Key Points
MyD88L265P is present in the EVs secreted by WM cancer cells and triggers signaling in the recipient cells.
MyD88-containing EVs shape the proinflammatory microenvironment in the bone marrow.
Abstract
The link between inflammation and cancer is particularly strong in Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM), a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma wherein the majority of patients harbor a constitutively active mutation in the innate immune-signaling adaptor myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88). MyD88Leu265Pro (MyD88L265P) constitutively triggers the myddosome assembly providing a survival signal for cancer cells. Here, we report detection and a functional role of MyD88 in the extracellular vesicles (EVs) shed from WM cells. MyD88L265P was transferred via EVs into the cytoplasm of the recipient mast cells and macrophages, recruiting the endogenous MyD88 that triggered the activation of proinflammatory signaling in the absence of receptor activation. Additionally, internalization of EVs containing MyD88L265P was observed in mice with an effect on the bone marrow microenvironment. MyD88-loaded EVs were detected in the bone marrow aspirates of WM patients thus establishing the physiological role of EVs for MyD88L265P transmission and shaping of the proinflammatory microenvironment. Results establish the mechanism of transmission of signaling complexes via EVs to propagate inflammation as a new mechanism of intercellular communication.
Introduction
MyD88 is a signaling adapter protein that plays a pivotal role in innate immunity. Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) is recruited to the Toll/interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor (TIR) domains of activated Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and IL-1/-18 receptors (IL-1R/IL-18R), leading to myddosome complex formation with IL-1R–associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) and IRAK1/2.1,2 Myddosome activates pathways resulting in activation of transcription factors NF-κB, activator protein 1 (AP-1), interferon (IFN)-regulatory factors (IRFs), and others, which induce the transcription of numerous proinflammatory genes.3 Patients with germ line MYD88 loss-of-function mutations only survive into adulthood on a strict therapy of antibiotics.4 Conversely, somatic MYD88 gain-of-function mutations within the TIR domain of MyD88 enable constitutive activation.5-7 MyD88Leu265Pro (MyD88L265P) mutation triggers spontaneous assembly of the myddosomal complex with IRAKs, resulting in activation of STAT3, NF-κB, and secretion of IL-6, IL-10, and IFNβ.5,8 Activating mutations in MYD88 are frequently detected in the activated B-cell–like (ABC) subtype of diffused large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and are present in >90% of patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM).9,10 MyD88L265P supports the survival of lymphoma cells by upregulating Bcl-xL expression through the NF-κB pathway11 and activation of Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK).12 Inhibition of the signaling pathway downstream of MyD88 reduces proliferation of cancer cells.5-7
The role of extracellular vesicles (EVs; comprising microvesicles [MVs] and exosomes) has been described in cancer development and dissemination of signals to other cells.13 The number of EVs increases in stress conditions (reviewed in Ratajczak et al14 and Hugel et al15 ), and increased EV levels were detected in the peripheral blood of cancer patients.16 EVs encapsulate different cellular components including proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and noncoding regulatory RNAs, such as microRNA (miRNA). Tumor EVs promote directional cell motility through extracellular matrix (ECM)17 and ECM remodeling.18,19 They also alter physiology of both surrounding and distant nontumor cells, which in turn allows growth and dissemination of cancer cells.20,21 However, transmission of the proteins of signaling pathways that could directly activate the intracellular signaling pathway of recipient cells has not been described.
EVs are enriched in membrane-associated proteins that form aggregates.22 Mutant MyD88L265P has an intrinsic aggregation propensity and is found associated with the cellular membranes, thus it fulfils both of the enrichment criteria. We therefore surmised that MyD88 might be associated with the EVs released by lymphoma cells. This may be relevant if the transferred MyD88 mutant could trigger cell activation in recipient cells that internalize the EVs. Previous proteomic analysis of the exosomes from human thymic tissue identified MyD88 among many other protein components,23 giving credence to the hypothesis.
Although WM cells can influence their microenvironment through direct interaction with stromal cells, and by the release of cytokines,24,25 in this report, a mechanism of intercellular proinflammatory signaling mediated by EVs was investigated. Here, we show that the EVs from the lymphoma cell lines as well as EVs isolated from the bone marrow aspirates of WM patients contained MyD88. MyD88L265P-containing EVs are internalized by the recipient cells, where the transferred MyD88L265P recruits the wild-type MyD88 (MyD88wt) and triggers activation of the inflammatory pathway, thus propagating the inflammatory signaling independent of the TLRs and IL-1Rs. EVs with MyD88L265P injected IV were able to activate the reporter cells in mice thus demonstrating the possibility of the in vivo transfer of the functional signaling complexes. EVs that were injected into the bone marrow increased globulin concentration in blood and modified the bone marrow microenvironment by recruitment/differentiation of mast cells, which support the development and propagation of B-cell lymphomas. These results extend our understanding of how cancer cells can modify the tumor’s microenvironment and identified a mechanism of the transmission of signaling components via EVs as an additional mechanism of intercellular communication.
Methods
Materials
Materials used were as follows: LY294002 (Invivogen), Dynasore (Sigma), lipopolysaccharide (LPS; from Salmonella abortus equi HL83, provided by K. Brandenburg, Forschungszentrum Borstel, Borstel, Germany); antibodies against were MyD88, IRAK4 (Cell Signaling Technology), Tsg101 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and β-actin (Cell Signaling Technology), secondary horseradish peroxidase (HRP)–conjugated anti-mouse (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), or anti-rabbit antibody (Abcam).
Cell lines
The cell lines used in these studies were the human embryonic kidney HEK293 cell line (ATTC); HEK293 MyD88 knockout (MyD88KO) and HEK293 NEMOKO cell lines prepared with clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein-9 (Cas9) (a gift from D. Abbott); mouse immortalized bone marrow–derived macrophages (iBMDMs; a gift from K. Fitzgerald); and MWCL-126 and BCWM.127 cell lines established from the bone marrow aspirate of a patient with WM and the Ramos-Blue cell line (Invivogen).
