Abstract
Introduction: In large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) MYC translocation and MYC/BCL2 or BCL6 double hit (DH) is associated with poor prognosis and there is an unmet need for novel treatment targets in this patient group. Treatment targeting the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway has been successfully introduced in Hodgkin lymphoma and solid cancers but are still poorly elucidated in LBCL. PD-L1 expression might predict response to treatment targeting the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway. We therefore investigated the relationship between PD-L1 protein and mRNA expression levels and MYC and DH translocation in LBCL.
Material and Methods: MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 translocations were detected by fluorescent in situ hybridization in tissue samples from 130 patients randomly selected from two cohorts of patients with LBCL: 49 patients with MYC translocation of whom 36 patients had DH and 81 without MYC translocation. PD-L1 protein expression was detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in tissue samples from 77 patients and PD-L1 mRNA expression by next-generation RNA sequencing (NGS) in another 77 patients. 24 patients overlapped, i.e. were analysed with both IHC and NGS. Nonparametric tests were performed to evaluate intergroup differences.
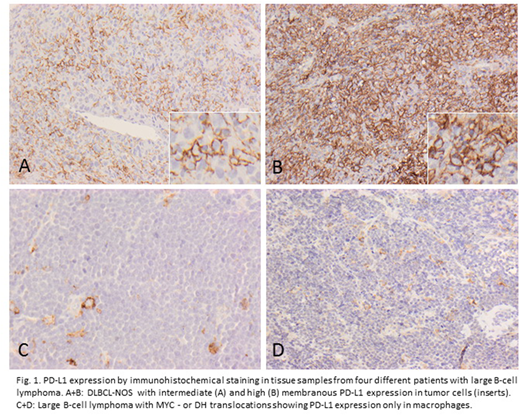
Results: PD-L1 protein expression level was lower in patients with MYC translocation (n=42, median=3,3%, IQR 0,0-10,8) or DH (n=31, median=3,3%, IQR 0,0-10,0) compared to patients with no MYC translocation (n=35, median=16,7%, IQR 3,3-30,0) or DH (n=46, 13,3%, IQR 2,5-30,0), P=0.004 and P<0,001 respectively (Fig.1). PD-L1 mRNA expression was also significantly lower in patients with MYC translocation or DH, P=0,001 and P=0,006 respectively. Higher PD-L1 protein and mRNA expression levels were associated with non-GC-type compared to GC-type DLBCL, P= 0,004 and P=0,002 respectively.
Conclusions: We report a highly significant association between low PD-L1 expression and MYC and DH translocation in patients with LBCL. Our findings may indicate that patients with MYC or DH translocation may benefit less from treatment with PD-L1/PD-1-inhibitors compared to patients without these translocations. This should be evaluated in larger, prospective, consecutive trials.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.