Background. Increasing age is a risk factor for vascular events but also for bleeding in immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). In elderly, meta-analysis of clinical trials of romiplostim (ROM) and eltrombopag (ELT) show that thrombopoietin receptor agonists (TPO-RA) are effective and safe with the exception of increased thromboembolic risk (Olney et al, 2011; Michel et al 2015).
Objective. To analyze how age influences the selection of TPO-RA, bleeding and thrombotic risk, comorbidities, and therapeutic management of ITP patients in a real-world setting.
Methods. We conducted a multicenter retrospective study that included 121 adult patients with primary ITP from 19 secondary and tertiary Spanish hospitals who had initiated long-term therapy with ROM or ELT between January 2012 and December 2014. Information was collected from medical records (November 2016 to January 2018) to assess variables related to patient characteristics and outcomes of elderly (> 65 years; n=54) compared with younger individuals (n=67).
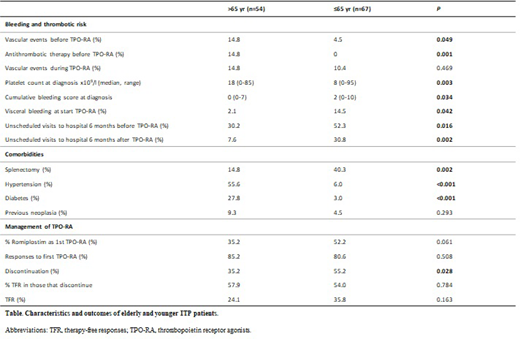
Results. Patients included initiated TPO-RA (ROM, n=54; ELT, n=67) and maintained this therapy for a median time to collection of data of 35.2 months (1 to 67.3 months). The median age at diagnosis of elderly and younger cohorts was respectively 75 years (66-96 years), and 48 years (19-65 years). Older age was associated with a previous history of vascular events (VE) (P=0.049), with more patients receiving antithrombotic therapy (P=0.001), and with a non-significant trend towards increased risk of current VE under TPO-RA therapy (Table). During treatment, 15 patients experienced 17 VE (9 arterial, 8 venous); no association was found between risk for VE in patients under TPO-RA and past history of thromboembolic or ischemic events (P=0.727). Patients that were offered TPO-RA at younger ages presented at diagnosis with significantly lower platelet counts, and increased cumulative bleeding score (Page et al, 2007) (P=0.003, and P=0.034) than elderly ones. Younger patients also had significantly higher visceral bleeding rates at the onset of TPO-RA therapy (P=0.042) and had increased requirement for hospital care (emergency treatment or hospital admission) both six months before and after the start of TPO-RA (P=0.016, and P=0.002, respectively). Older age was associated with comorbidities such as hypertension and diabetes (P<0.001), and with decreased exposure to splenectomy (P=0.002). In patients over 65 years experiencing VE on TPO-RA, a significant association with previous neoplasia was observed vs. those without that complication (50% vs. 2.2%, P<0.001), whereas in younger patients VE during TPO-RA therapy was only associated with previous splenectomy (100% vs. 33%, P=0.001). There was a trend towards a preferential use of ELT in older patients. While slightly higher platelet response rates to TPO-RA were seen among patients >65 versus ≤65 years, however a more conservative management in terms of discontinuation of therapies was confirmed. Therefore, the rate of tapering off TPO-RA was significantly lower in those >65 years (P=0.028), although the proportion of patients that achieved therapy free response (TFR) (platelet count >50x109/l for at least 6 months) upon discontinuation was similar in both groups (Table).
Conclusion. The management of older patients with chronic ITP is still challenging, and widespread effort is made to avoid potential complications such as those related to splenectomy. Our study reflects that the introduction of TPO-RAs has caused a change in the outcomes of these patients. The increased awareness of the unfavorable conditions that are present in this population induces a preferential use of TPO-RAs in elderly patients with a lower bleeding history than in younger patients. Although these drugs associate with a potential risk of increased thrombotic risk, our data indicate that past thrombotic history does not predispose to the development of VE; rather neoplasia in elderly patients, and splenectomy at younger ages are factors that increase the likelihood to suffer from these events. The compromise towards effective therapies in these fragile patients associates with low discontinuation of TPO-RA to test for TFR, although once tapered off, sustained platelet responses are similar to those in younger patients.
Mingot-Castellano:Novonordisk: Consultancy; Sobi: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; CSL Behring: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy. Jarque:Abbie: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Alexion: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; CellTrion: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Grifols: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; MSD: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Servier: Speakers Bureau; Shionogi: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Shire: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Campos:Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Speakers Bureau. Lopez Fernandez:Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Valcarcel:MSD: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Astellas: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; JAZZ: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Casado:Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Álvarez Roman:Takeda: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bayer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; CSL Behring: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; NovoNordisk: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Sobi: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.