Mice
C57BL/6 (wt and IRAK4KO), BALB/c, and SCID (C.B-17/lctHsd-PrkdcscidLystbg-J) mice were purchased from Harlan (Italy). Eight- to 12-week-old male and female mice were used for experiments. No sample size estimation was performed. All of the animal samples were included in the analysis. No blinding or randomization was performed. All animal experiments were performed according to the directives of the European Union (EU; 2010/63) and were approved by the Administration of the Republic of Slovenia for Food Safety, Veterinary, and Plant Protection of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Foods, Republic of Slovenia (no. U34401-3/2017/8).
Bone marrow–derived cultured mast cells (BMCMCs) were prepared from bone marrow cells from C57BL/6 mice using 10 ng/mL recombinant murine IL-3 (mIL-3; Peprotech) for 4 weeks. Bone marrow–derived macrophages (BMDMs) were prepared from bone marrow cells from C57BL/6 mice using 40 ng/mL macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) for 4 days.
Preparation of EVs
HEK293 cells were seeded in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (DMEM) plus 10% exosome-depleted fetal bovine serum (FBS; System Biosciences) and transfected with MyD88L265P. After 24 hours, supernatants were collected. MWCL-1, BCWM.1, or Ramos cells were seeded at a density of 2 × 107 cells in 20 mL of RPMI 1640 plus 10% exosome-depleted FBS. After 48 hours, supernatants were collected. To prepare control EV (EVCONT) supernatants from growing, HEK293 cells were collected. Supernatants were centrifuged at 800g for 15 minutes to remove the cells and at 100 000g for 1 hour to isolate the EVs. EVs were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and ultracentrifuged again, then resuspended in PBS; protein concentration was measured using the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay (Sigma).
Patient bone marrow aspirates were obtained after informed consent and approval by the institutional review board at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Bone marrow aspirates from patients with WM were centrifuged and serum was separated. One drop of EDTA per 5 mL was added, gently mixed, and left at 4°C overnight. To remove any precipitation, samples were centrifuged at 300g for 10 minutes then again at 2000g for 10 minutes. To pellet the MVs, supernatants were centrifuged at 16 000g for 20 minutes. Supernatants were filtered through 0.2-μm filters and ultracentrifuged at 120 000g for 1 hour to isolate exosomes. The pellet was washed with PBS and ultracentrifuged again. Exosomes and MVs were resuspended in PBS and stored at −80°C.
NF-κB luciferase reporter assay
HEK293 or HEK293 MyD88KO cells were transfected with firefly luciferase under NF-κB promotor and Renilla luciferase reporter plasmids. Cells were stimulated with EVs and luminescence was measured on an Orion luminometer (Berthold).
Quantitative PCR
BMCMCs, iBMDMs, or BMDMs were stimulated with EVs, RNA was isolated using Trizol (Roche) or the Purelink RNA mini kit (Invitrogen), complementary DNA (cDNA) was prepared using a high-capacity cDNA reverse transcription kit (Applied Biosystems), and quantitative polymerase chain reactions (qPCRs) for mouse Gapdh, Rantes, or Il6 were performed using the SYBR Green I master kit (Roche) on LightCycler 480 (Roche).
Immunoelectron microscopy
EVs were fixed with 4% formaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer and pelleted by centrifugation at 200g. The pellet was washed with PBS/0.15% glycine, embedded in 12% gelatin and cut into 0.5- × 0.5- × 0.5-mm blocks. The blocks were cryoprotected with 2.3 M sucrose, mounted on specimen holders, and frozen in liquid nitrogen. Ultrathin cryosections (50 nm thick) were cut at −120°C. Sections were retrieved with a 1:1 mixture of 2.3 M sucrose and 2% methyl cellulose on Au grids. Unspecific labeling was blocked with 1% BSA-c (Aurion). Sections were incubated with anti-MyD88 antibody and then with protein A conjugated to 10-nm gold (UMC Utrecht). Sections were embedded and stained with methyl cellulose/uranyl acetate and examined in a Philips CM100 transmission electron microscope at 80 kV.
Confocal microscopy
HEK293 or HEK293 MyD88KO cells were left untreated or transfected with MyD88wt fused with yellow fluorescent protein (MyD88wt-YFP). EVL265P fused with cyan fluorescent protein (EVL265P-CFP) or EVL265P-YFP were added to the cells. Cell membranes were dyed with cholera toxin B (CT-B)–Alexa 647 (Invitrogen). Cells were observed using a Leica TSC SP5 confocal microscope equipped with an HCX plan apo 963 (NA 1.4) oil-immersion objective. For acquisition and image processing, Leica LAS AF software was used.
In vivo internalization of EVs
HEK293 cells were transfected with firefly luciferase under the NF-κB promotor. After 24 hours, cells were collected. A total of 2 × 106 cells per mouse were subcutaneously (s.c.) injected into the right flank of BALB/c mice. Afterward, 150 μg per mouse of EVL265P or EVCONT was injected IV. After 24 hours, mice were anesthetized with isoflurane and d-luciferin (Xenogen); 150 mg/kg body weight was injected s.c. into the left flank. After 10 to 15 minutes, mice were imaged in vivo using IVIS Lumina Series III (Perkin Elmer). Data were analyzed with Living Image 4.5.2 (Perkin Elmer). Three mice were used in 2 separate experiments for each measurement.
