Abstract
Background: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common aggressive Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, with approximately one third of patients not responding (or relapsing) after receiving first-line (1L) therapy, typically a multi-agent chemoimmunotherapy regimen containing rituximab and doxorubicin. These patients may be treated with a second-line (2L) chemotherapy (CT) or chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) regimen, with the intention to proceed to a high-dose therapy followed by an autologous stem cell transplant (SCT). Unfortunately, a significant proportion of older patients are unable to tolerate such treatment. There is little data on treatment practices and outcomes in older DLBCL patients receiving 2L CT or CIT after failure of 1L therapy. Using electronic healthcare record data from the largest integrated health system in the United States, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), we examined real-world outcomes of DLBCL patients ≥ 65 years of age receiving 2L CT or CIT following 1L therapy with rituximab and doxorubicin containing regimens.
Methods: DLBCL patients diagnosed from 2001-2015 and treated at the VHA were identified by linking information from the VA Clinical Registry System (VACRS) in the VHA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) to administrative, laboratory and pharmacy data, and clinical notes in the CDW. Patients were included in the analysis if they: had no evidence of a prior malignancy, were diagnosed with DLBCL, received 1L therapy containing rituximab and doxorubicin for ≥ 21 days, then subsequently received a 2L CT or CIT, and were ≥ 65 years of age at time of 2L treatment. Patient age, gender, race/ethnicity; stage at diagnosis, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) were extracted from VACRS and/or CDW. Patients were censored at end of study observation period (Dec 31, 2016) or if a second cancer diagnosis occurred following their DLBCL diagnosis. Patients were divided into 2 groups: Group 1 included patients receiving a 2L regimen that, per the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, is typically used with intention to proceed to high-dose therapy; Group 2 included patients receiving a regimen that, per NCCN, is used in non-candidates for high-dose therapy. Receipt of SCT was identified using ICD codes and/or clinical notes.
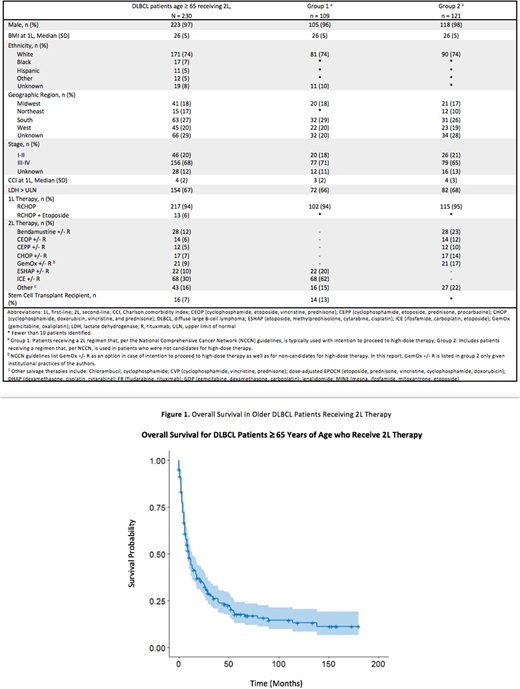
Results: 230 DLBCL patients met our inclusion criteria. Of these, 223 (97%) were male and 171 (74%) were of non-Hispanic, white ethnicity. Baseline characteristics (at time of 1L) were as follows: 156 (68%) had stage III-IV disease, 154 (67%) had LDH > ULN, and median CCI was 4 (IQR:2-5). The majority of patients (217, 94%) received RCHOP as 1L, with the remaining receiving RCHOP + etoposide (13, 6%). Two thirds of patients, (151, 66%) started 2L within 1 year of starting 1L with a median of 10.6 months between start of 1L and start of 2L. Patients were almost equally divided between the two groups, with Group 1 (109, 47%) and Group 2 (121, 53%). Of the 109 Group 1 patients, 68 (62%) received ifosfamide, carboplatin, etoposide (ICE) +/- rituximab (R), and 22 (20%) received etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine, cisplatin (ESHAP) +/- R. Of the 109 Group 1 patients, 14 (13%) proceeded to SCT within VHA (SCT outside VHA was not extracted for this study).
The remaining 121 Group 2 patients received 2L therapy with the following: bendamustine (B) +/- R (28, 23%), gemcitabine, oxaliplatin (Gem-Ox) +/- R (21, 17%), cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) +/- R (17, 14%), cyclophosphamide, etoposide, vincristine, prednisone (CEOP) +/- R (14, 12%), cyclophosphamide, etoposide, prednisone, procarbazine (CEPP) +/- R (12, 10%); CHOP + etoposide +/- R (6%), lenalidomide +/- R (6%). Fewer than 10 of these patients proceeded to SCT. The median OS of all patients was 8 months.
Conclusions: This is the first study that details treatment practices and outcomes in a nationwide cohort of older adult patients (≥ 65 years old) with relapsed/refractory DLBCL. Approximately half of these older patients did not receive or were not candidates for regimens typically used with intent for high-dose therapy and autologous transplant. OS for the entire cohort was less than a year. Despite significant advances in available treatments for DLBCL, there remains an unmet need in treatment of relapsed/refractory DLBCL, especially in older patients who have difficulty tolerating high-dose regimens.
Halwani:Takeda: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Miragen: Research Funding; Kyowa Hakko Kirin: Research Funding; Immune Design: Research Funding; Genentech, Inc.: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding. Schulz:Genentech: Employment, Equity Ownership; Roche: Equity Ownership. Li:Roche: Equity Ownership; Genentech: Employment. Masaquel:Genentech: Employment, Equity Ownership; Roche: Equity Ownership. Halloran:Genentech, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership; Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc: Employment, Equity Ownership. Delong-Sieg:Roche: Equity Ownership; Genentech, Inc.: Employment. Sauer:Genentech: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; COHRDATA: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.