Abstract
Background:
Brentuximab vedotin (BV), an antibody drug conjugate (ADC), selectively delivers anti-tubulin agent monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) to CD 30+ cells. In a multi-center phase II trial in patients with relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), BV showed an overall response rate (ORR) of 75%, a complete response (CR) rate of 34%, and a median duration of response (DOR) of 6.7 months (Younes A et al, JCO 2012). Although this drug has high response rates in HL, many patients will eventually develop resistance. We have shown that resistance to BV is associated with upregulation of MDR1 (multidrug resistance pump), and BV resistance cells have a decreased intracellular concentration of MMAE as a result of overexpression of drug export pump (Chen et al, MCT 2015).
Cyclosporine (CsA), an immunosuppressant, can inhibit drug export pump by competitive binding. It has been combined with non-targeted chemotherapy to overcome drug resistance in the past without significant benefits. However, it has never been combined with targeted therapies such as antibody drug conjugates. We found that addition of CsA to BV restores intracellular MMAE concentration in BV resistant cell lines and restores the IC50 to BV (Chen ASH 2017). In BV resistant mouse xenograft models, addition of CsA also restores BV sensitivity (Chen ASH 2017). We hypothesize that the combination of CsA and BV is safe and efficacious, thus we designed and conducted a phase I trial using the combination of CsA plus brentuximab vedotin in patients with R/R HL.
Patients and Methods:
This is a prospective, phase I trial with a 3 + 3 design in patients with relapsed/refractory HL. All patients had biopsy proven relapsed/refractory HL. Three dose levels are planned: 1) 1.2 mg/kg BV every 21 days and 5 mg/kg CsA PO BID on D 1-5, 2) 1.8 mg/kg BV every 21 days and 5 mg/kg CsA PO BID on D 1-5. 3) 1.8 mg/kg BV every 21 days and 7.5 mg/kg of CsA PO BID on D 1-5. DLT period is 21 days. Patients who were relapsed/refractory to BV were allowed. The primary endpoint was MTD. Secondary endpoints were safety, ORR, duration of response, and correlative analysis. Imaging studies were performed every two cycles with alternating CT and CT/PET scans. Response criteria were per Lugano 2014.
Results:
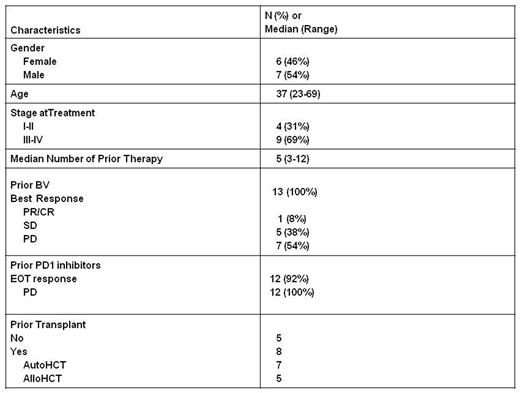
Thirteen patients were accrued, and all were evaluable for toxicity and 12/13 for efficacy. The baseline characteristics are shown in table 1 and include: previous BV (100%), previous PD1 inhibitor (92%), previous HCT (62%), male predominance (54%), Caucasian predominance (85%), median age of 37, stage III/IV (69%), refractory to previous BV (92%), progressed after PD1 blockade (92%). There was 0 DLT at dose level 1 (0/3), 1 DLT of abdominal pain (grade 3) and neutropenia at dose level 2 in the same patient (1/6 patients), and 4 DLT in 2 out of 3 patients treated at dose level 3. The DLTs were grade 3 hyperglycemia (1), grade 3 bone pain (1), grade 3 constipation (1), and grade 4 lymphopenia (1). Thus dose level 2 is the MTD. Grade 3 or higher possibly-related toxicities (excluding DLT) included neturopenia (6) anemia (4), lymphopenia (3), hyponatremia (3), hypophosphatemia (3), acidosis (1), pneumonitis (1), abdominal pain (1), colitis (1), AST elevation (1), weight loss (1), and hypokalemia (1). Grade II possibly related toxicities >20% included hypertension (46%), peripheral sensory neuropathy (31%), hypophosphatemia (31%), hypokalemia (31%), fatigue (31%), ALT increase (23%), elevated bili (23%), and myalgia (23%). Patients treated at the MTD experienced grade 3/4 possibly-related toxicities that were mainly laboratory based which included: neutropenia (4), anemia (2), hypophosphatemia (2), hypophosphatemia (1), hyponatremia (1), AST elevation (1), lymphopenia (1), abdominal pain (1), and colitis (1).
The best overall response (CR+PR) rate was 67%, CR rate was 33%, PR 33%, stable disease rate was 25%, 1 patient was inevaluable. The best overall response rate for patients treated at dose level 1 and 2 was 67% with a CR of 44%. Median number of cycles was 4 (1-14). 2 patients went to autoHCT and 2 patients went to alloHCT after protocol.
Conclusion:
Addition of CsA to BV is safe and feasible at the MTD. The MTD was determined to be 1.8 mg/kg BV every 21 days plus 5 mg/kg of CsA PO BID on D 1-5. The ORR of 67% and CR of 33 % is very encouraging in a primary BV refractory population. The study has opened the expansion phase.
Chen:Millennium Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck & Co., Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Genentech Inc.: Consultancy; Affimed: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding. Herrera:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Merck, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; KiTE Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Immune Design: Research Funding. Siddiqi:Juno Therapeutics: Other: Steering committee. Forman:Mustang Therapeutics: Other: Licensing Agreement, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.