Abstract
Introduction: Data on clinical response and factors associated with response in CP-CML outside clinical trials are limited.SIMPLICITY (NCT01244750) is an ongoing observational study of CP-CML pts in routine clinical practice receiving first-line (1L) imatinib (IM), dasatinib (DAS) or nilotinib (NIL) in the US and Europe. This analysis aims to describe the factors associated with achievement of complete CyR (CCyR) and major MR (MMR).
Methods: Clinical response after start of 1L TKI was assessed by CyR (karyotype or FISH) and MR (only tests by PCR on the international scale were included) as determined by the treating physician. Proportions of patients achieving CCyR and MMR between 30 days and either 12 or 24 months (mos) are presented; data at specified time points will be provided at presentation. Logistic regression models were used to identify factors associated with CCyR and MMR by 12 and 24 mos after 1L TKI initiation.
Results: By March 03 2017, 1242 pts were enrolled prospectively in SIMPLICITY, receiving IM (n=416), DAS (n=418) or NIL (n=408); 55% were male. The median (interquartile range; min-max) age of pts at initiation of 1L TKI was 57 (46-68; 18-91) years; 35% of pts were treated in Europe, 65% in the US; 53% at academic centers and 47% at community practices.
Numbers of pts followed by 3, 6, 12 and 24 months were 1233, 1224, 1195 and 1121, respectively. Of pts followed 12% (n=151), 31% (n=384), 44% (n=522) and 51% (n=567) had documented CyR testing by 3, 6, 12 and 24 mos; 23% (n=285), 55% (n=672), 72% (n=857) and 84% (n=937) of pts had documented MR testing by 3, 6, 12 and 24 mos; and 7% (n=82), 19% (n=231), 32% (n=379) and 42% (n=475) of pts had documented testing by both CyR and MR by 3, 6, 12 and 24 mos.
Proportions of pts remaining on their 1L TKI declined with duration of follow-up. Of pts with documented CyR testing, 93% (n=141), 93% (n=356), 89% (n=464) and 85% (n=484) had remained on their 1L TKI by 3, 6, 12 and 24 mos, respectively. Of pts with documented MR testing, 93% (n=266), 91% (n=610), 85% (n=728) and 78% (n=730) had remained on their 1L TKI by 3, 6, 12 and 24 mos, respectively.
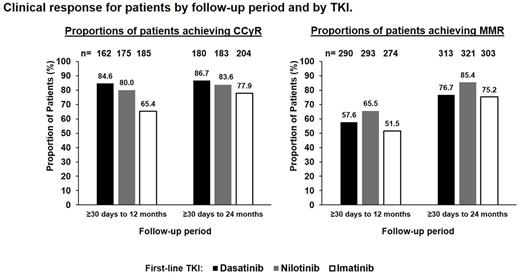
In this non-controlled study, proportions of pts achieving CCyR were similar for pts tested by 12 and by 24 mos. For both periods, the proportion of pts achieving CCyR was highest for pts on 1L DAS, lower for 1L NIL, and lowest for 1L IM. Proportions of pts achieving MMR were higher for pts tested by 24 mos than by 12 mos. For both periods, the proportion of pts achieving MMR was highest for pts on 1L NIL, lower for 1L DAS, and lowest for 1L IM. Proportions were lower when calculated among pts followed through the period but not necessarily tested (intention-to-treat).
Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified factors associated with MMR or CCyR by 12 and 24 mos after 1L TKI initiation. Receiving a second-generation (2G) TKI (i.e. DAS or NIL) as 1L therapy was associated with CCyR by 12 mos (odds ratio [OR]=2.6; p<0.001) and by 24 mos (OR=1.8; p=0.024), but not with MMR in either timeframe. BCR-ABL<10% by 3 mos was associated with MMR by 12 mos (OR=3.2, p<0.001) and by 24 mos (OR=2.4, p=0.002). Compared with switching in 3-12 mos, switching to a second-line (2L) TKI in 30 days-3 mos was associated with CCyR (OR=6.2; p=0.004) and MMR (OR=3.3; p=0.001) by 12 mos. Also, compared with switching in 3-12 mos, not switching within 12 mos was associated with CCyR (OR=4.5; p<0.001) and MMR (OR=2.2; p<0.001) by 12 mos. Compared with switching in 6-24 mos, switching to a 2L TKI in 30 days-6 mos was associated with MMR (OR=2.1; p=0.012) by 24 mos. Compared with switching in 6-24 mos, not switching within 24 mos was associated with MMR (OR=3.1, P<0.001) or CCyR (OR=4.4, P<0.001) by 24 mos.
Conclusions: Response monitoring observed in clinical practice is not aligned with ELN/NCCN guidelines, so outcomes for the full SIMPLICITY cohort may differ from presented data on monitored patients. The lack of correlation between a 2G TKI as 1L therapy and achievement of MMR is unexpected, but may result from switches to 2L TKI in IM suboptimal responders or from differences in testing patterns in the individual cohorts; the uncontrolled nature of this study may have also contributed. Early switching of TKI treatment (previously found to be driven by toxicity, not response, and often from IM to 2G TKI) was associated with achieving MMR or CCyR by 12 mos. Not switching TKI, potentially a marker of better tolerance and adherence, was associated with achieving MMR or CCyR by 12 mos and 24 mos.
Cortes: Teva: Research Funding; ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sun Pharma: Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding. Goldberg: Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Jazz: Speakers Bureau; Ariad: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; COTA: Employment, Equity Ownership. Hehlmann: Novartis: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy. Mauro: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy. Zyczynski: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment. Sen: ICON Clinical Research: Employment. Foreman: ICON Clinical Research: Employment. Gajavelli: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment. Gambacorti-Passerini: BMS: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.