Abstract
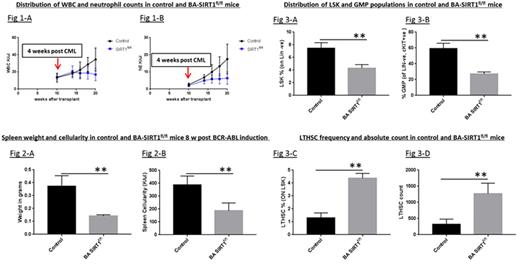
Despite the success of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in treatment of CML, cures remain elusive, as primitive leukemia stem cells (LSC) are retained in patients achieving remission. Previous studies from our group have suggested that Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) inhibition may represent a novel approach for elimination of LSCs in chronic phase CML. SIRT1 was shown to be overexpressed in CML LSCs, and SIRT1 inhibition using shRNA or a small molecule SIRT1 inhibitor selectively eliminated CML LSCs by increasing p53 acetylation and activity (Li et.al; Cancer Cell 2012). These studies were limited by possible off-target effects and limited duration of in vivo exposure. Here we used a genetic mouse model to definitively delineate the role of SIRT1 in CML development. A model for conditional SIRT1 deletion in hematopoietic stem cells was established by crossing homozygous SIRT1 exon-4 floxed (SIRT1fl/fl) mice with Mx1-Cre mice. To study the requirement of SIRT1 for development of CML, Mx1-cre SIRT1fl/fl mice were crossed with SCL-tTA/BCR-ABL mice, representing a tet-regulated inducible transgenic mouse model of CML, to generate SCL-tTA/BCR-ABL Mx1-Cre SIRT1fl/fl mice (BA Mx1-Cre SIRT1fl/fl). BA SIRT1fl/fl mice lacking Mx1-Cre were used as controls. The mice were maintained on doxycycline until CML induction. Cre mediated deletion of SIRT1 was induced by intraperitoneal pIpC injections (250µg/mouse) administered every other day for a total of 7 doses. SIRT1 knockdown was confirmed by PCR for excised exon-4 and by RT-Q-PCR. Bone marrow (BM) cells from either BA Mx1-Cre SIRT1fl/fl or controls (both CD45.2) were transplanted into irradiated (800 cGy) CD45.1 congenic recipients (2X106 cells/mouse). Cre-mediated deletion of SIRT1 was induced by pIpC injection starting at 4 weeks post-transplant, followed by withdrawal of tetracycline to induce BCR-ABL expression. Serial PB counts and phenotypic evaluation of cell types by flow cytometry (Fig 1 A-B) showed SIRT1 knockdown to have a profound effect on CML development. By 8 weeks after BCR-ABL induction, BA SIRT1fl/fl mice (n=10), showed significantly lower neutrophils (p=0.0003) and Gr-1/Mac-1 positive myeloid cells (p=0.0002) compared to control mice. Subsequently, control mice developed progressive neutrophilic leukocytosis and increasing morbidity from leukemia, whereas BA SIRT1fl/fl mice demonstrated significantly lower WBC counts, without evidence of progressive increase or morbidity (Fig 1 A). This cohort of mice continues to be followed for survival. Another cohort of BA Mx1-Cre SIRT1fl/fl mice was sacrificed at 8 weeks post pIpC injection and BCR-ABL induction to evaluate the effect of SIRT1 knockdown on stem and progenitor populations (n=6 each). SIRT1 deleted mice demonstrated significant reduction in spleen size, weight, cellularity, and myeloid infiltration (Fig 2 A-B), and in myeloid cell expansion in the BM compared to controls (p=0.002). Primitive lineage negative, Sca1 positive, c-Kit negative (LSK) cells and granulocyte-macrophage progenitors (GMP) were significantly reduced in BM and spleen of BA SIRT1 deletedmice compared to control mice, whereas megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitors (MEP) were increased (Fig 3 A-B). Long term hematopoietic stem cells (LTHSC) in the BM are reduced following CML development. The percentage and number of LTHSC were significantly increased in SIRT1 deletedmice compared to control mice (Fig 3C-D). We also evaluated the effect of SIRT1 deletion on normal hematopoiesis by studying Mx1-Cre SIRT1fl/fl mice lacking BCR-ABL. SIRT1fl/fl mice without Mx1-Cre were studied as controls. Mx1-Cre SIRT1fl/fl and control mice were treated with pIpC to induce SIRT1 deletion. SIRT1deletedmice did not show significant alteration in blood counts, but demonstrated significantly higher LSK and LTHSC numbers in BM compared to control mice. Upon secondary transfer, recipients of BM from SIRT1deleted mice showed a modest increase in donor cell engraftment at 12 weeks compared to controls (90.8% (83.2-92.2%) vs 83.6% (75.8-86.7%); p=0.001). We conclude that genetic deletion of SIRT1 markedly inhibits all aspects of CML development in transgenic BCR-ABL mice, without impairing normal hematopoiesis. These observations demonstrate a critical role for SIRT1 in leukemia development, and support further evaluation of SIRT1 as a therapeutic target in CML.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract