Abstract
BACKROUND
Lenalidomide (LEN) stimulates erythropoietin (EPO) signaling by stabilization of erythropoietin receptor (EPOR) through inhibition of the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF41 (ring finger protein 41) involved in ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of RNF41 in proteasomes (Basiorka et al. - Cancer Res 76, 3531-3540, 2016). This post-transcriptional mechanism of EPOR stabilization by lenalidomide may account for a possible beneficial effect of combined EPO+LEN treatment patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) especially in those with isolated deletion of chromosome 5 /del(5q) or 5q-/. Another possible mechanism may be an effect of EPO on CRBN gene expression through an antioxidant transcription factor, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) (Jin et al. - Ann Clin Lab Sci 41, 25-32, 2011; Lee et al. - Biochem Biophys Res Commun 399, 711-715, 2010).
AIMS
The aim of our study was to evaluate a prognostic significance of high level of full-length cereblon (CRBN) mRNA in mononuclear cells obtained from peripheral blood in lower-risk MDS patients with del(5q) in relation to the efficiency of lenalidomide treatment and to measure the effect of EPO on CRBN mRNA level and its relation to the clinical and laboratory effect of combined EPO+LEN treatment.
METHODS
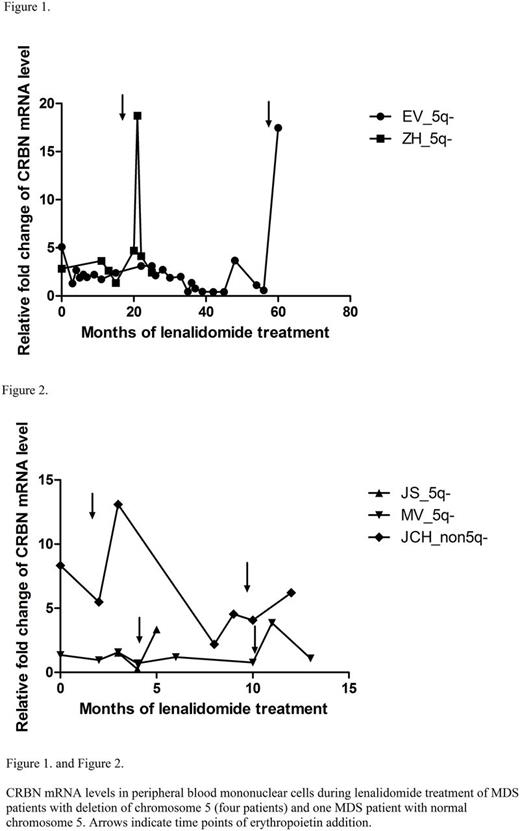
CRBN mRNA and protein levels were recorded in the course of lenalidomide therapy in twenty MDS patients with 5q- syndrome and three MDS patients with normal chromosome 5 (non5q-) who were previously resistant to EPO treatment. All patients were transfusion dependent before starting the lenalidomide (5 or 10 mg/day) therapy with median hemoglobin level 80 g/l. Recombinant human EPO (rHuEPO) was combined with LEN in nine MDS patients with del(5q) and in three non5q- MDS patient who relapsed during lenalidomide monotherapy or were resistant to LEN (two non5q- patients). Mononuclear cells were isolated by Ficoll-Paque PLUS gradient separation, then washed by phosphate buffered saline and remaining red cells were lysed. The level of CRBN mRNA was measured using the reverse transcriptase quantitative "best coverage" TaqMan PCR assay. CRBN protein level was detected by Western blot.
RESULTS
Increased CRBN mRNA levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells were found after addition of rHuEPO in dose of 40.000 IU s.c. per week to LEN in six MDS patients with del(5q) and in one non5q- MDS patient sensitive to lenalidomide therapy. The results of four these MDS patients with del(5q) are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2. This non5q- MDS patient had refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (RARS-T) without JAK2 mutation and high CRBN mRNA and CRBN protein level before lenalidomide therapy (Figure 2). Six MDS patients with del(5q) and one MDS patient with normal chromosome 5 responded to combination EPO+LEN treatment and the increase of CRBN mRNA level after EPO addition correlated with the increase in hemoglobin synthesis in MDS patients.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of our study give evidence for the usefulness of measurement of CRBN mRNA level as an important factor for prediction of the efficacy of not only lenalidomide treatment but also of combination of LEN and EPO.
This work was supported by the research project for conceptual development of research organization (00023736; Institute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion, Prague) and Grant Agency of Charles University, project number 924616.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.