Abstract
Introduction: Plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) is a rare and aggressive CD20-negative lymphoma with plasmacytic differentiation associated with poor outcomes. Multiple studies have shown a high relapse rate and median survival times of 12-18 months. Several case reports and small case series have suggested an increased response rate in PBL patients treated with bortezomib alone or in combination with chemotherapy. Due to its rarity, prospective studies in PBL patients are unlikely to be performed. Based on this, we decided to evaluate the potential therapeutic value of frontline bortezomib-containing regimens in patients with PBL.
Methods: We performed an international retrospective multicenter study looking for patients with a pathological diagnosis of PBL who received therapy with bortezomib-containing regimens in the frontline setting. Clinical (i.e. age, sex, HIV infection, stage, ECOG performance status, LDH level and CD 4 count) and pathological characteristics (i.e. expression of CD20, CD38, CD138, ki67, EBER, HHV8, ALK, and MYC rearrangement) were gathered and are presented descriptively. Kaplan-Meier overall (OS) curves were estimated.
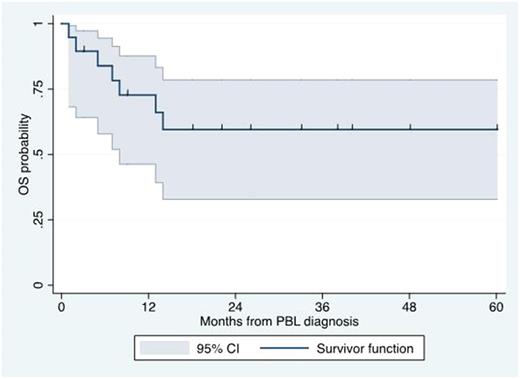
Results: Nineteen patients with a diagnosis of PBL and treated with bortezomib-containing regimens as frontline were included in our analysis. The median age at diagnosis was 51 years (range 31-77 years). Fifteen patients (79%) were men. ECOG performance status >=2 was seen in 8 patients (42%). LDH was elevated in 9 patients (47%). Stage III or IV was reported in 13 (68%). Seventeen patients (89%) had extranodal involvement. Extranodal sites included the gastrointestinal tract (n=5), bone marrow (n=4), skeletal bone (n=3), lungs (n=2), head & neck (n=2), kidney (n=2), testicles (n=2) and subcutaneous tissue (n=1). Eight patients (42%) were infected by HIV. Among HIV-infected patients, the median CD4+ count was 91 cells/mm3 (range 33-422 cells/mm3). Pathologically, all cases were negative for CD20 expression and positive for CD38 or CD138 expression. Median Ki67 expression was 90% (20-100%). MYC gene rearrangements were identified in 8 of 10 (80%) samples tested. EBER was identified in 9 of 14 (64%)o of samples tested. HHV-8 LANA was identified in 1 of 10 (10%) samples tested. ALK expression was negative in 7 of 7 (0%) samples tested. With regard to treatment, 10 patients (53%) received bortezomib-EPOCH, 2 patients (11%) received bortezomib-CHOP, 2 patients (11%) received VCD, 2 patients (11%) received VAD, 2 patients (11%) received VD, and 1 patient (5%) received alternating VCD and VAD. Complete response was seen in 11 patients (58%), partial response in 3 (16%) and no response in 5 (26%). Only 2 patients received ASCT in first remission. Eleven patients (58%) experienced relapsed disease, including one of the patients who achieved CR and underwent ASCT. Salvage therapy was provided to only 4 patients and included daratumumab-ICE, rituximab-ICE, DHAP and etoposide-cyclophosphamide and prednisone. With a median follow-up of 33 months, the median OS was not reached. The 3-year OS rate was 59% (95% CI 33-78%; see Figure). When evaluating the 12 patients who received bortezomib + CHOP or EPOCH, the CR rate was 75%, the relapse rate was 25%, and the 3-year OS rate was 64% (95% CI 30-85%). The most common adverse events (Grade 3 or higher) included infections, febrile neutropenia, neuropathy and thrombocytopenia.
Conclusion: Our study suggests that bortezomib-containing regimens are feasible and effective as frontline treatment in patients with PBL. Our results suggest a high response rate as well as 3-year OS rate of approximately 60%, in contrast with the previously reported median OS time of 12-18 months. Prospective studies are needed to confirm the therapeutic role of frontline bortezomib-containing regimens in PBL.
Cartron: Sanofi, BMS, Jansen, celgene, Roche, Gilead: Equity Ownership; Celgene: Consultancy, Employment; Roche: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Honoraria, Research Funding. Lansigan: Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy. Navarro: Celgene Spain: Research Funding; DKMS: Research Funding; la Caixa Foundation: Research Funding; Josep Carreras International Foundation: Research Funding; CERCA Programme/Generalitat de Catalunya: Research Funding. Reagan: Teva: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Castillo: Abbvie: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract