Introduction
CAR-T cells targeting CD19 positive B-cells have improved outcomes and remission rates in relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). Although toxicities contributing to non-progression related mortality (NRM) have been reported in the pivotal trials, its incidence in the standard of care setting post-approval is unknown. The following data includes toxicity profiles implicated in events leading to NRM obtained from the FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) with comparison to MD Anderson (MDACC-L) CAR-T Lymphoma cohort and to the pivotal CAR-T trials.
Methods
We retrospectively queried FAERS for all adverse events (AE) associated with tisagenlecleucel (T) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (AC) reported from January 1, 2013-June 30, 2019. FAERS contains AEs from clinical trials and healthcare providers and is standardized according to the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA), a clinically validated AE classification dictionary for pharmacovigilance monitoring. All cases with the outcome of death as reported by FAERS were queried. Cases in which the time to event with NRM was greater than 30 days or unknown were excluded. Total events recorded with NRM and disease progression were categorized according to the MedDRA coding system and compared using the chi-squared and a two-sided Fisher's exact test (statistical significance: p<0.05). NRM was compared between FAERS, MDACC-L, and the ZUMA-1, JULIET and ELIANA trials. Median days to NRM was measured. In the MDACC-L, a competing risk analysis using cumulative incidence function (CIF) between NRM and disease progression was calculated with Fine & Gray competing risk model.
Results
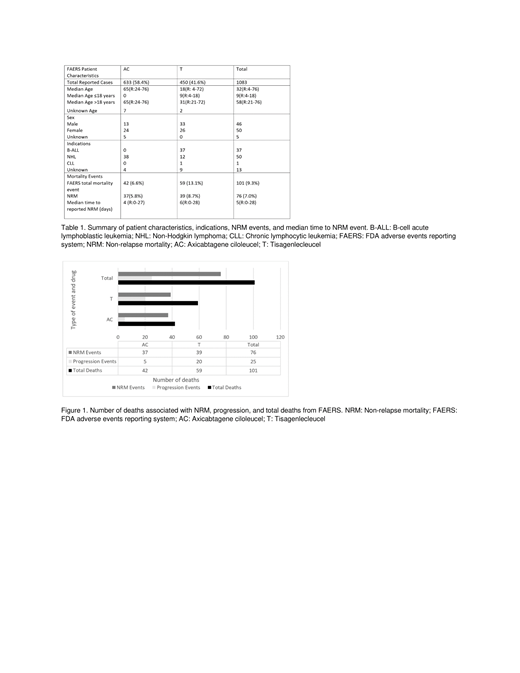
On FAERS, there were a total of 1184 reported cases, 669 with AC and 515 with T. Five cases were excluded because the reported event occurred 30 days after initiation of T (4) or AC (1), and 96 deaths were excluded because of missing start or event dates. As a result, there were 1,083 cases, 633 with AC and 450 with T. There were 101 (9.3%) deaths; 59 (13.1%) with T and 42 (6.6%) with AC. Seventy-six (7.0%) deaths were attributed to NRM; 39 (8.7%) with T and 37 (5.8%) with AC (Table 1) (Figure 1). AC had a significantly greater proportion of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) (p=0.027) and neurologic events (0.038) compared to T. The median number of days to the reported event was 4 (R: 0-27) for AC and 6 (R: 0-28) for T. There was no significant difference amongst cardiac, vascular, respiratory, or infectious events.
There were 112 patients in the MDACC-L (108 received A and 4 received T), with 3 cases excluded due to non-availability of cause of death. There were 7 deaths for competing risk analysis between progression and NRM. At 30 days, the competing risk analysis for MDACC-L using the CIF for NRM was 2.74% (0.8-8.9%) when progression was used as a competing event. In comparison, the proportion of 30 day NRM with ZUMA-1 was 3%, JULIET was 0%, while ELIANA was 1.3%.
Conclusions
NRM, an important outcome measure in stem cell transplantation, needs to be clearly defined in CAR-T therapies. We present NRM events based on the largest dataset available, FAERS. This analysis highlights the major toxicities associated with NRM, time to event occurrence, and indicates potential opportunities for mortality reducing interventions. Competing risk analysis suggests NRM is 2.74% following axicabtagene ciloleucel treatment for lymphoma. The comparative data highlights the differences in the reporting, and the need for close monitoring of CAR-T specific AEs. It also reflects the limitation of FAERS such as missing data that may change the actual NRM, inability to differentiate the grade of a reported AE, and inability to determine the exact date of death. We plan to present this data with a profile of NRM events at the upcoming ASH meeting in Orlando.
Westin:Novartis: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Kite: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; 47 Inc: Research Funding; Unum: Research Funding; MorphoSys: Other: Advisory Board; Genentech: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Curis: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Juno: Other: Advisory Board; Janssen: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Celgene: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding. Nastoupil:Spectrum: Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria; Genentech, Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bayer: Honoraria. Nieto:Novartis: Research Funding; Affimed: Consultancy; Astra-Zeneca: Research Funding; Affimed: Research Funding. Parmar:Cellenkos Inc.: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Wang:Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; MoreHealth: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; BioInvent: Consultancy, Research Funding; Loxo Oncology: Research Funding; BeiGene: Research Funding; Aviara: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Dava Oncology: Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pulse Biosciences: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; VelosBio: Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics: Research Funding. Hawkins:Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Other: advisory panels. Fowler:TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Neelapu:Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Precision Biosciences: Consultancy; Allogene: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; BMS: Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; Karus: Research Funding; Unum Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Research Funding; Cell Medica: Consultancy; Poseida: Research Funding. Iyer:Arog: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.