as clinically significant bleeding events. The primary efficacy endpoint was time to reach a plt count above 50 x 109/L free of plt transfusion. Secondary endpoints were the durable plt response defined as a plt count above 50 x 109/L during 8 consecutive weeks independent of plts transfusions, the 1-year cumulative incidence (CumI) after HSCT of Graft versus host disease (GvHD), relapse and non-relapse mortality rates. All pts had a bone marrow biopsy before treatment and at one year. This study was approved by the research review board of the Hospital Saint-Louis (Paris, France). Statistical analysis was based on a modified intent-to-treat basis, excluding pts who did not fulfill the inclusion criteria. CumI were estimated using nonparametric methods, where deaths prior to the event of interest defined competing risks.
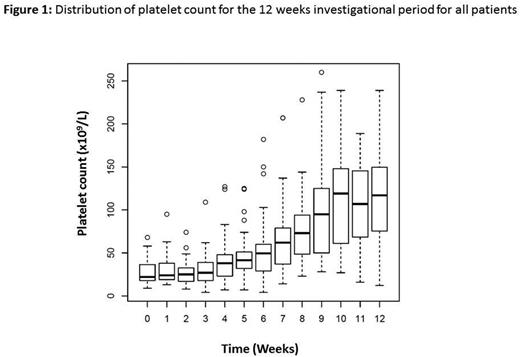
Results: 25 pts were included in 4 different HSCT French units between April 2013 and November 2015. The analysis was restricted to 24 pts (one pt with plt count > 20x109/L after inclusion). All but one pt have malignant disease (13/24 acute leukemia). Donor type was related for 12 pts. Stem cell source was peripheral blood in 15 pts and bone marrow in 9 pts, myeloablative conditioning regimen was used in 17 pts. Median time between HSCT and romiplostim initiation was 85 days (interquartile range, IQR 63 - 117). Nineteen pts completed the 12 investigational injections of romiplostim, while five did not due to 3 deaths (1 post transplantation EBV-related lymphoproliferative disorder, 1 relapse and 1 septic shock), 1 boost of donor stem cells and one pt with plt count above 50 Giga/L after 8 injections. A total of 21 adverse events (grade 3, n=10; grade 4 n=11) considered possibly related to romiplostim were reported in 6 pts. Hematological complications appeared in 4 pts (2 neutropenia, 1 anemia and 1 pancytopenia) and liver dysfunction was present in 2 pts (mild cytolysis). Overall, romiplostim was well tolerated with a 6 months adverse events CI of 25.2% (95%IC 7.3 - 43.2). No bleeding event as well as no thrombotic complications appeared. None of the pts developed fibrosis 1 year post treatment (2 pts not yet at 1 year). After romiplostim initiation, 20 pts received a plt transfusion. The median time to reach a plt count above 50 x 109/L free of plt transfusion was 36 days (Figure 1), with required doses of 4 mg/Kg (IQR, 3-6). Fifteen pts obtained a durable plt response. A total of 17 and 12 pts experienced aGVHD and cGVHD, respectively, with 100 days CumI of aGVHD of 67% (95%CI, 47-87) and 1-year CumI of cGvHD of 55% (95%CI, 32-78), respectively. Six pts died during the study (1 PTLD, 1 relapse, 1 septic shock, 1 lung aspergillosis and 2 acute distress respiratory syndrome of unknown origin). CumI of non-relapse mortality was thus of 21% (95%CI, 7-42%).
Conclusion: Romiplostim can be safely administered and improves plt count in pts with thrombocytopenia after allogeneic HSCT. The required dose to reach plt count above 50 x 109/L is 4 mg/Kg with a median time of 36 days.
Research support was provided in part by Amgen.
Peffault de Latour:Alexion: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.