Background: Anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody therapy has become an integral component of treatment for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) but not all patients respond. Identification of predictive biomarkers could help clinicians identify the best treatment course for a patient. We present baseline biomarker analyses on samples from a Phase 1 (Study 1; NCT02283775) and Phase 3 (Study 2; NCT02990338 [ICARIA-MM]) clinical study that evaluated the addition of isatuximab (Isa), an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, to pomalidomide and dexamethasone (Pd) for the treatment of RRMM. CD38 receptor density (RD), FCGR3A (Fc immunoglobulin receptor) genotype, and bone marrow or peripheral blood immunophenotyping were evaluated as potential predictive biomarkers for a response to the Isa-Pd regimen.
Methods: Both studies enrolled similar patient populations with RRMM who had received ≥2 prior lines of therapy including lenalidomide and a proteasome inhibitor. Baseline blood samples were taken prior to first treatment in both studies; in addition, a bone marrow sample was taken during screening in Study 1. In Study 1, bone marrow plasma cells were analyzed for CD38 RD. Immune cell populations (CD19+ B-cell, CD3+ T-cell, CD4+ T-cell, regulatory T-cells (Tregs) and natural killer (NK) cells [CD56+ bright CD16+ low subset and CD56+ dim CD16+ bright subset]) were characterized using blood samples and bone marrow aspirates. Blood samples from both studies were analyzed for FCGR3A genotyping (V158 and F158 high- and low-affinity alleles). Biomarker results were correlated with response, defined as at least partial response according to IMWG criteria.
Results: Study 1 enrolled and treated 45 patients with Isa-Pd. Study 2 randomized 154 patients to Isa-Pd and 153 patients to Pd. Baseline patient demographics were similar for both studies and the median number of prior lines of therapy was 3 (range: 1-10) for Study 1 and 3 (2-11) for Study 2. The overall response rates (ORR) with Isa-Pd were 62.2% (28/45) in Study 1 and 60.4% (93/154) in Study 2. In Study 1, the median CD38 RD, for 31 patients with evaluable results, was 108,172 receptors/cancer cell (range: 12,950-337,335). In patients responding to Isa-Pd (n=21), the median CD38 RD value was 120,931 (48,770-337,335) receptors/cancer cell; in patients not responding to Isa-Pd (n=10), the median CD38 RD value was 85,370 (range 12,950-309,003) receptors/cancer cell. Univariate analysis in Study 1 showed no association between CD38 RD and ORR (p=0.2870). Across five Phase 1/2 clinical studies with Isa, 4/198 patients (2.0%) had a CD38 RD level below 48770, the lowest value in a responder patient.
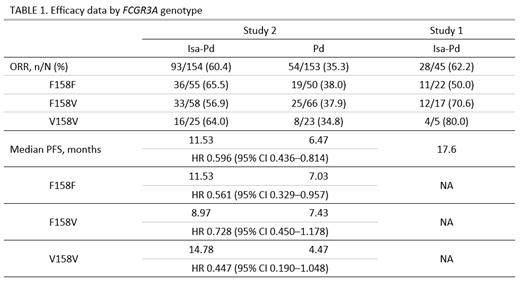
FCGR3A genotyping results were available for both studies. Across both studies, the distribution of the F158V single nucleotide polymorphism of FCGR3A gene was 42% for F/F, 42% for F/V and 16% for V/V. In both studies, responses were observed for all 3 genotypes (Table 1). In Study 1, the observed ORRs with the Isa-Pd regimen for the 3 genotypes ranged from 50.0% to 80.0%, whereas in the larger Phase 3 Study 2, the ORR was more similar across genotypes (range 56.9% to 65.5%). Median progression-free survival (PFS) ranged from 8.97 months to 14.78 months and Isa-Pd showed a PFS benefit vs Pd for all 3 genotypes (Table 1).
In Study 1, 42 patients had at least one baseline peripheral blood immune biomarker value; of these, 17 patients were non-responders and 25 patients were responders. In addition, 41 patients had at least one baseline bone marrow immune biomarker measurement (16 were non-responders and 25 were responders). No significant difference was observed between responders and non-responders for the tested immune biomarkers in bone marrow during screening. P-values were 0.2817 (CD19+ B-cell), 0.6446 (CD3+ T-cell), 0.7780 (CD4+ T-cell), 0.1620 (Tregs), 0.9591 (NK cell), 0.8275 (CD56+ bright/CD16+ low NK cell), and 0.7389 (CD56+ dim/CD16+ bright NK cell). Similarly, there was no significant difference between responders and non-responders for the immune biomarkers in baseline blood samples.
Conclusion: Biomarker analyses on samples from patients treated with Isa-Pd did not find a significant association between tumor response and baseline bone marrow plasma cell CD38 RD, FCGR3A genotype, or immunophenotypes in bone marrow plasma cells or peripheral blood. These results suggest there is no benefit in prescreening patients for these parameters before treatment with Isa-Pd.
Richardson:Karyopharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oncopeptides: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Facon:Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Bensinger:Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Merck, Karyopharm: Other: Grant; Amgen, Celgene: Other: Personal Fees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Takeda, Janssen: Speakers Bureau. Macé:Sanofi: Employment. Chiron:Sanofi: Employment. van de Velde:Sanofi: Employment. Campana:Sanofi: Employment. Liu:Sanofi: Employment.
Isatuximab is an investigational agent and has not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration or any other regulatory agency worldwide for the uses under investigation.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.