Abstract
EZH2 is critical in a process known as the Germinal Center (GC) reaction during which B-cells undergo somatic hypermutation and isotype switching in order to develop a large antibody repertoire. EZH2 is a histone methyltransferase serving as the catalytic subunit of the Polycomb Repression Complex 2 (PRC2), which is responsible for tri-methylation of histone 3 lysine 27 (H3K27), a mark of transcriptional repression. EZH2 recruits HDAC1/2 and DNMTs through its cofactor EED to further inhibit transcription. Mutations in EZH2 are found in 7-12% of FL and 22% of GC-DLBCL. EZH2 overexpression secondary to MYC and miRNA dysfunction has also been described. EZH2 also plays a role in T-cell differentiation and has been found in various T-cell malignancies. Histone acetyltransferases (HAT), notably CBP and p300, have also been implicated in B- and T-cell lymphomas and are mutated/deleted in 39% of GC-DLBCL and 41% of FL.
Given the presence of EZH2 and HAT dysregulation in lymphoma, we evaluated the potential synergy of EZH2 and HDAC inhibitors co-treatment. Single agent activity for GSK126, an EZH2 inhibitor, and romidepsin, a pan-HDAC inhibitor, was established in a panel of lymphoma cell lines (GC-DLBCL, Non-GC DLBCL, MCL and T-Cell lymphoma, n=21). Cell lines with known EZH2 dysregulation (GC-DLBCL and ATLL) were more sensitive to EZH2 inhibitors as exhibited by lower half maximal effective concentration (EC50) after 6 day exposure (EC50 0.01-16 µM). There was no association between HAT mutation/deletion and romidepsin sensitivity.
A panel of lymphoma cell lines was treated for 72 hr with GSK126 and romidepsin using concentrations represented by their EC30-50 (0.5-4.0 µM), and EC20-40 (1.0-4.0 nM), respectively. Synergy was assessed by Excess over Bliss (EOB), where EOB > 10 represents synergy. Simultaneous exposure to GSK126 and romidepsin in GC-DLBCL cell lines demonstrated potent synergy as represented by EOB > 30. Synergy was also present in ATLL cell lines (EOB 28), which are known to have EZH2 dysregulation, as well as non-GC DLBCL cell lines (EOB 47). Although these cell lines do not have EZH2 mutations, some possess relative EZH2 over-expression compared to other lymphomas. Evaluation of drug schedule using GSK126 pretreatment prior to romidepsin exposure did not impact synergy.
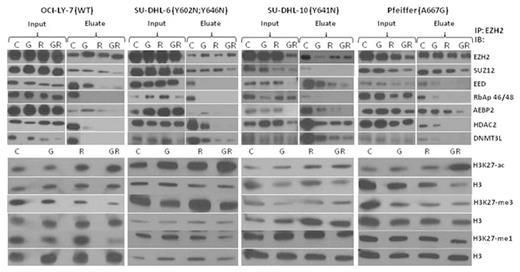
Compared to single agent activity, the combination of GSK126 (2 µM) and romidepsin (1-4 nM) led to a more pronounced decrease in H3K27 tri-, di-, and mono-methylation and increased acetylation in 4 GC-DLBCL cell lines (OCI-LY7, Pfeiffer, SU-DHL-6, SU-DHL-10) at 24 or 48 hrs. The impact of the combination on the function of the PRC2 complex was assessed via co-immunoprecipation in these cell lines. The combination demonstrated dissociation of the PRC2 complex (EZH2, SUZ12, EED, and RbAp46/48) as compared to single agent exposure. Treatment with the combination also induced dissociation of HDAC2 and DNMT3L. In addition, we observed decreased protein expression of PRC2 complex members and increased p21/CDKN1A, which was more notable in the combination treatment as compared to single agent. This may be due to the removal of HDACs from the p21 transcriptional start site through the disruption of the PRC2 complex and direct inhibition of HDACs, thus leading to increase expression of p21. The combination also led to decreased nuclear localization of EZH2 and its cofactors. Apoptosis was confirmed by caspase 3 and PARP cleavage, and was more potently cleaved after exposure to the combination. Based on the findingthat HDAC2 dissociated from PRC2 complex after treatment with GSK126 and romidepsin, a selective HDAC1/2 inhibitor, ACY-957 (Acetylon Pharmaceuticals), was combined with GSK126 which demonstrated potent synergy in 4 GC-DLBCL cell lines (EOB 37).
This data suggests that concomitant inhibition of EZH2 and HDAC is highly synergistic and leads to the dissociation of PRC2 complex. By releasing transcriptional inhibition key tumor suppressors and cell cycle regulators may be re-expressed. Potency of this epigenetic combination may be predicted by gene expression signatures for which RNA-seq libraries are currently in production. Reversing transcriptional inhibition using a combination of EZH2 inhibitors and HDAC inhibitors may lead to a potent treatment option for lymphomas dependent upon EZH2 and HAT activity.
O'Connor:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Spectrum: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Spectrum: Research Funding; Mundipharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Mundipharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. Amengual:Acetylon Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.