Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Healthy adults with clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) are at increased risk of death from vascular disease. CHIP-associated genetic mutations such as ASXL1, TET2 and DNMT3A have been linked to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (Jaiswal et al, 2017). MDS and CHIP share common genetics events; in fact, certain MDS cases are believed to arise from preexisting clonal hematopoiesis. A recent SEER study demonstrated that 60 months from diagnosis, patients (pts) with low-risk MDS are at higher risk of death from cardiovascular causes than from MDS itself (Brunner et al, 2017). As the relationship between vascular disease and clonal hematopoiesis is delineated, management of vascular disease in patients with MDS is becoming increasingly important. Here we performed a retrospective analysis of MDS pts from Roswell Park to evaluate whether MDS-related factors such as morphologic subtype, treatment, cytopenias, iron status, blast percentage and karyotype modify atherosclerosis risk when molecular events are taken into account.
METHODS:
Over the past decade, 850 pts were diagnosed with MDS were seen and treated at Roswell Park. For the purpose of this study, 192 pts with a confirmed diagnosis of MDS seen between 2012- 2017 were investigated for cardiac events, blood counts, iron or inflammatory status as ferritin, MDS-related morphology, molecular profile and treatment. Cases were comprehensively annotated for the presence of vascular events, (defined as imaging or procedure verified coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular accident, or peripheral vascular disease) by review of the medical record. Conventional karyotype information was present in 98% of the cohort and NGS based multi-gene sequencing results through FoundationOne Heme was evaluated in 30% of the cohort. Numeric variables were summarized using simple descriptive statistics. A logistic regression model was used to investigate the association between vascular events and a set of explanatory variables for multivariate analysis.
RESULTS:
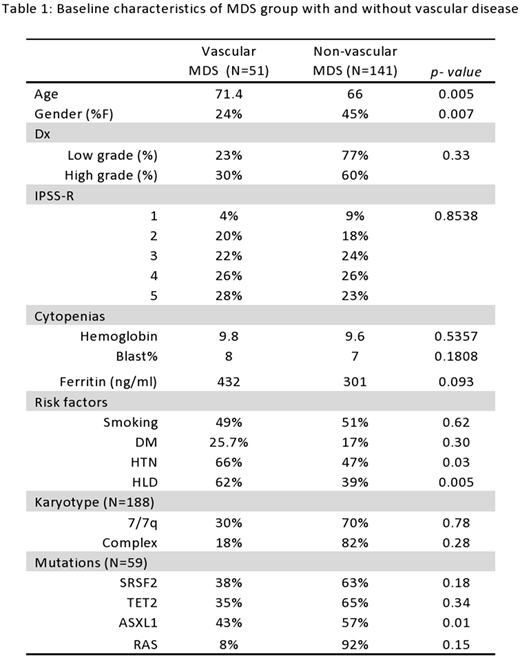
The median age at diagnosis for this cohort is 69 (range: 21-91) years; 60% were male and 57% had MDS with excess blasts. By IPSS-R, 25% had very low/low risk MDS, 22% had intermediate risk MDS and 46% had high risk MDS. The most common karyotypic abnormalities were normal (42%), complex (17%), trisomy 8 (10%) and del 7/7q (10%). Of the 59 patients with molecular data, the most common recurrent somatic mutations were in ASXL1 (47%), TET2 (30%), SRSF2 (27%), RAS pathway (22%) SF3B1 (22%), RUNX1 (20%) and TP53 (17%). The overall incidence of vascular events in this cohort was 27%.
Vascular disease was noted at similar frequencies for pts with low grade and high grade MDS (based on subtype of MDS), 23% vs. 30% (p=0.33) respectively. Women with MDS were significantly less likely to develop to vascular events than were men, 16% vs. 34% (p=0.007) and the mean age of pts with vascular disease was significantly higher, 71 vs. 65 years (p=0.005). Traditional risk factors such as hypertension and hyperlipidemia were more prevalent in MDS pts with vascular disease. Baseline hemoglobin, transfusion requirements and blast % levels were comparable in MDS patients with or without vascular disease. MDS pts with vascular disease had higher median ferritin levels, 432 vs. 301 ng/ml (p=0.093). When stratified by the IPSS-R, pts with very low risk MDS had a non-significant lower incidence of cardiac events, 14% vs. 25% (p=0.30), compared to other groups. Treatment with erythropoietin, lenalidomide or hypomethylating agents was not associated with vascular events. MDS pts with mutations in ASXL1 and SRSF2 had a higher incidence of vascular disease, 43% vs. 13% (p=0.01) and 38% vs 20% (p=0.18) respectively. On multivariable analysis, older age and male gender were most strongly predictive for vascular events.
CONCLUSION:
Here we retrospectively examined the potential factors associated with cardiovascular events in MDS pts treated at our institute over a 5-year time span. Male gender and older age were positively associated. Treatment regimen (erythropoietin injections or lenalidomide) and IPSS-R were not associated with an increased risk for vascular events. Factors independent of traditional cardiac risk factors, such as somatic mutations in ASXL1, iron overload and/or an inflammatory milieu i.e, ferritin, may contribute to atherosclerotic vascular disease in pts with MDS.
Baron:Pfizer Pharmaceuticals: Other: Previously served as a consult on the Advisory Boards (May 2017).. Wang:Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy; Jazz: Speakers Bureau; Jazz: Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Griffiths:Pfizer, Inc.: Research Funding; Celgene, Inc: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astex/Otsuka Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis, Inc.: Research Funding; Alexion Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding. Thota:Incyte: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.