Abstract
Introduction: Serotonin Release Assay (SRA) is today considered as the "gold standard" to detect pathogenic Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) antibodies. However, this method is time-consuming, expensive and necessitates the use of 14C-radio-labelled serotonin, this implicating a specific agreement and secured premises, with a non-negligible environmental impact. These limitations explain that the use of SRA is restricted to a few laboratories worldwide. Finding a more accessible method with similar performances is therefore a challenge, and other different functional assays, such as Heparin-Induced Multiple Electrode Aggregometry (HIMEA), Light Transmission Aggregometry (LTA) using platelet rich plasma (PRP) or washed platelet (WP), ATP release, and Flow Cytometry (FC), are available. However, the sensitivity of these assays has never been comparatively evaluated with a standardized reagent.
Objectives:
The objective of our study was therefore to evaluate the sensitivity of these 5 functional methods for the detection of HIT antibodies in comparison with SRA, using 5B9, a monoclonal chimeric anti-PF4/H IgG recently developed in our laboratory, which fully mimics the effects of human HIT antibodies (Kizlik-Masson et al, J Thromb Haemost, 2017).
Material and Methods: Platelet activation induced by 5B9 with heparin was assessed by the 6 following methods with blood samples from 10 consecutive unselected healthy donors:
HIMEA performed with whole blood (Multiplate Analyzer® Roche),
LTA performed with PRP (Chronolog®, Chrono-Log corporation),
FC based on the assessment of P-selectin expression and performed with PRP (HIT Confirm®, Emosis on AccuriC6 plus®, Becton Dickinson),
ATP release performed with WP (Chronolog®, Chrono-Log corporation),
LTA performed with WP (Chronolog®, Chrono-Log corporation),
SRA performed with WP (LSC scintillation counter, Perkin Elmer).
For each method, different concentrations of 5B9 (10-20-50 µg/mL) were tested without heparin, and with "therapeutic" or high concentrations of unfractionated heparin (ranging from 0.1 to 1 and from 10 to 200 IU/mL respectively, according to the functional assay performed). The 3 concentrations of 5B9 were previously defined as "low" (10 µg/mL inducing in most cases a serotonin release <50% and no platelet aggregation in PRP), "high" (50 µg/mL always inducing a serotonin release >50% and platelet aggregation in PRP) or "intermediate" (20 µg/mL yielding variable results).
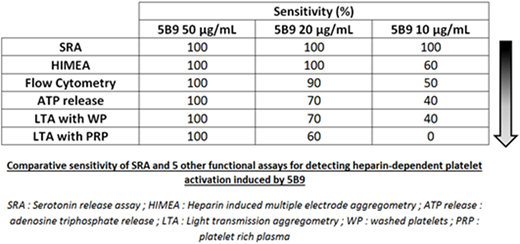
Results: With the highest concentration of 5B9 (50 µg/mL), a strong platelet activation was detected with all methods and donors tested. HIMEA exhibited similar sensitivity (Ss 100%) than SRA to detect the activation induced by 20 μg/mL 5B9. FC was also able to detect the effect induced by 20 μg/mL 5B9 with 9/10 donors tested (90%). Alternatively, the measurement of ATP release, and LTA performed with WP or PRP failed to detect the effect of 20 μg/mL 5B9 in 30, 30 and 40 % of donors tested, respectively. SRA was the only method able to detect platelet activation induced by 10 μg/mL 5B9 with all donors tested, and the other methods were less sensitive (table). LTA performed with PRP was always negative (Ss= 0%). Platelet washings increased LTA sensitivity for detecting 10 or 20 μg/mL 5B9 (40% and 70% with WP vs. 0 and 60% with PRP, respectively), and the measurement of ATP release exhibited similar sensitivity. When platelet activation was evaluated in whole blood by HIMEA or in PRP using FC, the sensitivity to detect HIT antibodies was also improved (60% and 50%, respectively).
Conclusion: These results confirm that SRA is likely the more sensitive functional assay to detect low concentrations of HIT antibodies. Indeed, apart from SRA, none of the other methods was able to detect the lowest concentration of 5B9 with 100% of donors. Interestingly, FC or HIMEA, which are rapid assays, also exhibit a high sensitivity, close to 100%, for detecting "intermediate" concentrations of HIT antibodies (i.e. corresponding to 20 μg/mL 5B9). We will further study the performances of these functional tests, including their specificity, by assessing patient's samples with confirmed HIT or having developed non-pathogenic antibodies (study in progress).
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.