Background: Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is characterized by chronic anemia and recurrent ischemia-reperfusion episodes that contribute to high output heart failure. The effects of SCD on the heart are significantly underrecognized.
Methods: SCD patients who underwent echocardiography between March 2016 and March 2018 were retrospectively analyzed. Patients with reduced Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF) and valvular heart disease were excluded. Cardiac chamber size, systolic and diastolic function parameters, and LV and RV strain were compared between hemoglobin SS (most severe form of SCD) and SC (less severe form) subtypes and against healthy controls. Wilcoxon signed rank test was used for statistical analysis.
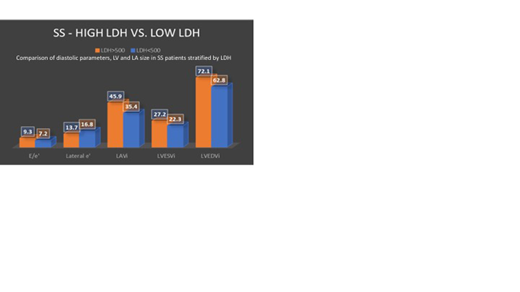
Results: SS patients (n = 48, mean age 31.9) had lower mean hemoglobin 8.9 g/dl vs 11.3 g/dl (p < 0.001) and hematocrit 25.8% vs 31.4% (p = 0.008) and higher LDH 437 IU/L vs 258 IU/L (p < 0.001) compared to SC patients (n = 11, mean age 34.4). Both SS and SC patients had worse diastolic function compared to healthy controls: higher E velocity 98.9 cm/s (SS), 86.4 cm/s (SC), 76.4 cm/s (control) (SS vs control, p < 0.01; SC vs control, p < 0.05) and higher E/A ratio 1.76 (SS), 1.59 (SC), 1.15 (control) (SS vs control, p < 0.001; SC vs control, p < 0.01). SS patients had larger indexed left atrial volume compared to SC patients (39.3 ml/m2 vs 28.4 ml/m2, p = 0.007). There was no significant difference in LVEF, left ventricular global longitudinal strain, or right ventricular strain between SS and SC subtypes compared to healthy controls. Furthermore, SS patients with a serum LDH > 500 IU/L had higher E/e' ratio (11.3 vs 7.2, p=0.001) and larger indexed Left Ventricular End Diastolic Volume (LVEDVi) (80.8 ml/m2 vs 53.4 ml/m2, p=0.002) compared to SS patients with LDH < 500 IU/L.
Conclusion: SCD genotype adversely determines the degree of cardiac dysfunction in patients with SCD. LVEDVi, left atrial size, E velocity, E/A ratio, and E/e' ratio may serve as useful echocardiographic parameters to follow in this patient population. Serum LDH has been associated with poor clinical outcomes in patients with SCD, and as demonstrated by our study, it also portends worsening cardiac function in this population at high risk for heart failure.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.