Introduction: Sickle cell anemia (SCA) causes impaired tissue oxygenation. Children with SCA have lower peak fitness levels compared to controls. The contribution of alterations in skeletal muscle and cerebral tissue oxygenation to exercise limitation in SCA remains unclear. Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a validated, non-invasive method to measure tissue oxygen saturation. We hypothesize that compared to controls, children with SCA will exhibit greater reductions in regional tissue oxygen saturation (StO2) measured in the quadriceps (vastus lateralis) and pre frontal cortex (PFC) across all workloads during maximal cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET).
Methods: We used the CASMED ELITE NIRS tissue oximeter to measure tissue oxygen saturation in the PFC and vastus lateralis (VL) muscle during all phases of maximal CPET, including warm up, active exercise and recovery, in 17 subjects with SCA (mean age 13.5 years) and 13 controls (mean age 15.2 years). Maximal CPET was conducted by cycle ergometry using a standard ramp protocol until volitional exhaustion was reached by all participants. Peak oxygen consumption (VO2) was measured from breath-by breath gas exchange data collected during CPET.
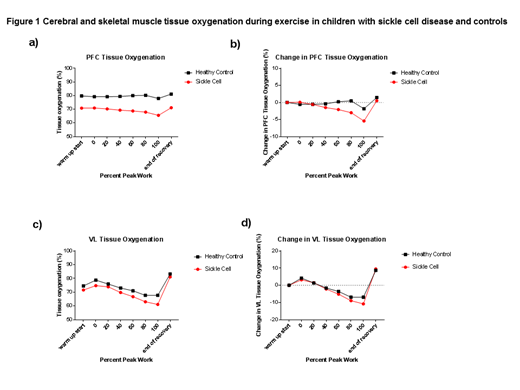
Results: All subjects and controls completed maximal CPET without adverse events. Peak VO2 was not statistically different in subjects with SCA versus controls (25.3±4.7 vs 29.5±8.9 mL/kg/min, p=0.22). Compared to controls, subjects with SCA had significantly lower PFC StO2 at all time points during exercise, including warm up, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100% of peak work load (p<0.01) (Figure 1a). Subjects with SCA demonstrated a significant decrease in PFC StO2 from warm up to 80% peak work load (-3.0±2.9% , p=0.002) and from warm up to 100% peak work load (-5.4±3.4 %, p<0.001) (Figure 1b). In contrast, controls did not demonstrate significant decreases in PFC StO2 from warm up to any point during exercise testing. VL StO2 did not significantly differ between subjects and controls during exercise (p=0.149, Figure 1c). Subjects with SCA demonstrated a significant increase in VL StO2 from warm up to 0% (+3.2±2.8%, p<0.001) and 20% peak work load (+2.3±2.5%, p=0.002) and a significant decrease in StO2 from warm up to 60% (-4.8±4.6%, p<0.001), 80% (-8.6±5.9%, p<0.001) and 100% peak work load (-10.5±6.3%, p<0.001) (Figure 1d). Controls had significant increase in VL StO2 from warm up to 0% peak work load (+4.3±4.0%, p=0.02) and a significant decrease only at 80% (-6.5±6.3%, p=0.003). Differences in PFC and VL StO2 between subjects and controls were also examined at the highest VO2 achieved by all participants. At a VO2 of 17.6 mL/kg/min, PFC StO2 was significantly lower in subjects with SCA versus controls (69.2±6.6 vs 79.5±5.3%, p<0.001). There was a trend toward lower VL StO2 in subjects versus controls (67.7±9.0 vs 73.2±7.9%, p=0.09).
Conclusion: Unlike VL tissue oxygenation, PFC tissue oxygenation is relatively well preserved in subjects with SCA and controls during maximal CPET. However, compared to controls, subjects with SCA have lower PFC tissue oxygenation at warm up and during exercise as well as demonstrate significantly greater decreases in PFC tissue oxygenation during later stages of exercise. In contrast, VL tissue oxygenation is similar at warm up and during exercise for subjects and controls. VL tissue oxygenation increases during initial stages of exercise in a similar fashion in subjects with SCA and controls but subsequent decreases from warm up are greater in subjects with SCA during later stages of exercise. Future studies may further elucidate how SCA contributes to these observed differences in regional tissue oxygenation during exercise and their potential impact on exercise safety and fitness in this population.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.