Abstract
Introduction
Patients (pts) with CLL who achieve blood or bone marrow (BM) undetectable minimal residual disease (U-MRD), assessed with a sensitivity of at least 10-4 (MRD4), have long PFS after 1st-line treatment with FCR. A proportion of pts with mutated immunoglobulin heavy chain variable gene (M-IGHV) may be cured of CLL, given the reported PFS beyond 10 yrs. In contrast, most pts with unmutated (UM)-IGHV relapse, despite achieving BM U-MRD4. The likelihood of relapse and relapse kinetics relate to CLL biology, including depth of remission and proliferation rate. MRD testing using next generation sequencing (NGS) can achieve sensitivity up to 10-6 (MRD6) and can also be used to test for circulating tumor DNA in plasma, which may reflect residual tumor in the tissue (eg. lymph nodes), not detectable in the cellular fraction of blood or BM.
To better assess the depth of remission following first-line FCR treatment for CLL, we performed NGS MRD6 testing in BM, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and plasma of pts enrolled in a single center, prospective, phase II study. All pts had BM U-MRD4 by 4-color flow cytometry (FLC) at the end of treatment (EOT).
Methods
The following EOT samples from 62 pts were analyzed for MRD6: 57 BM, 29 PBMC and 32 plasma. Adaptive Biotechnologies' NGS MRD assay uses multiplex PCR and NGS to amplify rearrangements within the B cell receptor CDR3 and identify disease associated clonotypes. Specifically, the assay utilizes multiplexed primers complementing V-J rearrangements (IGH, IGK/L) and D-J (IGH) rearrangements. Pre-treatment samples were sequenced to determine the malignant clonotype, which was then quantitated in the EOT samples, within the polyclonal background.
Results
Regardless of assay sensitivity, U-MRD rates by HTS according to sample type were: 14/57 (25%) in BM; 16/29 (55%) in PBMC; 24/32 (75.0%) in plasma. All pts with MRD+ in plasma simultaneously had detectable disease in either BM or PBMC. Of 16 pts who had U-MRD in PBMC, 7/12 with simultaneous BM samples were MRD+ in BM. In all patients, there was a trend toward increased likelihood of U-MRD in pts with M-IGHV [12/30 (40%) vs 4/24 (17%), OR 3.3 (0.9-12.2), p = 0.06].
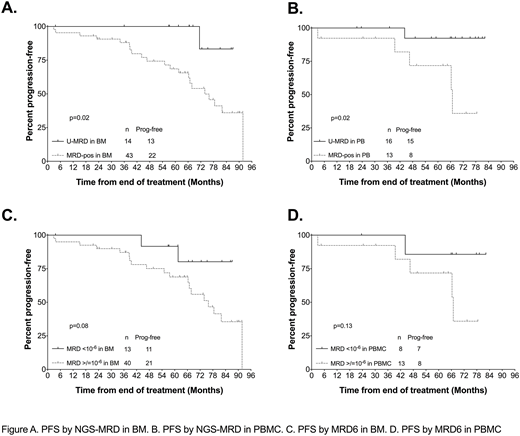
Assay sensitivity varies according to amount of DNA in the sample and with malignant clonotype. Sensitivity of at least 10-6 was achieved in 74% and 62% of samples in BM and PBMC, respectively. Among patients with U-MRD by NGS: 4/14 BM (1.06-3.2 x 10-6, median 1.96 x 10-6) and 8/16 PBMC (1.001 x 10-6 to 3.56 x 10-6, median 1.54 x 10-6) samples did not have sensitivity of 10-6. Notably, 3 pts also had detectable disease at a level <10-6 in BM, 2 of whom relapsed (Figure C).
Median follow-up was 82 months (mo) (range: 28-112.4). Fifty-six of 62 (90.3%) pts are alive; 28 are progression-free. Median PFS for the whole cohort was 89 mo. When PFS was analyzed according to whether MRD was detected or not (regardless of sensitivity), pts with U-MRD at the EOT had superior PFS vs pts with MRD+, whether the sample type used was BM (p=0.02, median NR vs 67 mo) or PBMC (p=0.02, median NR vs 74 mo), Figure A, B. When analyzed according to whether MRD was <10-6vs >/=10-6 (MRD6), 40/53 (75%) in BM and 13/21 (62%) in PBMC were MRD6+. For this analysis, pts were excluded if they had U-MRD but assay sensitivity did not reach at least 10-6. Despite smaller n, there were trends toward shorter PFS for pts with MRD6+ vs U-MRD6 (Figure C, D).
Discussion
The majority of pts with BM U-MRD4 after first-line FCR were MRD6+ and these patients had shorter PFS; MRD analysis with a more sensitive assay may therefore more accurately assign prognosis. Not accounting for sensitivity, a higher proportion of BM than PBMC samples were MRD+. Plasma analysis was uninformative as all pts MRD+ in plasma were MRD+ in simultaneous BM or PBMC samples.
Defining prognostically-relevant thresholds for MRD using more sensitive methodology is important, particularly if U-MRD is used a surrogate for PFS in clinical trials or as an endpoint for treatment cessation. MRD6 may become increasingly relevant if venetoclax-based regimens and the addition of novel agents to chemoimmunotherapy achieve U-MRD6 in more patients than FCR. In this retrospective study, a number of samples did not achieve 10-6 sensitivity; optimization of sample collection is important to achieve 10-6 sensitivity in most pts. Finally, additional studies will be required to determine the risk for and kinetics of relapse in patients with low-level MRD6+.
Thompson:AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Srivastava:Adaptive Biotechnologies: Employment. Hether:Adaptive Biotechnologies: Employment. O'Brien:Acerta: Research Funding; Sunesis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Vaniam Group LLC: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Aptose Biosciences Inc.: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Alexion: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding. Jain:ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Servier: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; Verastem: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologioes: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Servier: Research Funding; Verastem: Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cellectis: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Adaptive Biotechnologioes: Research Funding; Verastem: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astra Zeneca: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ADC Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Verastem: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ADC Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novimmune: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novimmune: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Wierda:Genentech: Research Funding; AbbVie, Inc: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.