Injection of EVs into the bone marrow and analysis
PKH67-labeled EVs were intramedullary injected into femurs of C57BL/6 mice as described in Zilber et al.28 After 16 hours, bones were collected and PKH fluorescence in cells was detected using a CyFlow space flow cytometer (Partec). EVMWCL, EVCONT, or PBS were intramedullary injected. After 8 days, mice were euthanized, blood was collected, and serum was prepared (Sarstedt; 3000 rpm per 30 minutes). Blood profile was determined from sera using a VetScan comprehensive diagnostic profile reagent rotor and analyzed on VetScan VS2 (Abaxis). For rouleaux formation, blood smears were prepared from a drop of whole blood using a Hemacolor rapid staining of blood smear kit (Merck). Femurs were collected for immunohistochemistry. Bones were decalcinated using 9% formic acid and embedded in paraffin (Leica Paraplast). The paraffin blocks were cut 7 μm thick with a rotation microtome RM 2245 (Leica). Mast cells were labeled using anti-CD40L (CD154) (BioLegend) and detected by an HRP-conjugated anti-goat Armenian hamster (Abcam) using TMB reagent (Sigma) under Leica DMi8 with a Leica MC170 HD camera.
Statistical analysis
Representative experiments are shown. For the analysis of experimental data, a Student t test was used (*P < .1; **P < .05; ***P < .01; ****P < .005; n.s., not significant).
Results
Presence of the MyD88 in EVs and transmission of the signal to the recipient cells
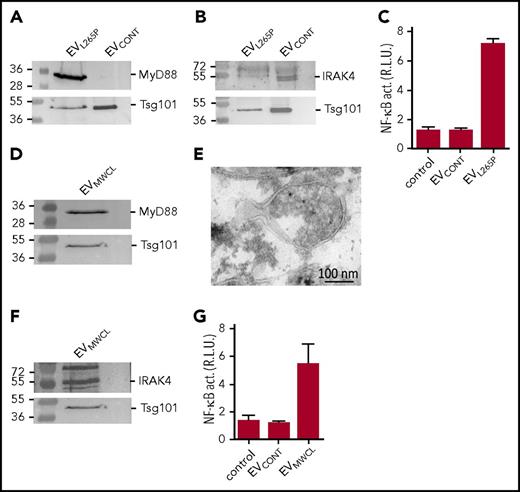
For the initial characterization of the ability of the MyD88L265P mutant to be incorporated into the vesicles, the EVs were isolated from the supernatant of unstimulated MyD88L265P transfected HEK293 cells and characterized by the dynamic light scattering (DLS) (supplemental Figure 1A, available on the Blood Web site), which showed the presence of MVs and exosomes. As shown by WB, EVL265P contained MyD88, which was absent from the EVCONT, isolated from the control HEK293 cells where both types of EVs contained exosomal marker Tsg101 (Figure 1A). To show that the EVs carrying the constitutively active MyD88L265P can be taken up by the recipient cells and that this form of the delivery of MyD88 is sufficient to trigger activation of the signaling pathway in the recipient cells, activation of the NF-κB–dependent luciferase reporter was monitored in HEK293 cells. Addition of EVL265P but not EVCONT to the reporter cells activated NF-κB (Figure 1C) thus supporting the hypothesis that the constitutively active signaling protein can be transmitted to the recipient cells, where it can activate the signaling pathway.
MyD88L265Pis secreted from the cells in EVs, which can activate signaling pathway in recipient cells. EVL265P and EVCONT were isolated and (A) MyD88 (protein load 10 μg) and Tsg101 or (B) IRAK4 (protein load 30 μg) and Tsg101 were detected by WB. (C) HEK293 cells expressing luciferase under NF-κB promotor and Renilla luciferase for normalization were stimulated with EVL265P and EVCONT (12 μg/mL) for 24 hours. EVMWCL were isolated and (D) MyD88 (protein load 10 μg) and Tsg101 or (F) IRAK4 (protein load 30 μg) and Tsg101 were detected by WB. (E) EVMWCL were isolated, fixed, and sections were prepared for immune labeling with anti-MyD88 antibody and protein A conjugated to 10-nm gold. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was performed. (G) HEK293 cells expressing luciferase under NF-κB promotor and Renilla luciferase for normalization were stimulated with EVMWCL and EVCONT (80 μg/mL) for 24 hours. Negative controls are transfected but unstimulated cells. Dual luciferase tests for NF-κB activity (NF-κB act.) were performed.
MyD88L265Pis secreted from the cells in EVs, which can activate signaling pathway in recipient cells. EVL265P and EVCONT were isolated and (A) MyD88 (protein load 10 μg) and Tsg101 or (B) IRAK4 (protein load 30 μg) and Tsg101 were detected by WB. (C) HEK293 cells expressing luciferase under NF-κB promotor and Renilla luciferase for normalization were stimulated with EVL265P and EVCONT (12 μg/mL) for 24 hours. EVMWCL were isolated and (D) MyD88 (protein load 10 μg) and Tsg101 or (F) IRAK4 (protein load 30 μg) and Tsg101 were detected by WB. (E) EVMWCL were isolated, fixed, and sections were prepared for immune labeling with anti-MyD88 antibody and protein A conjugated to 10-nm gold. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was performed. (G) HEK293 cells expressing luciferase under NF-κB promotor and Renilla luciferase for normalization were stimulated with EVMWCL and EVCONT (80 μg/mL) for 24 hours. Negative controls are transfected but unstimulated cells. Dual luciferase tests for NF-κB activity (NF-κB act.) were performed.
MWCL-1 is a WM cell line established from the bone marrow aspirate of a WM patient.26 We observed that MWCL-1 cells which harbor the constitutively active MyD88L265P mutation release high amount of EVs EVMWCL1 were isolated from the supernatant and compared with the EVL265P. As shown by DLS and TEM MWCL-1 cell line secreted EVs (exosomes and MVs) of similar size to those from HEK293 cell line (supplemental Figure 1B-C). WB revealed the presence of MyD88 in EVMWCL, along with the exosomal marker Tsg101 (Figure 1D) and was not present in the cell supernatant after ultracentrifugation (supplemental Figure 1D). Moreover, the presence of MyD88 was confirmed inside MVs by the immunoelectron microscopy (Figure 1E). Importantly, IRAK4, which is a constituent of the active myddosomal complex, was also detected in the EVMWCL1 (Figure 1F) though it was hardly detected in EVL265P (Figure 1B). Furthermore, EVMWCL1 triggered activation of the NF-κB–mediated signaling in the recipient cells (Figure 1G), demonstrating that cancer cells can indeed release EVs with inflammatory properties.
