Abstract
Background:
Ibrutinib, a Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor was approved for the treatment of Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia (WM) in January, 2015 based on the results of a clinical trial of 63 previously-treated patients with WM. Data on outcomes with ibrutinib outside of clinical trials are limited.
Methods:
Medical records of patients with WM seen consecutively between 02/01/2015 and 06/01/2018 at Mayo Clinic, MN, FL and AZ were reviewed and those treated with ibrutinib at any point during their disease were included. Refractoriness to prior therapy was defined as disease progression on therapy or within 2 months of stopping treatment. The response rates were assessed by WM VI International Workshop Criteria. Adverse events were graded using National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events (AEs) v4.03. All time-to-event analyses were performed from the time of initiation of ibrutinib.
Results:
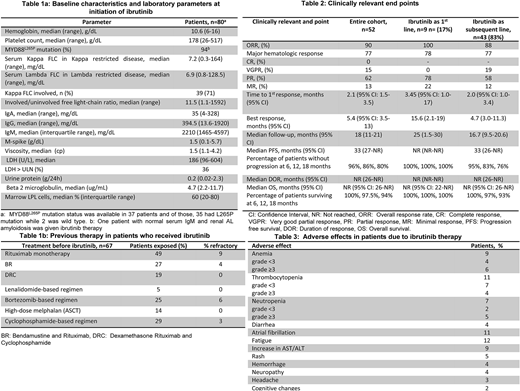
Eighty patients [previously treated, n=67 (84%), treatment-naïve, n=13 (16%)] received ibrutinib for active WM. Median follow-up was 18 months (95% CI: 12-19) and the median overall survival (OS) was not reached (NR) (95% CI: 27-NR) for the entire cohort at the date of last follow-up. The median age was 67 years (range: 50-88) and the median ECOG performance score was 1 (range: 0-3) at the time of ibrutinib initiation. Median lines of therapies prior to ibrutinib for the previously-treated patients was 2 (range: 1-9) and 35 patients (44%) had received ≥3 prior lines of therapy. Of the 80 patients, 52 patients (43 previously treated, 9 treatment-naïve) had data for response assessment.
The baseline characteristics and laboratory parameters at initiation of ibrutinib are outlined in Table 1a and prior therapies are mentioned in Table 1b.
Overall response rate (ORR) was 90% (100% in patients with ibrutinib as primary therapy and 88% in salvage therapy setting); major-response rate (MRR) was 77%. Median time to first and best response was 2.1 months (95% CI: 1.5-3.5) and 5.4 months (95% CI: 3.5-13), respectively. Other clinically relevant endpoints and AEs related to ibrutinib therapy are outlined in Table 2 and 3, respectively. The median time-to-next therapy was 33 months (95% CI: 28-NR).
At last follow-up, 25 (32%) patients had discontinued ibrutinib therapy. The reasons for discontinuation was progression (n=8), elevated liver enzymes (n=4), cognitive changes (n=1), inability to achieve better than MR (n=1), atrial fibrillation (n=3), consolidation with autologous stem cell transplantation after PR with ibrutinib (n=1), transition to hospice care due to progressive head and neck cancer (n=1), infection in lower extremity (n=1), transformation to DLBCL (n=1), blistering rash which resolved after ibrutinib discontinuation (n=1), obscure GI bleed that resolved after ibrutinib discontinuation (n=1), fatigue (n=1) and for unclear reasons recorded as treatment intolerance (n=1). Following discontinuation of ibrutinib, 21 patients received salvage therapy. Of these, data regarding the response to salvage therapy was available in 9 (43%) patients (VGPR=2, PR=3, SD=3 and progressive disease=1); median PFS from the salvage therapy following ibrutinib discontinuation was 18 months (95% CI: 2-25). Of the 4 patients who were not treated following ibrutinib discontinuation; 1 elected hospice care due to concurrent head and neck cancer progression, and the other 3 patients elected to be monitored off therapy (one had achieved SD and two had PR from ibrutinib).
Fourteen patients were evaluable for IgM rebound following ibrutinib discontinuation. Of those, 5 (36%) had sudden increase in IgM level [median: 158% from the IgM level after ibrutinib discontinuation (range: 22%-1368%)] within a median of 2 months (range: 1-3 months) and 1 patient required plasmapheresis for symptomatic hyperviscosity. Four of 5 patients received salvage therapy between 0-15 months. At last follow-up, 11 patients (14%) had died of whom 3 were on ibrutinib at the time of death [CNS involvement, (n=1), causes unrelated to WM, (n=2)].
Conclusions: Ibrutinib is an effective agent in WM patients with MYD88L265Pmutation. Our data regarding outcomes in non-trial setting appear comparable to the results observed in the pivotal clinical trial. Hematologists should be aware of unique ibrutinib associated toxicities and clinically relevant IgM rebound phenomenon following abrupt discontinuation of ibrutinib.
Ailawadhi:Celgene: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy. Gertz:janssen: Consultancy; Prothena: Honoraria; Medscape: Consultancy; Teva: Consultancy; celgene: Consultancy; annexon: Consultancy; Alnylam: Honoraria; Physicians Education Resource: Consultancy; spectrum: Consultancy, Honoraria; Apellis: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Ionis: Honoraria; Research to Practice: Consultancy. Kumar:Novartis: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; KITE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; KITE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Lacy:Celgene: Research Funding. Dispenzieri:Celgene, Takeda, Prothena, Jannsen, Pfizer, Alnylam, GSK: Research Funding. Witzig:Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Dingli:Millennium Takeda: Research Funding; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Other: Participates in the International PNH Registry (for Mayo Clinic, Rochester) for Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Other: Participates in the International PNH Registry (for Mayo Clinic, Rochester) for Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Millennium Takeda: Research Funding. Kapoor:Celgene: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.