Background:
Metabolic tumor volume (MTV) measured by FDG-PET/CT is becoming established as an independent risk factor for treatment failure in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). Moreover, response to treatment with novel agents including checkpoint inhibitors may be better reflected by a decrease in MTV than by currently used response criteria. Our aim was to evaluate the early response to first-line HL treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor nivolumab using MTV.
Methods:
The analysis set included 59 patients with newly diagnosed, early-stage unfavorable HL treated within the prospective, multicenter, open label, randomized, phase II NIVAHL trial of the German Hodgkin Study Group (GHSG). Patients in NIVAHL were randomized to receive either four double cycles of nivolumab, doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (4x Nivo-AVD, group A, n=31) or a sequential therapy starting with 4x nivolumab monotherapy followed by 2xNivo-AVD and 2x AVD (group B, n=28). Early response to treatment was assessed at a 1st interim restaging after either 2x Nivo-AVD or 4x nivolumab. All NIVAHL patients who underwent PET at both initial staging and early response assessment, with images available to the central review panel for quantitative analysis before April 30th 2019, were included. MTV was calculated using a fixed SUV threshold of 4 for both staging and restaging.
Results:
Patient characteristics of the MTV analysis subset presented here did not differ in any relevant way from the overall NIVAHL trial population. Median age of the 59 patients was 27 years (range 18-57) with a female predominance (61%). All patients presented with stage II disease (IIB 27%) and ≥3 involved areas was the most common risk factor (75%) followed by elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (51%), extranodal disease (17%) and large mediastinal mass (14%).
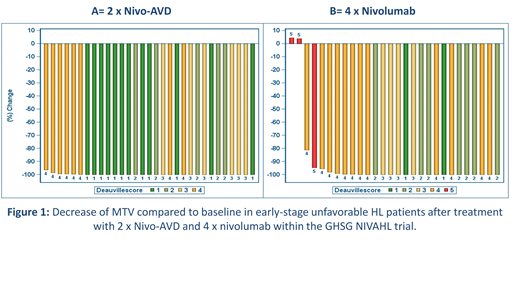
Mean MTV at initial staging was 124 ml (range 4 - 578 ml) and 177 ml (11 - 581 ml) in groups A and B, respectively. In both groups a marked decrease in MTV was observed at the 1st interim restaging (Figure 1): After 2x Nivo-AVD all patients in group A showed a reduction of MTV >80% (mean percentage change in MTV -99.8%). In group B a reduction of MTV >80% was observed in 26/28 patients (93%), while in 2/28 patients an increase <10% was observed (mean percentage change in MTV -91%; Figure 1). The mean residual MTV at interim restaging after 2x Nivo-AVD was 0.4 ml (range 0 - 8) in group A and 11 ml after 4x nivolumab in group B (range 0 - 176). The reduction of MTV was observed irrespective of initial MTV with a similar mean percentage change in patients above and below the median MTV in both groups. When applying the Deauville score, however, the number of patients presenting with a Deauville score ≥4 was higher in the group with an initial MTV above the median MTV than in the group where initial MTV lay below the median value.
Using the Lugano criteria and a Deauville score of 4 or higher as cut-off for PET-positivity, early interim complete remission was observed in 81% of patients after 2xNivo-AVD, as compared to 51% after 4x nivolumab monotherapy. Further analyses regarding MTV and response at the 2nd and end-of-treatment restaging as well as survival data are not yet available due to limited follow-up. These data will be available at the time of presentation and shown at the meeting.
Conclusions:
Marked reductions of MTV demonstrate an excellent early efficacy for both 2x Nivo-AVD and 4x nivolumab as 1st-line therapy for early-stage unfavorable HL. The unexpectedly and previously unreported high MTV reduction with nivolumab monotherapy indicates a relevant potential of anti-PD1 mono- or debulking-therapy in the 1st-line treatment of early-stage unfavorable HL. Early interim response assessment based on MTV may help to identify HL patients treated with anti-PD1 antibodies in whom a significant reduction or even omission of chemotherapy could be considered. MTV appears to have the potential to accurately measure response to immune checkpoint inhibition. However, correlation of early MTV reduction with response at the end of treatment or with survival data is pending.
Borchmann:Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding. Bröckelmann:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Other: Travel Support, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support, Research Funding; MSD Sharpe & Dohme: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.