Background: Optimal treatment for medically less fit adults with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains uncertain. Retrospective data suggest intensive therapy may lead to better outcomes in these patients. However, these findings must be interpreted cautiously because of the possibility of selection bias and other confounders. Ideally, the optimal treatment intensity is defined via randomized trial but whether patients and their physicians are amenable to such a study is unknown. We therefore designed a trial (NCT03012672) to 1) evaluate the feasibility of randomization between intensive and non-intensive therapy in this population and 2) examine the impact of treatment intensity on response rate and survival. We used CLAG-M as high-dose cytarabine-based intensive induction therapy. Rather than selecting different classes of drugs in the 2 treatment arms- which may have different modes of action and therefore confound the question of treatment intensity - we used reduced-dose ("mini") CLAG-M as the non-intensive comparator.
Methods: Adults ≥18 years were eligible if they had untreated AML or high-grade myeloid neoplasms (≥10% blasts in blood or marrow) and were medically less fit as defined by having a "treatment related mortality" (TRM) score of ≥13.1, corresponding to a >10-15% 28-day mortality with intensive chemotherapy. Left ventricular ejection fraction ≤45% was the only organ function exclusion. Patient-physician pairs were first asked if they were amenable to randomized treatment allocation. If so, they were randomized 1:1 to mini- vs. regular-dose CLAG-M. If not, in order to evaluate our secondary endpoints, the patient or physician could choose the treatment arm and still enroll on study. Patients and physicians then completed surveys elucidating their decision-making processes. Up to 2 induction courses were given with mini- vs. regular-dose CLAG-M: cladribine 2 or 5 mg/m2/day (days 1-5), cytarabine 100 or 2,000 mg/m2/day (days 1-5), G-CSF 300 or 480µcg/day for weight </≥76kg in both arms (days 0-5), and mitoxantrone 6 or 18 mg/m2/day (days 1-3). CLAG at identical doses was used for post-remission therapy for up to 4 (regular-dose CLAG) or 12 (mini-CLAG) cycles. The primary endpoint was feasibility of randomization, defined as ≥26/50 of patient-physician pairs agreeing to randomization. Secondary outcomes included rate of complete remission (CR) negative for measurable ("minimal") residual disease (MRD), rate of CR plus CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CR+CRi), and overall survival (OS).
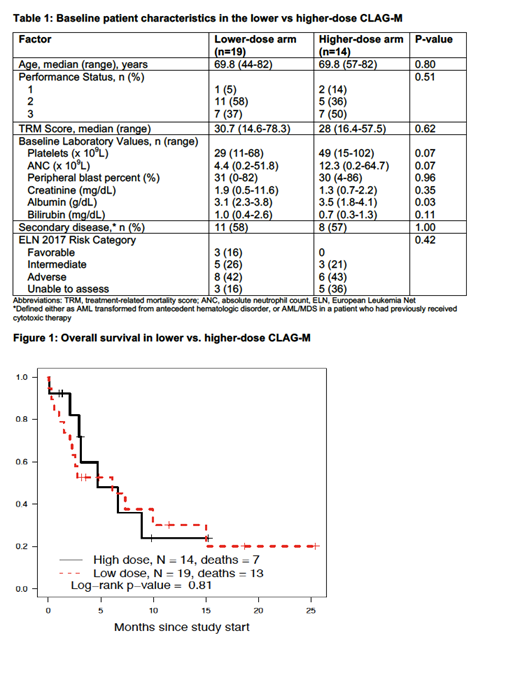
Results: This trial enrolled 33 patients. Only 3 (9%) patient/physician pairs agreed to randomization and thus randomization was deemed infeasible (primary endpoint). Eighteen pairs chose mini-CLAG-M and 12 regular-dose CLAG-M for a total of 19 subjects in the lower dose and 14 subjects in the higher dose arms. The decision favoring lower dose treatment was made largely by the physician in 5/18 (28%) cases, the patient in 11/18 (61%) cases and both in 2/18 (11%). The decision favoring the higher dose arm was made by the patient in most cases 9/12 (75%), both physician and patient in 2/12 (16%) and the physician in only 1/12 (8%) cases. Despite the limitations of lack of randomization, patients' baseline characteristics were well balanced with regard to age, performance status, TRM score, lab values and cytogenetic/mutational risk categories (Table 1). One patient was not yet evaluable for response or TRM at data cutoff. Rates of MRDneg CR were comparable: 6/19 (32%) in the lower and 3/14 (21%) in the higher dose groups (p=0.70). CR+CRi rates were also similar in both arms (43% vs. 56% in lower vs. higher dose arms; p=0.47). Three (16%) patients experienced early death in the lower dose arm vs. 1 (7%) in the higher dose arm (p=0.43). With a median follow up of 4.2 months, there was no survival difference between the two groups (median OS of 6.1 months in the lower vs. 4.7 months in the higher dose arm; p=0.81; Figure 1).
Conclusions: Randomization of medically unfit patients to lower- vs. higher-intensity therapy was not feasible, and physicians rarely chose higher intensity therapy in this patient group. Acknowledging the limitation of short follow-up time and small sample size, our trial did not identify significant differences in outcomes between intensive and non-intensive chemotherapy. Analysis of differences in QOL and healthcare resource utilization between groups is ongoing.
Halpern:Pfizer Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Bayer Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Othus:Celgene: Other: Data Safety and Monitoring Committee. Gardner:Abbvie: Speakers Bureau. Percival:Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer Inc.: Research Funding; Nohla Therapeutics: Research Funding. Scott:Incyte: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy. Becker:AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Glycomimetics, Invivoscribe, JW Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Trovagene: Research Funding; Accordant Health Services/Caremark: Consultancy; The France Foundation: Honoraria. Oehler:Pfizer Inc.: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines: Consultancy. Walter:BioLineRx: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Argenx BVBA: Consultancy; BiVictriX: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Amphivena Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Boehringer Ingelheim: Consultancy; Boston Biomedical: Consultancy; Covagen: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Race Oncology: Consultancy; Aptevo Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; New Link Genetics: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Cladribine is FDA-approved for Hairy Cell Leukemia. Here we describe its use for AML, where is is also widely used with prior publications supporting its use
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.