Introduction: Multiple myeloma (MM) is more common in men than women but the mechanism(s) driving this are not understood. In our previous study (Myeloma IX) we found sex disparities in the cytogenetic lesions present in myeloma cells at the time of diagnosis and that female sex was associated with reduced overall survival in the context of treatment with traditional chemotherapy (CVAMP/MP) and thalidomide combinations. Here, we evaluate sex differences in almost 4000 patients recruited to the UK NCRI Myeloma XI trial, in which treatment exposure to lenalidomide predominated.
Methods: Myeloma XI recruited newly diagnosed patients of all ages, with pathways for transplant eligible (TE) and ineligible (TNE) patients. An induction randomisation compared the triplet combination of cyclophosphamide, lenalidomide and dexamethasone to a similar combination with thalidomide (CRD vs CTD). Eligible patients underwent autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) and in both pathways a maintenance randomisation compared lenalidomide (+/-vorinostat) until disease progression versus observation. We compared baseline characteristics of males and females using Fisher's Exact test for categorical characteristics and the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test for continuous characteristics with p<0.05 the level considered statistically significant. We compared outcomes, progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS), using the log-rank test. Adverse cytogenetic lesions, analysed in a subset of 1610 patients, were defined as t(4;14), t(14;16), t(14;20), del(17p) and gain(1q). Standard risk (SR) was defined as the absence of any of these lesions, High-risk (HiR) as one lesion present and Ultra High-risk (UHiR) as >1 lesion present.
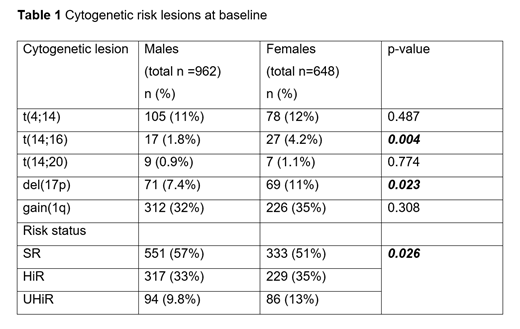
Results: Of 3894 patients enrolled in the trial 2268 (58%) were male and 1626 (42%) were female, in keeping with the known sex disparity in MM. There was no difference in the median age, WHO performance status, ethnicity and most laboratory values of the two groups. Females were more likely to have the molecular risk lesions t(14;16) and del(17p) and had proportionately more HiR and UHiR disease, Table 1. Despite these differences, PFS and OS from induction randomisation did not significantly differ (PFS: Males 25 months, [95% CI 24, 26], Females 24 months, [95% CI 22, 25] and OS: Males 67 months, [95% CI 62, 70], Females 70 months, [95% CI 64, 74]).
Molecular lesions that have been associated with outcome remained prognostic in both sexes, with a stepwise reduction in PFS and OS with cumulative risk lesions. PFS: Males SR 29 months, HiR 23 months, UHiR 16 months (p < 0.0001), Females SR 27 months, HiR 18 months, UHiR 17 months (p = 0.0007); OS: Males SR 77 months, HiR 59 months, UHiR 34 months (p < 0.0001), Females SR 82 months, HiR 54 months, UHiR 41 months (p < 0.0001). There was, however, no significant difference in PFS or OS when we compared males and females with a given cytogenetic lesion or cytogenetic risk.
There was a significant difference in the proportion of patients of either sex who continued through the trial and underwent ASCT in the TE pathway (Males 72%, Females 67%; p = 0.031), but no significant difference in those that entered the maintenance randomisation (TE: Males 56%, Females 50%, p = 0.107; TNE Males 45%, Females 42%, p = 0.249).
There was no significant PFS or OS difference by sex when analysed within each treatment pathway (TE, TNE), induction regimen (CTD, CRD) and maintenance approach (lenalidomide maintenance, observation).
Conclusions: Females had a higher proportion of the adverse molecular risk lesions del(17p) and t(14;16) and were more likely to have HiR and UHiR disease. In the context of Myeloma XI trial treatment this did not correspond to a difference in PFS or OS, either overall or within the induction or maintenance randomisation treatment options (even though males were more likely to undergo ASCT). This suggests that in women the treatment delivered may have been able to overcome some of the adverse effect of the risk lesions present or that other factors affecting outcome were more important.
on behalf of the NCRI Haematological Oncology Clinical Studies Group.
Cairns:Celgene, Amgen, Merck, Takeda: Other: Research Funding to Institution. Davies:Janssen, Celgene: Other: Research Grant, Research Funding; Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Oncopeptides, Roche, Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Consultant/Advisor. Boyd:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria. Cook:Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen, Takeda, Sanofi, Karyopharm, Celgene: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Drayson:Abingdon Health: Consultancy, Equity Ownership. Gregory:Abbvie, Janssen: Honoraria; Amgen, Merck: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding. Jenner:Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Novartis, Janssen, Sanofi Genzyme, Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Jones:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Kaiser:Takeda, Janssen, Celgene, Amgen: Honoraria, Other: Travel Expenses; Celgene, Janssen: Research Funding; Abbvie, Celgene, Takeda, Janssen, Amgen, Abbvie, Karyopharm: Consultancy. Owen:Celgene, Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene, Janssen: Consultancy; Celgene: Research Funding; Janssen: Other: Travel expenses. Russell:DSI: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Jazz: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer Inc: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Astellas: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Morgan:Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen, Janssen, Takeda, Celgene Corporation: Other: Travel expenses; Celgene Corporation, Janssen: Research Funding. Jackson:Celgene, Amgen, Roche, Janssen, Sanofi: Honoraria. Pawlyn:Amgen, Celgene, Takeda: Consultancy; Amgen, Janssen, Celgene, Takeda: Other: Travel expenses; Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Oncopeptides: Honoraria.
CTD/CRD induction therapy for myeloma, Lenalidomide maintenance 10mg 21/28 days
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.