Introduction: Emicizumab is a subcutaneously administered, humanized bispecific monoclonal antibody that is recently approved for hemostatic prophylaxis in people with hemophilia A (PWH) with or without factor VIII inhibitors. We hypothesize that the new route and frequency of administration would lead to better treatment adherence compared to factor or bypass products in PWH outside of clinical trials. We performed the current study to test the hypothesis and to examine potential predictors of non-adherence associated with emicizumab treatment.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study at the Washington Center for Bleeding Disorders. Inclusion criteria included PWH with moderate to severe hereditary hemophilia (FVIII <5%), clinician recommendation for routine prophylaxis, receipt of clinical care and medication from a hemophilia treatment center (HTC), at least 12 months of prior exposure to factor or bypass products, and at least 3 months of emicizumab treatment. For patients who were previously enrolled in emicizumab clinical trials, adherence data were collected from the time of first commercial product administration. Adherence percentage (%) was estimated as days of drug dispensed / days elapsed x 100 and non-adherence % was determined as 100 - adherence %. Relevant patient, condition, treatment, and socioeconomic variable data were collected from review of medical records. To assess the difference in drug adherence, we compared the adherence % of emicizumab versus that of factor or bypass product in the same patients using the paired t test. To assess predictors of non-adherence %, we used a generalized linear model (GLM) with log link and gamma distribution to account for the right skewed distribution of the outcome. A multivariable GLM was built to incorporate the most significant predictors of non-adherence.
Results: We identified 56 PWH that initiated commercial emicizumab from 1/2018 to 5/2019 at our HTC. Five patients were excluded for fewer than 3 months of follow-up on treatment and 3 patients were excluded for not having prior exposure to factor therapy. The remaining 48 patients had a median duration on emicizumab of 7 months (IQR 5-9) at the time of study. The most common dosing frequency was weekly administration (77%). The median age at treatment index date was 17 years (IQR 9-36), 65% were Caucasian, and 46% had Medicaid or Medicare insurance. The majority of patients had a diagnosis of severe hemophilia (90%), 42% had a history of inhibitor (15% active inhibitor), and 25% were previously enrolled in an emicizumab interventional trial. Prior to emicizumab initiation, 46% of patients had 5 or more self-reported annualized bleeds. The most common reason for emicizumab initiation was patient preference (35%), followed by breakthrough bleeding (33%), difficult venipuncture (21%), and shortened factor half-life (10%).
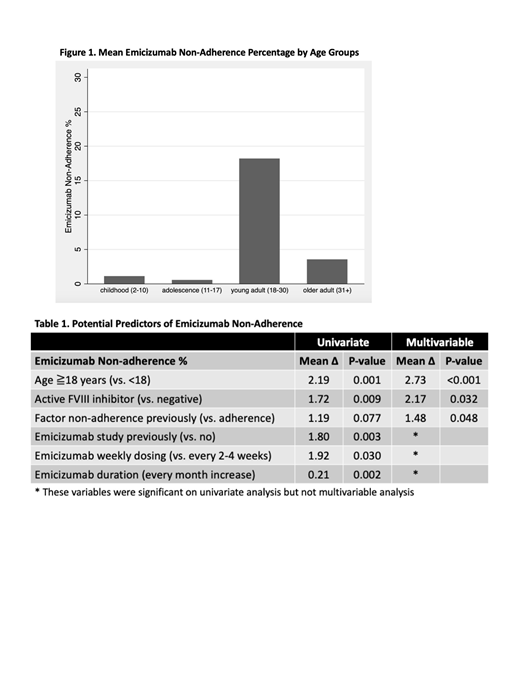
Among 12 patients who previously received only on demand treatment, their adherence on emicizumab was 89%. Among 36 patients who previously received routine prophylaxis, their adherence was significantly higher on emicizumab (98%) than factor/bypass products (89%) (p=0.002). Specifically, 18 out of 48 patients (38%) had factor/bypass adherence <75% (or refused prophylaxis) and 2 out of 48 patients (4%) had emicizumab adherence <75%. Various factors were associated with increased emicizumab non-adherence (Table 1). Age group had the strongest association where young and older adult PWH had more non-adherence % than children and adolescents (Figure 1). On multivariable analysis, age group, active inhibitor, and prior factor/bypass agent non-adherence (episodic or <75% usage) were significantly associated with increased emicizumab non-adherence.
Conclusions: In the current study, we found that PWH requiring routine prophylaxis were more likely to be adherent to emicizumab than previous factor or bypass agents. Age group (young adult), active inhibitor, and prior non-adherence to factor product were significant predictors for decreased emicizumab adherence but the differences were small. Given the long half-life of the drug, the significance of non-perfect adherence on bleeding outcomes needs to be studied prospectively with longer clinical follow-up.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.