Abstract
Triplet induction therapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) and maintenance therapy can render long-term remission for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) patients (pts). Robust post-ASCT immune-reconstitution correlates with lower minimal residual disease (MRD) and better clinical outcomes but immune signatures to define such responses are lacking (Ho et al. Blood Advances 1.15 (2017). Following ASCT, the Immunoglobulin Isotype Switch (IIS) results in a new serum M-protein on serum protein electrophoresis (SPE), distinct from the M-protein pattern present at diagnosis, may be associated with a good prognosis. The objective of this study was to analyze humoral immune reconstitution that presents as IIS after ASCT and to determine if there was a correlation with patient or disease characteristics, transplant parameters and to define the associated immune signature.
Methods
The Institutional Review Board-approved study evaluated MM pts who underwent ASCT between 2007 and 2016. Data collection included patients' characteristics, induction therapy, mobilization regimen, graft characteristics including CD34 cell dose, myeloid and erythroid progenitor cells (multi-potential colony forming unit or CFU-GM and erythroid burst-forming unit (BFU-E). Percentage of NK cells (CD56(+) CD3(-) and CD16(+)CD3(-)), T-cells ( CD3(+),CD56 (-)), B-cells (CD19(+)),and T-cell subpopulations (CD4(+), CD8(+),were measured with flow cytometry in pre- and post-ASCT bone marrow samples. IIS was defined as the appearance of a new serum monoclonal spike on SPE and immunofixation different from original heavy or light chain detected at diagnosis. Monoclonal proteins and quantitative immunoglobulins were assessed day+100 and with frequency of 2-8 times per year afterward.The start date for all time dependent variables was the day of transplant. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to assess overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). Two-tailed log-rank tests compared OS and PFS curves. Factors with a P -value <0.2 in univariate analysis were included in multivariate analysis, which was performed using the Cox regression hazard model. All analyses were performed utilizing SAS 9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).
Results
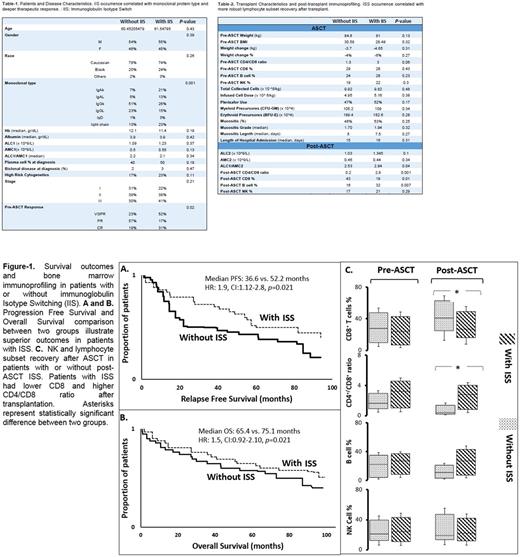
The analysis included 177 patients with median age of 60.7 years. IIS was detected in 39 pts (22.0%) with a significantly higher incidence in pts who received lenalidomide before ASCT (11.2% vs. 30.4%, P=0.001). Post-ASCT IIS was more frequent in IgA, light chain disease, and in pts who experience very good partial and complete response post-ASCT rather than less optimal response (Table-1 and 2). The occurrence of IIS did not correlate with ASCT toxicity, i.e., mucositis duration or grade as well as length of hospital admission (Table 2). IIS occurred more frequently in pts without suppressed un-involved immunoglobulin (92% vs 8%, p=0.001).The presence of post-ASCT IIS correlated significantly with PFS and OS (Figure.1.A and B). Age, cytogenetics, response category, presence of IIS and low LDH correlated with PFS by univariate analysis. Cytogenetics, LDH and IIS presence were also significantly associated with response as determined by multivariate analysis. The median time between pre- and post-ASCT BM was 92 days (range 79-123). Pts with IIS showed a trend toward faster B cell recovery in comparison to pts without IIS, however this difference did not reach statistical significance. All pts had low CD4/CD8 ratio, due to low number of CD4 and higher number of CD8. Appearance of post-ASCT IIS was associated with statistically lower CD8 T cell percentages and higher CD4/CD8 ratio in comparison to pts without IIS (Figure.1.C), suggestive of faster immune reconstitution in this group of pts. All pts who relapsed had an isotype different from IIS, highlighting the benign nature of this phenomenon.
Conclusion
Our data are consistent with the benign nature of IIS that may emerge in certain patients following ASCT. Association of a robust recovery of specific immune cell subpopulations with IIS occurrence and superior survival outcomes may represent an anti-myeloma protective effect resulted from cellular and humoral immunoreconstitution. Efforts to better understand how specific immune subpopulations trigger and regulate the immune response to tumors may improve long-term control of MM. Further research to define underlying anti-tumor effect of ISS is needed.
De Lima: Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene Corporation: Research Funding. Malek: Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.