OBJECTIVE: Patients with core binding factor (CBF) AML generally have a favorable prognosis, but the appropriate intensity of chemotherapy and number of courses are still key points for further exploration by the different leukemic group. Our prospective multicenter clinical study was designed to use high intensity, 4-courses of chemotherapy (backbone of MRC AML 15 protocol) to treat childhood CBF-AML and to observe the feasibility and effectiveness in China.
METHODS: Total of 101 children with CBF-AML from 9 centers of south of China were enrolled on the C-HUANAN Children AML 2015 protocol from 2015.1 to 2018.11, accounting for 30.6% of total AML (non-APL) cases. There were 59 boys and 42 girls, aged between 2- 14 years old. The diagnosis of CBF-AML was established by PCR-based detection of RUNX1-RUNX1T1 and CBFβ-MYH11 fusion gene transcripts or by FISH based detection of t(8;21) and inv(16) aberration, respectively. Nine cases were combined with FTL3-ITD. Eleven cases were combined with ASXL1 mutation, and 23 cases were combined with c-KIT mutation. The induction regimen were non-randomized to DAE group and FLAG-IDA group. The induction regimen of DAE group including coures 1 (DAE 3+5+10), course 2 (DAE 3+5+8) . The induction regimen of FLAG-IDA including two courses of FLAG-IDA. Consolidation treatment was same and consisted of 2 courses: 1.HAE or MACE; 2.MidAC. Follow-up observation was then started after 4 courses of treatment. All of patients were followed-up to 06/30/2019, median follow-up time was 25 months.
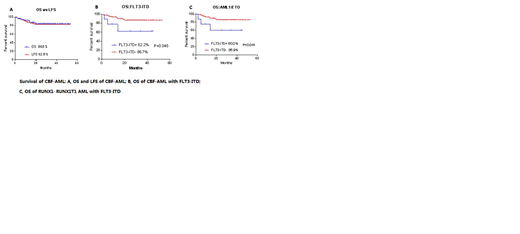
RESULTS: The overall complete remission rate was 93.1% after two courses of induction, 93.8% in the DAE group and 92.8% in the FLAG-IDA group. There was no statistical difference between the two groups. The MRD negative rate (<0.1%) detected by the flow cytometry after first course was 57/87 (65.5%) and 67/77 (87.0%) after second course respectively. The RUNX1-RUNX1T1 or CBFβ-MYH11 gene negative rate was 28/60 (46.7%) and 25/43 (58.1%) after first course and second course of treatment respectively .The overall survival rate (OS) was 83.2%, and the leukemia-free survival rate was 81.1%.Among them, the OS and LFS of the DAE group were 76.4% and 73.2%, respectively, and the OS and LFS of the FLAG-IDA group were 86.3% and 84.6%, respectively( P= 0.331 and 0.241).The OS and LFS of the RUNX1-RUNX1T1 group were 81.8% and 79.2%, respectively.The OS and LFS of the CBFβ/MYH11 group were both 88.9%( P= 0.542 and 0.403). The OS and LFS in CBF-AML with FLT3-ITD positive were both 62.2%. The OS and LFS in CBF-AML without FLT3-ITD were 85.3% and 82.9%, respectively (P=0.045 and 0.081),there was significantly inferior OS in CBF-AML with FLT3-ITD subgroup. Among them, the OS was 60.0% and 85.9% in RUNX1-RUNX1T1 with or without FLT3-ITD group respectively( P=0.041), there was significantly inferior OS in RUNX1-RUNX1T1 with FLT3-ITD subgroup. There were no significant differences in OS and LFS between the CBF with or without C-kit and ASXL1 genes. The overall relapse was 10.9%, and treatment related mortality was 6.9%.
Conclusion: The childhood CBF-AML accounted for 30.6% of children's newly diagnosed AML in the South China Children's AML Group. The complete remission rate reached to 93.1% by using 2 courses of intensive induction regimen of DAE or FLAG-IDA. Only 2 courses of consolidation chemotherapy were administered. Two years OS and LFS were higher than 80%.There were significant difference in OS of CBF-AML with FLT3-ITD, and RUNX1-RUNX1T1 AML with FLT3-ITD. There were no significant differences in that of LFS. The overall LFS was close to the outcome of the MRC AML 15 protocol, but there was a gap in OS. The main reason was that the most of relapsed patients abandoned treatment. On other hand the treatment related mortality need to be further reduced.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.