Internalization of the intact EVs is necessary for the activation of signaling in the recipient cells
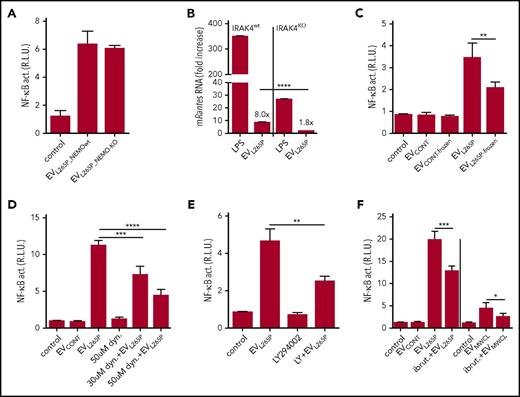
Cytokines can be released via EVs thus inducing stimulation of cells. MWCL-1, but not Ramos cells (containing MyD88wt), secreted IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, and TNFα into the supernatant (supplemental Figure 2A), of which only IL-6 and IL-8 were detected in the EVMWCL1 (supplemental Figure 2B). IL-1β, which signals via the MyD88 and could eventually stimulate the NF-κB in a positive feedback loop, was not detected. MyD88L265P constitutive activity promotes NF-κB–dependent cytokine expression. To rule out cytokine-triggered cell activation by EVs, the EVs were isolated from NEMOKO (IKKγ) HEK293 cells29 (supplemental Figure 3A-B) transfected with MyD88L265P, where the NF-κB signaling pathway and production of cytokines is inactivated. EVL265P_NEMOwt and EVL265P_NEMO-KO activated cells to a similar extent (Figure 2A), confirming that the activity is due to the EV-transmitted MyD88. Additionally, IRAK4KO BMDMs were stimulated with EVL265P, since MyD88 signaling pathway requires IRAK4 signaling kinase. Results demonstrate that Rantes mRNA expression almost completely diminished in IRAK4-defficient cells (Figure 2B), further confirming that MyD88 signaling pathway is indeed involved in the activation by the EVs
Internalization of the intact EVs is necessary for signaling. EVL265P were isolated either from the NEMOKO cells or NEMOwt cells. (A) HEK293 cells expressing luciferase under the NF-κB promotor and Renilla luciferase for normalization were stimulated with EVL265P (12 μg/mL) for 24 hours. EVL265P were isolated from HEK293 cells and (B) IRAK4wt and IRAK4KO BMDMs were stimulated for 16 hours (30 μg/mL). LPS was a positive control (10 ng/mL). RNA was isolated and qPCRs for Rantes was performed. (C) EVL265P and EVCONT were submitted to 3 frozen/thaw cycles and then added to cells (12 μg/mL). (D-F) Dynasore (30 and 50 μM), LY294002 (50 μM), or ibrutinib (4 μM) were added to cells 1 hour prior stimulation with EVL265P and EVCONT (12 μg/mL) or EVMWCL (80 μg/mL) and EVCONT (80 μg/mL). HEK293 cells expressing luciferase under NF-κB promotor and Renilla luciferase for normalization were stimulated for 24 hours. Negative controls are transfected but unstimulated cells. Dual luciferase tests for NF-κB activity were performed.
Internalization of the intact EVs is necessary for signaling. EVL265P were isolated either from the NEMOKO cells or NEMOwt cells. (A) HEK293 cells expressing luciferase under the NF-κB promotor and Renilla luciferase for normalization were stimulated with EVL265P (12 μg/mL) for 24 hours. EVL265P were isolated from HEK293 cells and (B) IRAK4wt and IRAK4KO BMDMs were stimulated for 16 hours (30 μg/mL). LPS was a positive control (10 ng/mL). RNA was isolated and qPCRs for Rantes was performed. (C) EVL265P and EVCONT were submitted to 3 frozen/thaw cycles and then added to cells (12 μg/mL). (D-F) Dynasore (30 and 50 μM), LY294002 (50 μM), or ibrutinib (4 μM) were added to cells 1 hour prior stimulation with EVL265P and EVCONT (12 μg/mL) or EVMWCL (80 μg/mL) and EVCONT (80 μg/mL). HEK293 cells expressing luciferase under NF-κB promotor and Renilla luciferase for normalization were stimulated for 24 hours. Negative controls are transfected but unstimulated cells. Dual luciferase tests for NF-κB activity were performed.
EVL265P were submitted to several freeze/thaw cycles to disrupt the membranes of the EVs Freezing substantially decreased the activity (Figure 2C) demonstrating that the intact EVs and their content are necessary for the transfer of the signaling activity. Several mechanisms of EV-mediated transfer of molecular cargo have been described.30-32 Dynasore, an inhibitor of dynamin-mediated endocytosis, partially inhibited NF-κB activation triggered by EVL265P (Figure 2D). Additionally, partial inhibition of the reporter cell activation was also observed after the addition of LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor (Figure 2E), which inhibits phagocytosis. Results therefore suggest likely involvement of several mechanisms that contribute to the EV-mediated signaling cargo internalization.
LPS-induced signaling activates BTK, which interacts with several TIR domain-containing proteins, including MyD88.33 MyD88L265P supports activation of BTK12 in WM and secretion of the proinflammatory cytokines.25 BTK inhibitor ibrutinib, in clinical use for the therapy of WM, was added prior to the stimulation with EVs. Decrease of the NF-κB activation (Figure 2F) was detected, corroborating signaling in the cytosol through pathway inhibited by ibrutinib.
