BACKGROUND: CMML is an aggressive myeloid neoplasm with no known disease modifying treatments. We have shown both that CMML PDXs recapitulate the genetic and pathologic features of this disease, and that the JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib is a promising therapeutic in a phase 1/2 clinical trial. However, whether CMML PDXs can recapitulate clinical responses is unknown. To explore this, we generated PDXs from bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMCs) of ruxolitinib clinical trial CMML patients and treated the resultant mice with pharmacologically equivalent doses of ruxolitinib or vehicle. These models were then used to determine if clinical trial responses could be recapitulated and if molecular analysis could identify novel therapeutic strategies for CMML.
METHODS: Two million BMMCs from patient samples harvested no later than 30 days before ruxolitinib initiation were transplanted into 3 vehicle and 3 drug-treated NSGS mice as described (Yoshima Blood 2017). Fourteen days post-transplant, mice received either 60 mg/kg ruxolitinib or vehicle via oral gavage twice daily. Treatment continued until the animals became moribund. The primary endpoint of the study was intrapatient PDX overall survival. Secondary PDX response assessments included: (1) reduction in splenomegaly as measured by spleen weight at necropsy, (2) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the spleen at baseline and at the time that the first mouse became moribund (3) and improvement in BM and spleen pathology to include decreases in human CMML engraftment. PDX responses were compared to those seen in the clinical trial per MDS/MPN IWG criteria. Human CD45+ cells from exemplary ruxolitinib- and vehicle-treated mice were sorted and subjected to targeted DNA sequencing and transcriptional and proteomic profiling using the Nanostring Hemeplatform.
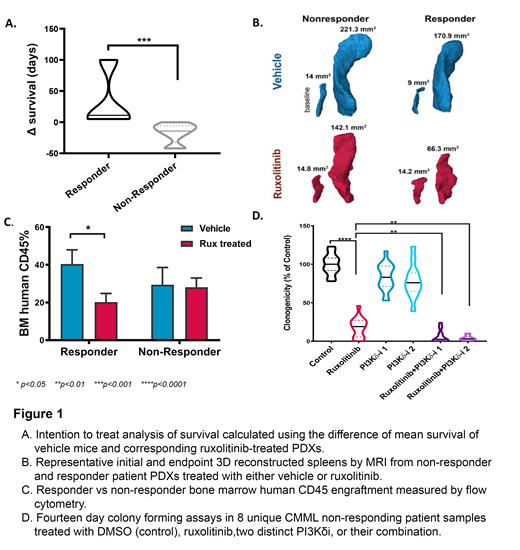
RESULTS: As we previously reported, the overall response rate of our single-arm ruxolitinib clinical trial (n=50) was 36% and 9 of 23 patients (40%) with splenomegaly had a > 50% reduction in spleen size by physical exam. PDX models were generated from 6 of the patients who had splenomegaly at baseline (3 responders, 3 nonresponders). A total of 34 CMML PDX models were generated and the mean duration on therapy was 63 days (range 7-199 days) for all models. The median overall survival of PDX mice was 59.5 days in the ruxolitinib cohort versus 52 days for the vehicle cohort (HR=1.062, p=0.88). However, ruxolitinib-treated xenografts derived from responders experienced a survival benefit (p=0.0002), a greater reduction in spleen volume when compared to corresponding vehicles (mean decrease in volume -43.9mm3 vs -16.6mm3), and a reduction in bone marrow leukemic engraftment compared to vehicle not observed in PDX mice from nonresponders (p<0.05 vs p=0.90) (Fig. 1 A-C). Metrics assessed at the time of necropsy such as blood counts and spleen weight did not statistically associate by treatment groups. In exemplary mice from 4 patient samples where sufficient cell numbers were recovered at necropsy, DNA-sequencing of sorted human splenocytes confirmed the identical mutations identified in the respective patient sample. In one nonresponding PDX cohort a PI3K/AKT expression signature was identified when comparing ruxolitinib versus vehicle treated mice, suggesting that combining ruxolitinib and PI3K inhibitors could be a viable therapeutic strategy for CMML. To test this, we performed 14-day colony formation assays using 8 unique BMMC CMML patient samples from ruxolitinib nonresponders treated with vehicle, ruxolitinib, and two distinct PI3Kδ inhibitors (PI3Kδi), or their combination. PI3Kδi were chosen as this represented the most highly expressed PI3K isoform in our in-house RNA-seq data set. Interestingly, the combination of ruxolitinib with either PI3Kδi reduced clonogenicity compared to vehicle or each single drug suggesting a novel combination strategy for CMML treatment (Fig. 1D).
CONCLUSION: Our CMML PDX platform confirmed the biologic impact of ruxolitinib in CMML, identified a novel combination therapy, and recapitulated clinical responses manifest in human patients. To our knowledge, this is the first report of PDX models recapitulating clinical trial responses in leukemia. A cohort of 6 additional patient samples are currently being assessed to validate these results.
DeZern:Celgene: Consultancy; Astex Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy. Lancet:Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Other: fees for non-CME/CE services ; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Agios, Biopath, Biosight, Boehringer Inglheim, Celator, Celgene, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Karyopharm, Novartis: Consultancy. List:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Roboz:Argenx: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amphivena: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Actinium: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astex: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celltrion: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Eisai: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MEI Pharma: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Orsenix: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Otsuka: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sandoz: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Trovagene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Steensma:H3 Biosciences: Other: Research funding to institution, not investigator.; Pfizer: Consultancy; Onconova: Consultancy; Summer Road: Consultancy; Aprea: Research Funding; Stemline: Consultancy; Astex: Consultancy; Arrowhead: Equity Ownership. Sekeres:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Syros: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Millenium: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Komrokji:JAZZ: Speakers Bureau; DSI: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; pfizer: Consultancy; celgene: Consultancy; Novartis: Speakers Bureau; JAZZ: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.