Abstract
Introduction: Although proteasome inhibitors (PIs), immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs), and PI+IMiD combinations have become the standard of care in multiple myeloma (MM), they are not considered curative. Most patients (pts) eventually relapse or become refractory to treatment, and outcomes are poor after treatment failure. A median overall survival (OS) of 13 mo was reported in pts with relapsed/refractory MM (RRMM) who were double-refractory to a PI and IMiD and received ≥3 prior therapies (Kumar et al, Leukemia 2017). Recently developed therapies with novel mechanisms of action (MoAs), including the monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) elotuzumab and daratumumab, are associated with prolonged progression-free survival (PFS) in clinical trials of RRMM (Dimopoulos et al, Cancer in press; NEJM 2016). However, there is little up-to-date information on real-world survival outcomes. Herein we report survival patterns across key milestone timepoints in pts with RRMM in a real-world clinical setting.
Methods: PREAMBLE (NCT01838512) is an ongoing international, prospective, observational cohort study. Adults with RRMM who were not participating in a clinical trial at the time of enrollment, had ≥1 prior therapy and documented disease progression, and began treatment with a PI, IMiD, PI+IMiD combination, or newer agent (those with newer MoAs, such as mAbs, histone deacetylase inhibitors, and novel combinations) ≤90 d before to 30 d after informed consent, were included and followed for up to 3 years. During the observational period, data were collected at each healthcare visit, and vital status was assessed every 6 mo throughout the follow-up period. Clinical efficacy and patient characteristic data were collected by healthcare providers using electronic case report forms. Descriptive statistics were used to describe pt characteristics and Kaplan-Meier plots were generated for time-to-event data. Multivariate Cox regression, with stepwise variable selection to select independent variables, was used to assess the association between baseline characteristics and PFS or OS.
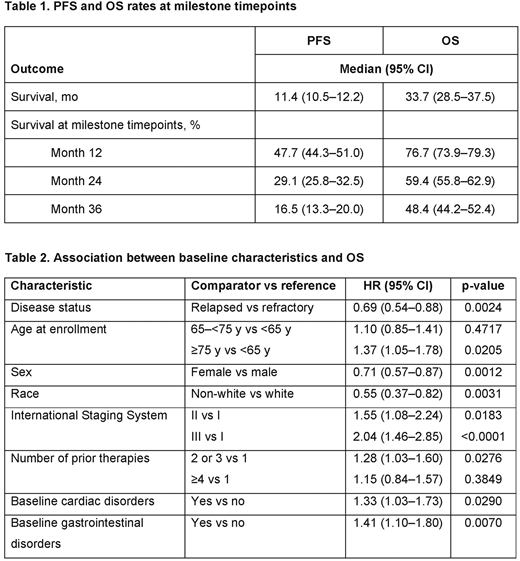
Results: At database lock (Nov 30, 2017), 1159 pts with RRMM were enrolled from the USA (31%) and Europe (67%), and included in this analysis. After a median (IQR) follow-up of 12.4 (6.3-24.9) mo, 39% of pts were still on study and 34% had died; most deaths (67%) were due to MM progression. At enrollment, median (range) age was 69 (34-92) y; 77% of pts had relapsed disease and 21% refractory disease. Among pts with a medical history, the most common comorbidities were vascular disorders (49%), metabolism and nutrition disorders (34%), and musculoskeletal/connective tissue disorders (29%). Pts received a median of 2 prior therapies before enrollment, with 50% having received an IMiD, 61% a PI, 21% a PI+IMiD, and 2% a newer agent. At enrollment, 45% of pts were receiving an IMiD, 41% a PI, 10% a PI+IMiD, and 4% a newer agent. Since enrollment, a total of 58% of pts received an IMiD, 49% a PI, 16% a PI+IMiD, and 10% a newer agent (including regimen received at enrollment). Median (95% CI) PFS was 11.4 (10.5-12.2) mo and OS was 33.7 (28.5-37.5) mo. Survival rates at milestone timepoints are shown in Table 1. Among pts who died due to MM progression (n=266), MM-related mortality was 56% at 12 mo, 85% at 24 mo, and 97% at 36 mo. In multivariate analysis, risk of disease progression/death was lower in pts with relapsed vs refractory disease at baseline (hazard ratio [HR] 0.82; 95% CI 0.68-0.99; p=0.0425) and higher in pts who had received 2-3 (HR 1.37; 95% CI 1.15-1.64; p=0.0004) or ≥4 (HR 1.54; 95% CI 1.22-1.95; p=0.0003) vs 1 prior therapy. Multivariate analysis for OS identified younger age, female sex, non-white race, relapsed disease, early-stage disease, fewer prior therapies, and the absence of baseline cardiac or gastrointestinal disorders as independent predictors of longer OS (Table 2).
Conclusions: Real-world data suggest that over the last decade, survival has improved for pts with RRMM; however, OS remained low (48%) after 3 years in this analysis and most deaths were attributed to MM. Baseline comorbidities may also increase the risk of death and should be carefully considered when selecting treatments. Newer treatment options are still needed to further extend survival in pts with RRMM.
Study support: Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS). Writing support: Janice Zhou, Caudex, funded by BMS.
Cook:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Glycomimetics: Consultancy, Honoraria. Cella:Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen Global services: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding. Chen:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment. Davis:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment. Durie:Amgen: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy. Goldschmidt:Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; Chugai: Honoraria, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnology: Consultancy; ArtTempi: Honoraria. Moreau:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Vij:Karyopharma: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jansson: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.