EV-transferred MyD88L265P recruits the endogenous MyD88wt to potentiate the signaling
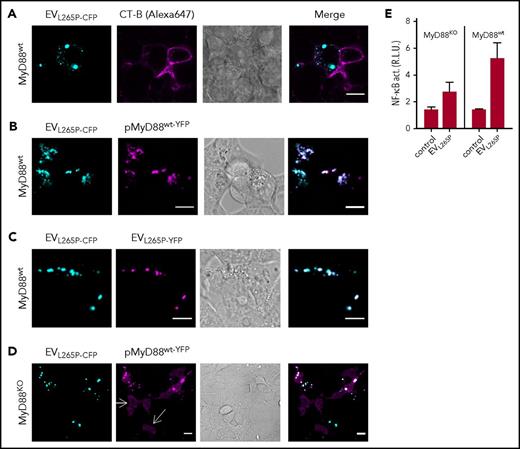
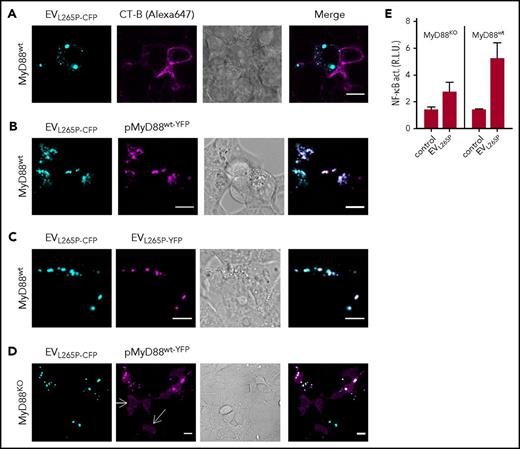
In the previous study, we showed that MyD88L265P can recruit the MyD88wt.6 This suggested that the introduction of the constitutively active MyD88 mutant into the recipient cells might trigger the inflammatory response by the recruitment of the endogenous MyD88wt. MyD88L265P-CFP-containing EVs were therefore prepared to monitor trafficking and interactions of the MyD88 in the recipient cells. Incubation of EVL265P-CFP with target HEK293 cells and subsequent addition of membrane dye CT-B showed mainly cytosolic localization of the MyD88 within the recipient cells (Figure 3A). When EVL265P-CFP were added to the HEK293 cells expressing MyD88wt-YFP (Figure 3B), we observed that MyD88L265P and MyD88wt formed mixed aggregates inside recipient cells, demonstrating that the EV-mediated uptake of MyD88L265P enabled its release into the cell cytoplasm, where it interacted with the endogenous protein. Furthermore, upon addition of a mixture of EVs isolated from cells producing MyD88L265P-CFP or MyD88L265P-YFP to the recipient cells, mixed aggregates were observed inside recipient cells (Figure 3C), demonstrating cytoplasmic interaction between proteins that enter the cells via EVs. Similar experiments were performed in MyD88KO cells. The MyD88KO HEK293 cell line was prepared by using CRISPR/Cas9 technology (M. Avbelj, G. Panter, I. Hafner-Bratkovič, D.L., M.B., B. Gole, U. Potočnik, S.P.T., and R.J., manuscript in preparation; supplemental Figure 3C-D). In wt cells, the overexpressed MyD88 is observed in the cytoplasm in the form of aggregates even at very low expression levels due to the formation of complex with endogenous MyD88, but in MyD88KO cells disperse cytosolic localization of MyD88wt-YFP was observed (white arrows) (Figure 3D). Internalization of EVL265P-CFP led to the formation of aggregates with MyD88wt-YFP. In agreement with this, MyD88KO cell line responded less efficiently to the EVL265P stimulation (Figure 3E left) than MyD88wt cells (Figure 3E right), demonstrating that the transmitted MyD88L265P is able to form active myddosomes by recruitment of the endogenous MyD88wt, which potentiates the activation of the signaling pathway.
MyD88L265Ptransferred by the EVs forms aggregates with endogenous MyD88 in the recipient cells. (A) EVL265P-CFP (cyan) were isolated and added (5 μg/mL) to the HEK293 cells for 16 hours. Cell membranes were dyed with CT-B Alexa 647 (magenta). (B,D) HEK293 and HEK293 MyD88KO cells were transfected with MyD88wt-YFP (magenta) or (C) left untreated. After 4 hours, EVL265P-CFP (cyan) or EVL265P-YFP (magenta) (both 5 μg/mL) were added for 16 hours. Confocal imaging was performed. Bar for all images, 10 μm. (E) HEK293 and HEK293 MyD88KO cells expressing luciferase under NF-κB promotor and Renilla luciferase for normalization were stimulated with EVL265P (12 μg/mL) for 24 hours. Negative controls are transfected but unstimulated cells. Dual luciferase test for NF-κB activity was performed.
MyD88L265Ptransferred by the EVs forms aggregates with endogenous MyD88 in the recipient cells. (A) EVL265P-CFP (cyan) were isolated and added (5 μg/mL) to the HEK293 cells for 16 hours. Cell membranes were dyed with CT-B Alexa 647 (magenta). (B,D) HEK293 and HEK293 MyD88KO cells were transfected with MyD88wt-YFP (magenta) or (C) left untreated. After 4 hours, EVL265P-CFP (cyan) or EVL265P-YFP (magenta) (both 5 μg/mL) were added for 16 hours. Confocal imaging was performed. Bar for all images, 10 μm. (E) HEK293 and HEK293 MyD88KO cells expressing luciferase under NF-κB promotor and Renilla luciferase for normalization were stimulated with EVL265P (12 μg/mL) for 24 hours. Negative controls are transfected but unstimulated cells. Dual luciferase test for NF-κB activity was performed.
