Abstract
Background: BCL-2 and MCL-1 promote multiple myeloma (MM) cell survival. Venetoclax (VEN) is a potent, selective, orally bioavailable small-molecular inhibitor of BCL-2. When combined with bortezomib, which can inhibit MCL-1, VEN can enhance the activity of bortezomib in MM cell lines and xenograft models.
Methods: In this Phase 1b, open label, dose escalation study, patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) MM received daily VEN (50 - 1200 mg per designated dose cohort) with bortezomib and dexamethasone. The objectives of the study were to assess the safety, pharmacokinetics, maximum tolerated dose, recommended phase 2 dose (R2PD), and efficacy (objective response rate [ORR], time to progression [TTP], and duration of response [DoR]) of combination therapy in this patient population.
Results: As of 01July2016, 66 patients were enrolled, with 54 in the dose escalation cohort and 12 in the safety expansion at R2PD of 800 mg. The median age was 64 years and 39 (59%) were ISS stage II/III. The median number of prior therapies was 3 (range: 1 - 13), and 21 (32%) were refractory to prior bortezomib, 37 (56%) were refractory to prior lenalidomide, and 41 (62%) had prior stem cell transplant.
Forty-three (65%) patients discontinued the study for the following primary reasons: 33 related to disease progression, 5 due to AEs (1 each: respiratory failure and cardiac failure, lung adenocarcinoma, sepsis, renal impairment, and Guillain-Barre syndrome; none were considered by the investigator as related to VEN), 2 withdrew consent, and 3 for other reasons not specified. Adverse events (AEs) were reported in 65 (99%) patients, with common AEs in ≥20% of patients being diarrhea (41%), thrombocytopenia (39%), constipation (38%), nausea (36%), insomnia (32%), peripheral neuropathy (30%), peripheral edema (29%), anemia (27%), peripheral sensory neuropathy (27%), dyspnea (24%), fatigue (24%), and asthenia (24%). Grade 3/4 AEs in ≥10% of patients included thrombocytopenia (29%), anemia (15%) and neutropenia (14%). Serious AEs in ≥2 patients were febrile neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, cardiac failure, pyrexia, influenza, lower respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, sepsis, acute kidney injury, respiratory failure, embolism, and hypotension. One dose-limiting toxicity of lower abdominal pain was reported for a patient who received 1200 mg VEN. Five deaths were reported during the study, 4 due to disease progression and 1 due to respiratory syncytial virus infection (not considered by the investigator as related to VEN). After co-administration with bortezomib and dexamethasone, dose-normalized VEN exposure at steady-state appeared to be within the exposure range observed with VEN monotherapy in patients with MM.
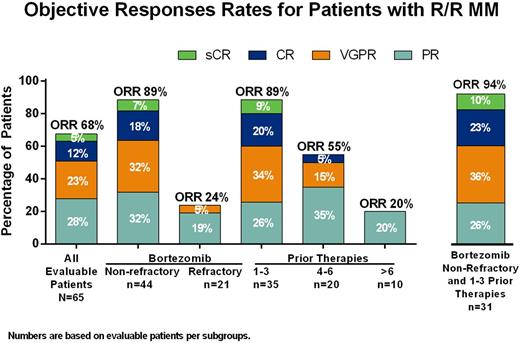
The ORR for all evaluable patients was 68% (44/65) and 26 (40%) achieved very good partial response (VGPR) or better (3 stringent complete response [sCR], 8 CR, 15 VGPR) (Figure). For all patients, median DoR was 8.8 months (95% CI: 7.2, 15.8) and TTP was 8.6 months (95% CI: 5.7, 10.2), with a median follow up of 4.9 months (range: .03 - 26.7). High ORR of 89% was seen in patients who were non-refractory to prior bortezomib (39/45) or who had 1 - 3 prior therapies (31/35). In 31 patients who were non-refractory to bortezomib and had 1 - 3 prior therapies had ORR of 94% (29/31), 68% (21/31) with VGPR or better; median DoR was 10.6 months and TTP was 11.3 months for this subgroup. Moreover, patients who were bortezomib naïve and had 1 - 3 prior lines of therapy had ORR of 100% (12/12), and median DoR was 15.8 months and TTP was 17.1 months.
In patients who were non-refractory to prior bortezomib but who were refractory to lenalidomide, the ORR was 86% (19/22) as compared with 91% (20/22) in those non-refractory to lenalidomide. Clinical responses were comparable in patients with t(11;14) MM (ORR, 78% [7/9]) and without t(11;14) MM (ORR, 66% [37/56]). In the t(11;14) group, 3 patients were bortezomib-refractory, and 2 of them achieved a PR as best response. Also, 4 patients had more than 3 prior lines, with 3 of them achieving PR.
Conclusions: VEN in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone has an acceptable safety profile in patients with R/R MM. Efficacy results, including 68% ORR in all patients and 94% ORR in patients not refractory to bortezomib and who received 1 - 3 prior lines of therapy, indicates promising efficacy of this novel combination and supports the ongoing Phase 3 trial with this regimen in patients with R/R MM.
Moreau:Janssen: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria. Roberts:Genentech: Patents & Royalties: Employee of Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research which receives milestone payments related to venetoclax; AbbVie: Research Funding; Servier: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Agarwal:AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Millennium: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Onyx: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau. Facon:Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Millenium/Takeda: Consultancy; Bristol: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Karyopharm: Consultancy. Kumar:Glycomimetics: Consultancy; AbbVie: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Onyx: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Array BioPharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Millennium: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kesios: Consultancy; Skyline: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Noxxon Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding. Touzeau:AbbVie: Research Funding. Cordero:AbbVie: Employment. Ross:AbbVie: Employment, Equity Ownership. Munasinghe:AbbVie: Employment. Jia:AbbVie: Employment. Salem:AbbVie: Employment. Leverson:AbbVie: Employment, Other: Shareholder in AbbVie. Maciag:AbbVie: Employment. Verdugo:AbbVie: Employment, Other: may own stock. Harrison:Janssen Cilag: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract