Abstract
Despite the advances in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), a major fraction of adult patients still succumb to leukemia- or treatment-related events. In particular, the outcome of elderly ALL patients remains dismal. Our aim was to discover new or repurposed drugs for B-cell ALL in a clinically relevant ex vivo drug sensitivity testing platform.
We analyzed 19 primary B-ALL samples using a well-established drug sensitivity and resistance testing platform and a drug panel including 65 drugs in five different concentrations. The main drug classes were glucocorticoids, MDM2 antagonists, and inhibitors of BCR-ABL1, VEGFR, BCL-2, BCL-XL, BET, MEK, JAK, Aurora kinase, PI3K, MTOR, IGF1R, ERK, STAT3, STAT5, HSP90 and NAMPT proteins. The samples were viably frozen bone marrow (BM) mononuclear cells collected at diagnosis. The cohort included both Philadelphia-positive (Ph+) (n=10) and Ph-negative (Ph-) (n=9) patients with a median age of 43 years (range 22-68). Cell viability (CellTiter-Glo) was measured after plating and after a three-day incubation with the drugs. A drug sensitivity score (DSS) was calculated from the viability readouts, which takes into account the area under the dose response curve, measuring both drug efficacy and potency. DSS values >10 are considered effective and >20 highly effective.
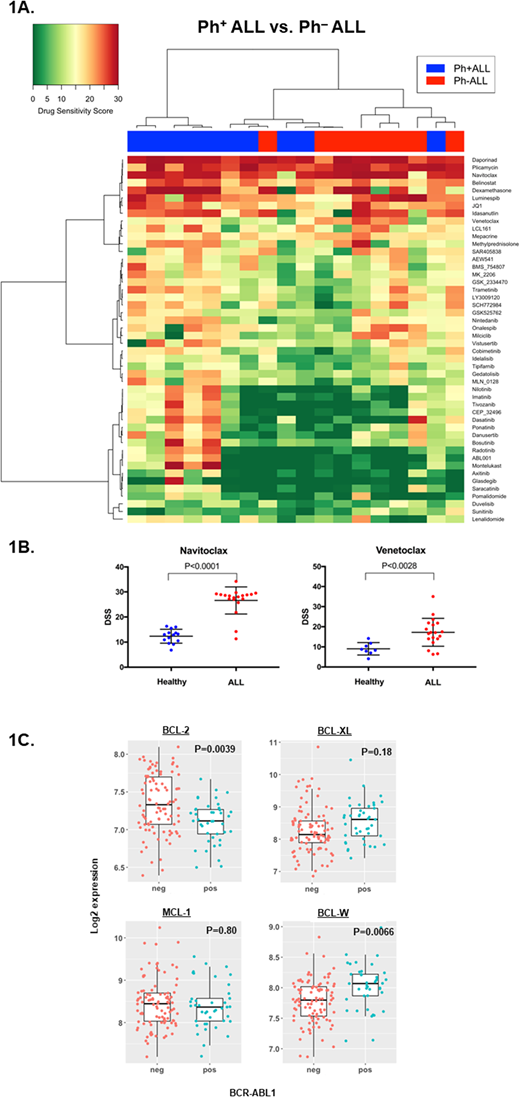
As an overall view of drug sensitivity, a heatmap and dendrograms from DSS values are shown in Figure 1A. As expected, most patients were sensitive to glucocorticoids and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) showed efficacy in Ph+ ALL. In addition, two Ph-negative patients were sensitive to TKIs, suggesting a Philadelphia-like disease. Drugs that showed pan-ALL efficacy included BCL-2 family inhibitors, idasanutlin (MDM2 inhibitor), luminespib (HSP90 inhibitor), daporinad (NMPRT inhibitor) and plicamycin (antineoplastic antibiotic). For the other drugs, only individual patients showed sensitivity, in line with the diverse molecular background of ALL.
Strikingly, 17/19 (89%) of patients in our cohort were highly sensitive (DSS>20) to navitoclax (a BCL-2, BCL-XL and BCL-W inhibitor), whereas the BCL-2-specific inhibitor venetoclax was effective only in a distinct subset of patients (Figure 1B). 6/19 (32%) of patients were highly sensitive (DSS>20) to venetoclax and represented all risk classes based on age, white blood cell counts and karyotype, but interestingly, all were Ph-negative. Overall, response to venetoclax correlated with response to navitoclax (Spearman, r=0.85; P<0.0001).
To examine differential gene expression of anti-apoptotic proteins between Ph+ and Ph- patients, we analyzed microarray gene expression data from ArrayExpress public database (www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress, E-MTAB-5035). The analyzed cohort included 96 Ph- and 41 Ph+ adult B-ALL patients. Ph-negative samples were characterized with higher BCL-2 expression, whereas Ph-positive samples showed higher BCL-W expression and a trend to higher BCL-XL expression (Figure 1C). Thus, lack of venetoclax efficacy ex vivo in Ph-positive ALL indicated dependence on BCL-W and BCL-XL, as also reflected in the gene expression analyses.
Inhibitors of BCL-2, such as navitoclax and venetoclax, potently induce apoptosis in a variety of cancer cells. Both inhibitors showed promising efficacy in our B-ALL samples. Dose-limiting thrombocytopenia has limited the use of navitoclax in solid tumors. However, in our assay navitoclax showed more uniform potency, particularly in Ph+ samples suggesting a rational combination with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Similar to conventional cytotoxic agents used in ALL, a therapeutic window may exist for safe use of navitoclax in acute leukemia. In conclusion, targeting the multidomain anti-apoptotic proteins (BCL-2, BCL-XL, BCL-W, MCL-1) and TP53 with MDM2, possibly in combination, is a promising strategy for improving outcome of adult B-ALL.
Hohtari:Incyte: Research Funding. Heckman:Novartis: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Orion Pharma: Research Funding. Wennerberg:Novartis: Research Funding. Mustjoki:Ariad: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding. Porkka:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.