Macrophages and mast cells respond to the MyD88L265P containing EVs
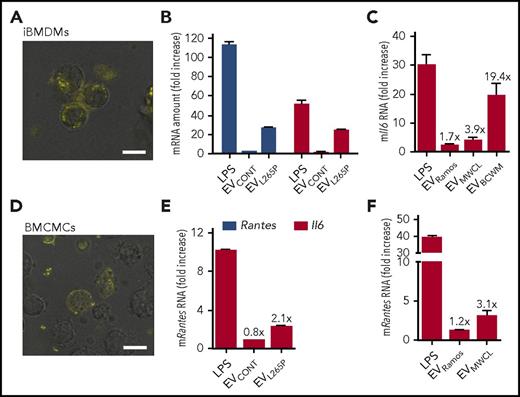
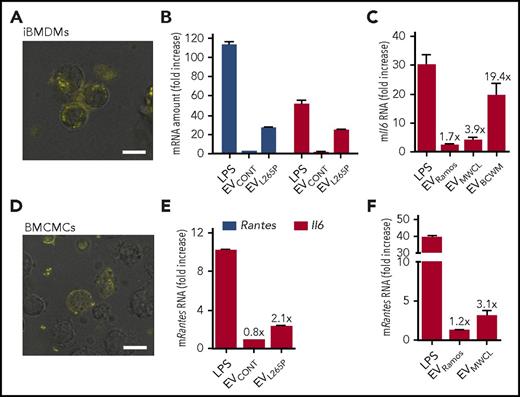
Efficiency of the EV internalization can strongly differ between cells. EVMWCL1 were stained by a lipophilic dye PKH67 and added to several cell types. After 6 hours, HEK293, THP1, macrophage cell line, iBMDMs as well as BMCMCs were able to uptake the EVs, but no uptake was observed by B cells and PBMCs, a minor uptake was probably due to macrophages (Figure 4A; supplemental Figure 4). Interestingly, fusion of the EVMWCL with the plasma membrane was observed in HEK293 cells and BMCMCs (Figure 4D; supplemental Figure 4), which could contribute to the efficient delivery of the myddosomal components into the cytosol, bypassing the endocytosis and phagocytosis. In accordance with this observation no stimulation of B cells with EVL265P was observed (data not shown), but cytokine expression was detected in iBMDMs (Figure 4B-C) as well as in BMCMCs (Figure 4E-F) after treatment with EVL265P, EVMWCL, or EVBCWM, implying those cells as the likely targets of the EV delivery, which is particularly relevant for the bone marrow environment.
Macrophages and mast cells respond to EV treatment. PKH67-labeled EVMWCL (yellow) were added to iBMDMs (A) and BMCMCs (D) to observe EV internalization. Bar, 10 μm. iBMDMs (B-C) were seeded and stimulated with EVCONT, EVL265P (30 μg/mL), or EVMWCL, EVBCWM, and EVRamos as negative control (100 μg/mL) and LPS as positive control (10 ng/mL) for 16 hours. BMCMCs (E-F) were seeded and stimulated with EVCONT, EVL265P (30 μg/mL), or EVMWCL and EVRamos as negative control (100 μg/mL) and LPS as positive control (50 ng/mL) for 16 hours. RNA was isolated and qPCRs for Rantes and Il6 were performed.
Macrophages and mast cells respond to EV treatment. PKH67-labeled EVMWCL (yellow) were added to iBMDMs (A) and BMCMCs (D) to observe EV internalization. Bar, 10 μm. iBMDMs (B-C) were seeded and stimulated with EVCONT, EVL265P (30 μg/mL), or EVMWCL, EVBCWM, and EVRamos as negative control (100 μg/mL) and LPS as positive control (10 ng/mL) for 16 hours. BMCMCs (E-F) were seeded and stimulated with EVCONT, EVL265P (30 μg/mL), or EVMWCL and EVRamos as negative control (100 μg/mL) and LPS as positive control (50 ng/mL) for 16 hours. RNA was isolated and qPCRs for Rantes and Il6 were performed.
EVs carrying myddosomal complex modulate bone marrow microenvironment
Clinical manifestations of WM are mainly due to the monoclonal IgM protein and infiltration, predominantly by the lymphoplasmacytic cells into the bone marrow. Mast cell hyperplasia is common and can stimulate WM cell proliferation.34 In WM, blood smears also show a characteristic striking rouleaux formation (reviewed in Stone and Pascual35 ). To demonstrate that EVs can remain in the circulation and be internalized by the recipient cells in vivo EVs were labeled with PKH67 and injected intraperitoneally or IV. After 4-hour uptake of EVs was detected in cells from peritoneal lavage (supplemental Figure 5A) as well as in organs such as liver, spleen, and lungs (supplemental Figure 5B). Moreover, to show that signaling competent MyD88 can be transmitted into the recipient cells in vivo, HEK293 cells expressing NF-κB dependent luciferase reporter were introduced s.c. into the BALB/c mice. EVCONT or EVL265P were subsequently administered IV (150 μg). After 24 hours, we were able to detect the luciferase activity in animals only when EVL265P were injected (Figure 5A), confirming that EVs can transmit the MyD88 signal systemically.
