Background: Adolescents and young adults (AYA) surviving classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (cHL) commonly face significant treatment-related morbidity that can result in premature death. It is not known if changes in therapy in recent years have resulted in reduction of excess mortality among long-term survivors of AYA-cHL.
Methods: We used data from the National Cancer Institute's Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results program (SEER-18) to determine the excess mortality rate (EMR) for 10-year survivors of cHL. We included patients age 15-39 years diagnosed with cHL as first malignant neoplasm from 1993 until 2003. Cases reported from death certificates or autopsy only were excluded. Follow up was updated at the end of 2013. EMR was calculated using the difference between the observed mortality in the cohort of interest and the adjusted expected mortality among age, gender and race-matched individuals in the general population.
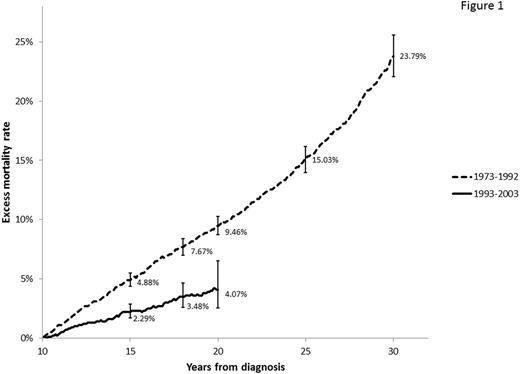
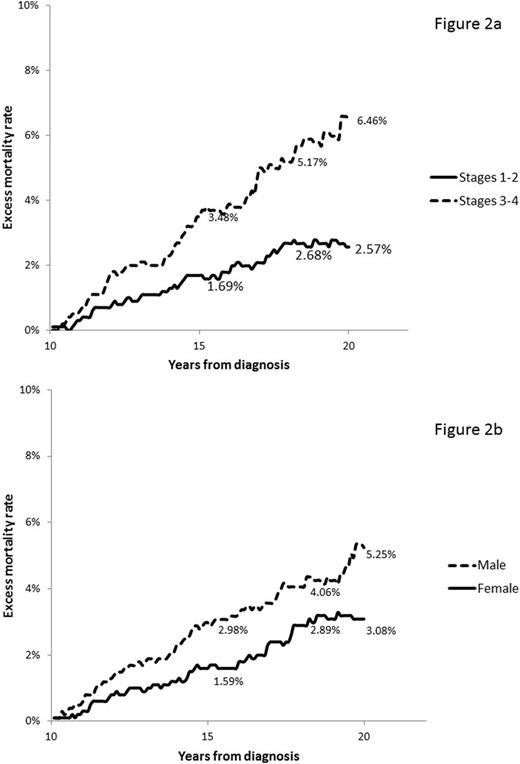
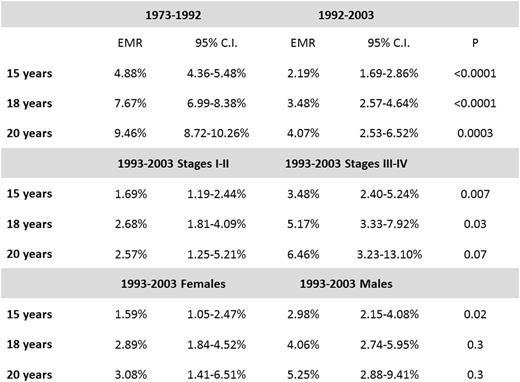
Results: A total of 6,480 cases of cHL were included in the analysis with median follow up of 42.5 months. Median age of patients was 27 years at the time of diagnosis, 3,172 (48.9%) were male, 4,405 (68%) had stage I or II, 1,750 (27%) had stage III or IV, and in 325 (5%) cases stage was not available. Most patients were non-Hispanic white (4,783, 73.8%), 761 (11.7%) Hispanic, 615 (9.5%) non-Hispanic black, 276 (4.3%) other ethnicity, and 45 (0.7%) unknown. Five thousand and sixty eight (78.2%) had nodular sclerosis cHL, 616 (9.5%) had mixed-cellularity cHL, 606 (9.4%) had cHL non-otherwise specified, 153 (2.4%) had lymphocyte-rich cHL, and 37 (0.57%) had lymphocyte depleted cHL. The 15-year, 18-year, and 20-year EMR for 10-year survivors was 2.19% (95% C.I, 1.69%-2.86%), 3.48% (95% C.I. 2.57%-4.64%) and 4.07% (95% C.I. 2.53%-6.52%), respectively. EMR among 10 year AYA cHL survivors with diagnosis between 1993 and 2003 was substantially improved when compared to a similar cohort of 5,870 survivors with diagnosis between 1973 and 1992 (Figure 1). EMR at 15 and 18 years of diagnosis was higher among survivors of stage III-IV cHL than among survivors of stages I-II (Figure 2a), and higher at 15 years among males than female survivors (Figure 2b). Use of radiation therapy for early stage disease did not seem to affect the risk of excess mortality among 10-year survivors (Table). Causes of death were similar for stages I-II vs. stages III-IV. Most common causes of death were second malignancy (27.2%), cardiovascular disease (19%), and Hodgkin lymphoma (18.5%). Among male survivors there was a higher proportion of deaths due to cardiovascular disease (23.7% vs. 11.5%, p <0.038).
Conclusion: Excess mortality rates for 10-year survivors of AYA-cHL has decreased with adoption of less toxic therapies. However, mortality rates continue high for several years for long term AYA HL survivors, mainly due to second malignancies and cardiovascular diseases. Less toxic therapies, control of cardiovascular diseases and implementation of cancer prevention programs for survivors of AYA-cHL are needed.
Costa:Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.