Background: Minimal residual disease (MRD) status is an independent prognostic marker for response duration in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Rituximab-based therapy led to a molecular remission (MR) in 48% young MCL patients treated with intense chemo-immunotherapy. More recently, 4 courses of R-DHAP were reported to yield a 66% MRD negativity rate prior to high dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplant (HDC-ASCT). Ofatumumab is a humanized type 1 anti-CD20 mAb that binds to a unique, more membrane-proximal epitope on the CD20 antigen. Pre-clinical studies have demonstrated that ofatumumab (O) is more active than rituximab in eliciting complement-mediated cytotoxicity (CMC) in MCL cell lines, primary tumor cells and murine lymphoma xenograft models. Hence, we evaluated the safety and efficacy of combining ofatumumab with HyperCVAD/MA (O-HyperCVAD) in newly diagnosed MCL (NCT01527149).
Study design: This was a single-arm, open-label, multi-center (2 centers), prospective, phase 2 clinical trial. Thirty-seven transplant-eligible patients with newly diagnosed MCL were enrolled. Ofatumumab (1000mg) was given every 3 weeks on day 1, followed by standard doses of alternating HyperCVAD and MA starting on day 3. A total of 6 cycles were given at 3-week intervals followed by HDC-ASCT. Maintenance rituximab 375 mg/m2 every 2 months for 3 years post-ASCT was added after protocol amendment following publication of the LyMa study. Primary objectives were to determine the overall response rate (ORR) and CR rate (CRR) at the end of therapy. Secondary objectives included MRD negativity, progression free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), feasibility of successful mobilization of autologous stem cells and safety assessment. MRD assessment was performed in peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) using high sensitivity multiparametric flowcytometry at baseline, after 2 cycles, after 4 cycles, pre-ASCT, post-ASCT and 6 months post-ASCT. Exploratory endpoints included correlation of MRD with survival, correlation of surface CD20 levels with response and to compare differences in ORR according to Cheson and modified Cheson (MC) criteria.
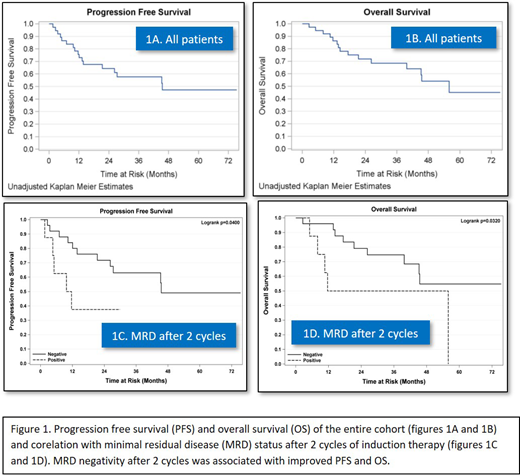
Results: Median age was 60yrs; 73% of patients were male, 92% had an ECOG PS 0-1, majority (81%) had stage 4 disease with 86% having bone marrow involvement; 22% had low risk, 43% had intermediate risk and 35% had high risk MIPI score; 11% had blastoid and 11% had pleiomorphic variants of MCL; 25% harbored p53 deletion. MRD was assessed in 28 of 37 patients; 9 patients from partner site were excluded due to time lag in sample delivery for flowcytometry. MRD positivity was noted in 75% patients in PB and 71.4% patients in BM at baseline. Subsequent samples showed an MRD negativity rate of 82.1% and 64.3% after 2 cycles and 76% and 96% pre-ASCT in PB and BM respectively. Post-ASCT, MRD in BM and PB was found negative in 58% and 90%, respectively. Attainment of early MRD negativity (after 2 cycles) was associated with improved PFS (p=0.04) and OS (p=0.03). Since majority of patients were MRD negative pre-ASCT, we could not demonstrate correlation between pre-ASCT MRD and survival outcomes. The ORR and CRR were 95% and 62% by Cheson and 97% and 84% respectively by modified Cheson criteria. At the end of induction therapy, ORR was 86% and CRR was 62% by Cheson criteria. 73% pts underwent HDC-ASCT. Only one patient failed stem cell collection. The median PFS and OS were 45.5 months and 56 months respectively. There were 3 deaths while on therapy- 2 from sepsis and one from acute myeloid leukemia. Grade 3 and 4 adverse events (AEs) were observed in 22% and 68% of the patients, most of them were hematological AEs related to the chemotherapy regimen. Correlation of surface CD20 expression using mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) and response rates is currently under analysis and will be reported at the meeting.
Conclusion: The addition of ofatumumab to HyperCVAD/MA led to high rates of MRD negativity by flowcytometry in patients with newly diagnosed MCL. Early MRD negativity (after 2 cycles) was associated with better PFS and OS. Despite higher ORR, CR and MRD negativity rates, survival outcomes were similar to historical cohorts using rituximab-HypeCVAD/MA. This may be in part due to increased number of patients with high-risk disease in our study.
Reddy:KITE Pharma: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Genentech: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding. Sait:Celgene: Consultancy.
Ofatumumab was investigated in combination with chemotherapy in newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma in this clinical trial.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.