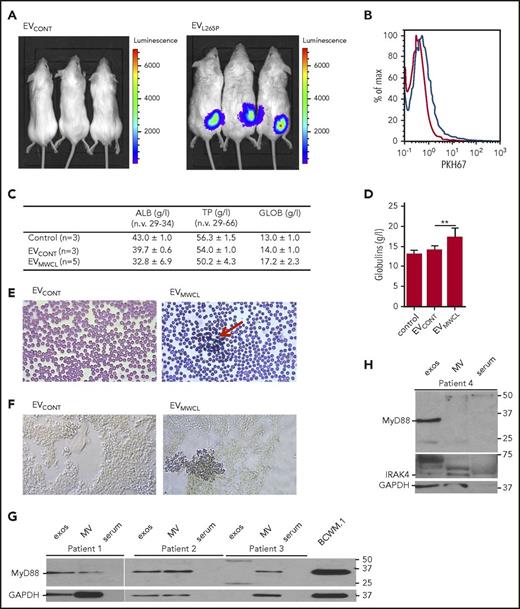
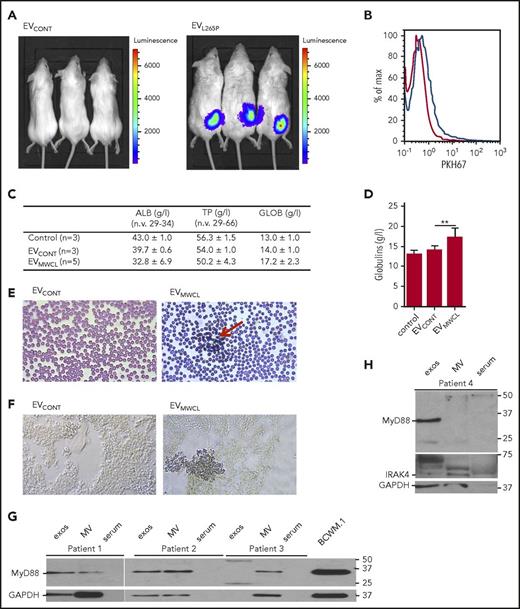
EVs are internalized in vivo and modify the bone marrow microenvironment. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with luciferase under NF-κB promotor for 24 hours. A total of 2 × 106 cells per mouse were injected s.c. after 30 minutes, EVCONT or EVL265P (150 μg per mouse) were injected IV and incubated for 24 hours. Luciferin was added and, after 10 to 15 minutes, luminescence was measured. PKH67-labeled EVs (100 μg) were injected into bone marrow. After 16 hours, uptake of EVs by bone marrow cells was measured (B). EVCONT or EVMWCL (150 μg) were injected into bone marrow. After 8 days, blood was taken to measure albumin, total protein, and globulin (C-D) concentrations and blood smears (E) for detection of rouleaux formation (red arrow) were prepared. (F) Tissue sections from femurs were prepared and stained for the presence of mast cells (CD40L) (blue). Original magnification ×630 for panels E-F. MVs and exosomes were isolated from bone marrow aspirates of untreated WM patients. MVs, exosomes, serum, and BCWM.1 cell lysate as positive control were used for MyD88 (G) and IRAK4 (H) detection by WB. GAPDH was used as a positive control for EVs and cell lysate.
EVs are internalized in vivo and modify the bone marrow microenvironment. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with luciferase under NF-κB promotor for 24 hours. A total of 2 × 106 cells per mouse were injected s.c. after 30 minutes, EVCONT or EVL265P (150 μg per mouse) were injected IV and incubated for 24 hours. Luciferin was added and, after 10 to 15 minutes, luminescence was measured. PKH67-labeled EVs (100 μg) were injected into bone marrow. After 16 hours, uptake of EVs by bone marrow cells was measured (B). EVCONT or EVMWCL (150 μg) were injected into bone marrow. After 8 days, blood was taken to measure albumin, total protein, and globulin (C-D) concentrations and blood smears (E) for detection of rouleaux formation (red arrow) were prepared. (F) Tissue sections from femurs were prepared and stained for the presence of mast cells (CD40L) (blue). Original magnification ×630 for panels E-F. MVs and exosomes were isolated from bone marrow aspirates of untreated WM patients. MVs, exosomes, serum, and BCWM.1 cell lysate as positive control were used for MyD88 (G) and IRAK4 (H) detection by WB. GAPDH was used as a positive control for EVs and cell lysate.
As the main pathology of the WM takes place in the bone marrow, PKH67-labeled EVs were injected into the C57BL/6 mice femurs. The uptake by cells in the bone marrow was confirmed by flow cytometer after 16 hours (Figure 5B blue line). EVMWCL or EVCONT were injected (150 μg per mouse) into the femurs to see if the uptake of EVs can change the microenvironment and contribute to the bone marrow pathology. After 8 days, all mice had normal levels of total proteins (TPs) and albumins (ALBs) in the serum (Figure 5C). However, mice injected with EVMWCL but not EVCONT and PBS exhibited increased globulin concentrations (GLOBs) (Figure 5C-D) in all mice (5 of 5), and induced rouleaux formation in blood (red arrow) (Figure 5E) in 2/5 mice. Bone marrow slides were stained with antiCD40L (antiCD154) antibodies for mast cell detection. Increased number of mast cells was detected in bone marrow only in mice that formed the rouleauxs (Figure 5F) in comparison with the EVCONT injection, demonstrating that EVs can directly influence the microenvironment.
Finally, the presence of MyD88 in the EVs from samples of patients with WM was investigated to establish the relevance of our observations for pathology. Using differential ultracentrifugation exosomes and MVs were isolated from the bone marrow aspirates of WM patients. MyD88 (Figure 5G) as well as IRAK4 (Figure 5H) were detected in the EVs (MVs and exosomes), but not in the serum, confirming the presence MyD88L265P in the EVs under the pathological conditions.
Discussion
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) including TLRs and TLR-signaling pathways have been implicated in a number of hematological malignancies (reviewed in Wang et al36 ) and in other tumors.37-39 Although the mechanisms by which inflammation promotes neoplastic transformation are not fully understood, cancer has strong connection to chronic inflammation.40,41 Persistent inflammation establishes a microenvironment, which contains macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells and T and B lymphocytes in addition to the surrounding stroma.42,43 These diverse cells communicate with each other by means of a direct contact or soluble mediators, which support cell proliferation, survival, and resistance to apoptosis thus influencing the tumor formation and growth.43,44 EVs are able to mediate the transfer of different kinds of molecules. Due to the small amount of the cellular content transmitted by the EVs, a potent physiological effect can only be expected from the components whose activity is amplified in target cells, such as RNAs, enzymes, transcription factors (TFs), or components that could engage endogenous molecules in the target cells thus triggering the signaling cascade. As an example, TFs NF-κB and COUP-TF I were detected in MVs released from platelets and transmitted to neutrophils, but activation of target genes in recipient cells has not been investigated.45 Here, we report the transfer and activation of target cell signaling by the constitutively active MyD88L265P as well as IRAK4 as the components of the myddosomal complex. We demonstrated that MyD88L265P can be delivered by the EVs and can reach the cytosol using several internalization pathways. Fusion of EVs with plasma membrane enables direct release of the content into the cytoplasm, whereas upon EV phagocytosis or endocytosis, the EVs need to fuse with organelle membranes by a process referred to as back-fusion (reviewed in Cocucci and Meldolesi46 ). We demonstrated that the EV-delivered MyD88L265P engages the endogenous MyD88wt resulting in potentiated activation of the inflammatory pathway, including activation of the NF-κB and inflammatory cytokine/chemokine production in macrophages and mast cells, both important for the pathogenesis of WM (Figure 6). The presence of the MyD88L265P was detected in bone marrow aspirates of patient samples, where the local concentration of EVs is very high and persistent and which could strongly contribute to the inflammation in the cancer cell microenvironment. Bacterial or viral infection, characterized by activation of TLRs, might also promote the release of MyD88wt in the EVs. However, in proteomic analysis of exosomes released after LPS stimulation of BMDMs,47 MyD88 has not been detected, suggesting that the dissemination by EVs may be specific to MyD88L265P in certain types of the lymphoma.
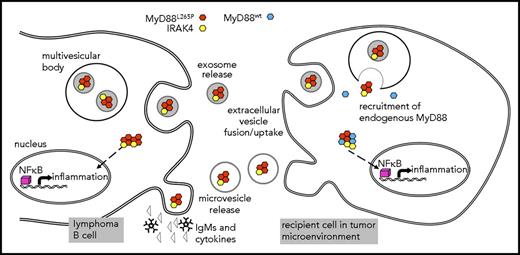
Schematic representation of EV-mediated MyD88 signaling. Lymphoma cells release IgMs and cytokines as well as myddosome-containing exosomes and MV. Recipient cells such as macrophages and mast cells uptake EVs and myddosomes are released into the cytosol, where MyD88wt can be recruited. Myddosomes induce inflammation without receptor activation thus changing the tumor microenvironment.
Schematic representation of EV-mediated MyD88 signaling. Lymphoma cells release IgMs and cytokines as well as myddosome-containing exosomes and MV. Recipient cells such as macrophages and mast cells uptake EVs and myddosomes are released into the cytosol, where MyD88wt can be recruited. Myddosomes induce inflammation without receptor activation thus changing the tumor microenvironment.
By injecting EVs into the bone marrow of mice, we detected a significant increase in globulins in all mice, with increased mast cells observed in the bone marrow along with blood rouleaux formation. It has been recently reported48 that mice with MyD88L252P (an analog of human L265P) spontaneously developed signs of DLBCL-like neoplasms, but no changes typical for WM such as infiltration of lymphoid cells to the bone marrow were observed. Also no engraftment in the bone was observed when BCWM.1 cells were injected s.c. to immunocompromised mice. Interestingly, the pathology developed when human bone chip from a fetal femur was transplanted into mice, showing that human bone marrow environment was important for the engraftment of tumor cells27 where the EVs might play an important role. It is likely that other constitutively active signaling pathway components that are able to engage endogenous mediators might be transferred between cells and activate signaling in the recipient cells. The apoptosis-associated specklike protein containing a CARD (ASC) adaptor plays a similar role in the inflammasome activation as the MyD88. ASC overexpression leads to the constitutive activation of caspase-1 and formation of large aggregates, called specks, resembling the myddosomal complex. ASC specks have been observed in the extracellular milieu, where they can be taken up by other cells. Those aggregates enabled nucleation of the soluble ASC in the recipient cells and triggered signaling.49,50 Although it has been proposed that ASC particles have to be released by cells into the extracellular medium and taken up by target cells by phagocytosis, recently, NLRP3 and ASC were found in the exosomes secreted from the LPS/nigericin-stimulated BMDMs.47 Interestingly, those exosomes were able to activate NF-κB signaling and induce pyroptosis, suggesting that the EV-mediated transfer may play an important role as well.
In conclusion, we report that the transfer of constitutively active signaling mediators via EVs represents a new mechanism of intercellular transfer that is amplified in the recipient cells by the recruitment of the endogenous signaling mediators. This process may play an important role in cancer development by triggering inflammation in the nontransformed cells independently of the membrane receptors.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank M. Avbelj for preparing MyD88L265P-FP plasmids, G. Panter for preparing HEK MyD88KO cells, D. Abbott (Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH) for HEK NEMOKO cells, and K. Fitzgerald (University of Massachusetts, Worcester, MA) for iBMDMs.
This work was supported by the Slovenian Research Agency (research core no. P4-0176 and project no. J3-8196) and by Peter S. Bing and The Edward and Linda Nelson Fund for WM.
Authorship
Contribution: M.M.-K. designed and performed most of the experiments; D.L. designed and performed animal experiments; M.B. and M.M.-K. performed confocal microscopy experiments; R.R. designed and performed electron microscopy; J.G.C. and Z.R.H. isolated EVs from human samples and performed WB; and M.M.-K., R.J., and S.P.T. wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Mateja Manček-Keber, Department of Synthetic Biology and Immunology, National Institute of Chemistry, Hajdrihova 19, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia; e-mail: mateja.mancek@ki.si; and Roman Jerala, Department of Synthetic Biology and Immunology, National Institute of Chemistry, Hajdrihova 19, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia; e-mail: roman.jerala@ki.si.